Mn Income Tax
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the Minnesota Income Tax, a critical component of the state's fiscal framework. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the tax system, offering a clear understanding of its structure, rates, and implications for residents and businesses alike. With a focus on expert analysis and real-world examples, we aim to provide a valuable resource for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of Minnesota's tax landscape.
Understanding the Minnesota Income Tax System

The Minnesota Income Tax is a fundamental revenue source for the state, playing a pivotal role in funding public services, infrastructure development, and various governmental initiatives. It is a progressive tax system, which means that higher incomes are taxed at progressively higher rates, ensuring a fair and equitable distribution of tax burden.
Tax Rates and Brackets
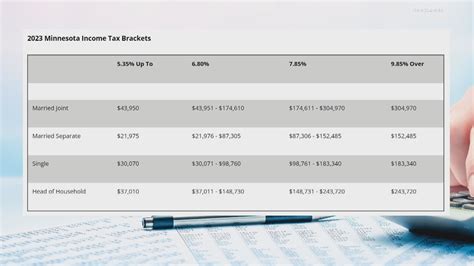
The income tax rates in Minnesota are structured into six tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. These brackets are adjusted annually to account for inflation and changing economic conditions. As of the 2023 tax year, the tax rates for Minnesota residents are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $21,600 | 5.35% |
| $21,601 - $38,300 | 7.05% |
| $38,301 - $76,600 | 7.85% |
| $76,601 - $153,200 | 9.85% |
| $153,201 - $320,000 | 9.85% |
| Over $320,000 | 9.85% |

These rates apply to Minnesota residents' taxable income, which is calculated after deductions and credits. The state also offers various tax credits and deductions to help reduce the tax burden for individuals and families, including the Working Family Credit, the Minnesota Property Tax Refund, and deductions for medical expenses and charitable contributions.
Tax Filing and Due Dates
For most individuals, the tax filing deadline in Minnesota aligns with the federal deadline, which is typically April 15th of each year. However, if this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. It’s important to note that payments for estimated taxes are due quarterly, with specific due dates throughout the year.
The Minnesota Department of Revenue provides a comprehensive tax calendar that outlines important dates for filing and payment, helping taxpayers stay organized and avoid penalties.
Income Tax Implications for Minnesota Residents

The Minnesota Income Tax has significant implications for residents, impacting their financial planning, investment strategies, and overall financial well-being. Understanding these implications is crucial for effective tax management and long-term financial stability.
Impact on Disposable Income
The income tax rate an individual falls into directly affects their disposable income, or the money they have left after taxes. This disposable income is crucial for meeting daily expenses, saving for the future, and making investments. For example, let’s consider a single taxpayer with an annual income of 50,000. Based on the 2023 tax rates, this taxpayer would fall into the third tax bracket (income between 38,301 and 76,600), resulting in a tax rate of 7.85%. This means that they would pay approximately 3,925 in state income tax, leaving them with a disposable income of $46,075.
| Income | Tax Rate | Approximate Tax Amount | Disposable Income |
|---|---|---|---|
| $50,000 | 7.85% | $3,925 | $46,075 |
Tax Planning Strategies
To optimize their financial position, Minnesota residents can employ various tax planning strategies. This may include maximizing deductions and credits, such as the Working Family Credit or the Minnesota Property Tax Refund, which can significantly reduce tax liabilities. Additionally, contributing to tax-advantaged retirement accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s can provide immediate tax benefits and long-term growth potential.
For those with complex financial situations or high incomes, seeking professional tax advice can be beneficial. A tax professional can help navigate the intricacies of Minnesota's tax code, identify potential tax savings opportunities, and ensure compliance with state regulations.
Minnesota Income Tax for Businesses
The Minnesota Income Tax also applies to businesses operating within the state, whether they are sole proprietorships, partnerships, or corporations. Understanding the tax obligations and implications for businesses is essential for effective financial management and strategic planning.
Business Tax Rates and Filing
Businesses in Minnesota are subject to a corporate income tax, which is separate from the personal income tax. The corporate income tax rate is a flat rate of 9.8% for all businesses, regardless of their size or industry. This rate applies to the taxable income of the business, which is typically calculated after deductions for business expenses and credits.
Businesses are required to file their tax returns and make payments by specific due dates, which vary depending on the type of business entity. The Minnesota Department of Revenue provides detailed guidelines and resources to help businesses understand their tax obligations and ensure compliance.
Business Tax Incentives and Credits
Minnesota offers a range of tax incentives and credits to support businesses, encourage economic development, and attract new investments. These incentives can significantly reduce a business’s tax liability and include tax credits for job creation, research and development, and investment in renewable energy sources. For example, the Minnesota Angel Tax Credit provides a credit against state income tax for investments in qualifying startup companies, encouraging investment in the state’s innovative businesses.
Impact on Business Decisions
The Minnesota income tax has a significant impact on business decisions, influencing where and how businesses operate within the state. For instance, the tax rate and potential tax incentives can factor into a business’s decision to expand, relocate, or invest in new projects. A lower tax burden can make Minnesota more attractive for businesses, potentially leading to increased economic activity and job creation.
Additionally, the availability of tax credits and incentives can provide businesses with the financial support needed to pursue strategic initiatives, such as research and development or workforce training, ultimately enhancing their competitiveness and long-term success.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
The Minnesota Income Tax system is subject to ongoing review and potential changes, driven by economic conditions, legislative priorities, and public policy considerations. Keeping abreast of these potential changes is essential for both individuals and businesses to effectively plan their financial strategies and ensure compliance with evolving tax laws.
Proposed Tax Reforms
Over the years, there have been various proposals for tax reforms in Minnesota, aimed at improving the fairness, efficiency, and competitiveness of the state’s tax system. These proposals often include suggestions for tax rate adjustments, changes to tax brackets, and the introduction of new tax credits or deductions. For instance, some proposals have advocated for a flatter tax rate structure, while others have focused on expanding tax credits to support specific industries or social initiatives.
While not all proposed reforms are enacted, they can provide insights into the potential direction of the state's tax policy and offer opportunities for taxpayers to engage in the legislative process and voice their preferences.
Economic and Legislative Factors
The future of the Minnesota Income Tax system is closely tied to economic conditions and legislative priorities. During periods of economic growth, the state may consider tax reforms to support continued growth and investment, while economic downturns may prompt discussions on tax relief measures to stimulate the economy. Additionally, changes in political leadership and shifts in legislative priorities can influence the focus and direction of tax policy.
Staying informed about these economic and legislative factors is crucial for understanding the potential trajectory of the state's tax system and making informed financial decisions.
Tax Policy Impact on Residents and Businesses
Changes to the Minnesota Income Tax system can have significant implications for both residents and businesses. For residents, tax reforms may impact their disposable income, the cost of living, and the availability of public services. A reduction in tax rates, for example, could provide residents with more disposable income, potentially stimulating local economies. Conversely, an increase in tax rates could lead to a higher cost of living and potentially impact residents’ ability to save and invest.
For businesses, tax policy changes can influence their financial strategies, investment decisions, and overall competitiveness. A more favorable tax environment can encourage businesses to expand, invest, and create jobs, while less attractive tax conditions may lead to businesses reconsidering their operations or investments within the state.
Conclusion

The Minnesota Income Tax system is a critical component of the state’s fiscal framework, playing a pivotal role in funding public services and supporting economic development. By understanding the tax rates, brackets, and implications for both individuals and businesses, residents can effectively manage their finances and businesses can make strategic decisions. Additionally, staying informed about potential tax reforms and their impact is essential for navigating the evolving tax landscape and ensuring compliance with state regulations.
FAQ
How do I calculate my Minnesota state income tax?
+
To calculate your Minnesota state income tax, you’ll need to determine your taxable income, which is your total income minus any deductions and exemptions. Then, you’ll apply the appropriate tax rate based on your income bracket. For example, if your taxable income is $50,000, you would fall into the third tax bracket with a tax rate of 7.85%. Multiply your taxable income by the tax rate to find your approximate state income tax.
Are there any tax deductions or credits available in Minnesota?
+
Yes, Minnesota offers a variety of tax deductions and credits to help reduce your tax liability. These include the Working Family Credit, Minnesota Property Tax Refund, and deductions for medical expenses and charitable contributions. It’s important to review the eligibility criteria and requirements for each deduction or credit to ensure you can take full advantage of them.
What is the corporate income tax rate in Minnesota?
+
The corporate income tax rate in Minnesota is a flat rate of 9.8% for all businesses, regardless of size or industry. This rate applies to the taxable income of the business after deductions for business expenses and credits.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in Minnesota?
+
Yes, Minnesota offers several tax incentives to support businesses and encourage economic development. These include tax credits for job creation, research and development, and investment in renewable energy. Additionally, the state provides resources and programs to help businesses understand and utilize these incentives.
How can I stay updated on potential changes to Minnesota’s tax system?
+
To stay informed about potential changes to Minnesota’s tax system, it’s recommended to follow news and updates from the Minnesota Department of Revenue, local media outlets, and tax industry publications. Additionally, engaging with tax professionals and staying involved in tax-related discussions and forums can provide valuable insights into potential reforms and their impact.