Marginal Vs Effective Tax Rate
Understanding the intricacies of the tax system is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. Two key concepts that often arise when discussing taxation are the marginal tax rate and the effective tax rate. These terms are fundamental to grasping how tax policies impact one's financial obligations and overall economic decisions. Let's delve into these concepts, exploring their definitions, calculations, and the implications they have on tax strategies.
Unraveling the Marginal Tax Rate
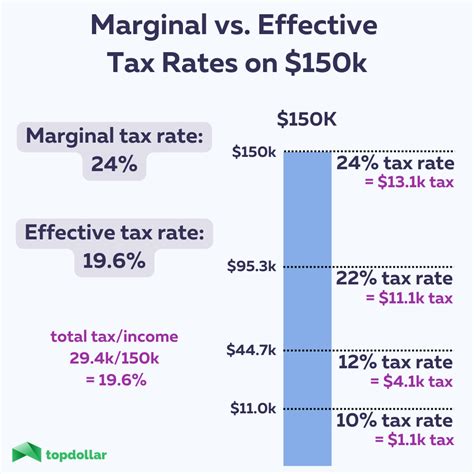
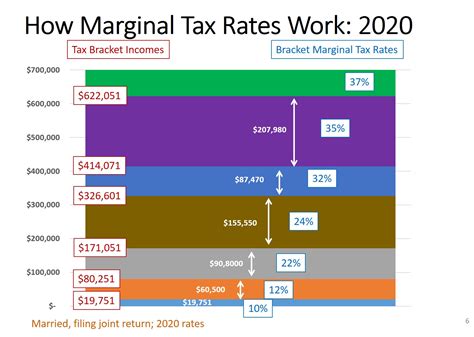
The marginal tax rate is a critical concept in taxation, representing the rate at which an individual or entity is taxed on the next dollar of income earned. It is calculated as a percentage and varies based on income brackets and the prevailing tax system. For instance, in a progressive tax system, like the one employed in many countries, the marginal tax rate increases as income rises, with higher earners facing a higher rate.
| Income Bracket | Marginal Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $10,000 | 10% |
| $10,001 - $20,000 | 15% |
| $20,001 - $50,000 | 20% |
| Over $50,000 | 25% |
In the above example, an individual earning $25,000 would have a marginal tax rate of 20%. This means that any additional income earned beyond $20,000 will be taxed at this rate. It's important to note that the marginal tax rate doesn't reflect the overall tax burden but rather the rate applied to the highest income bracket an individual falls into.
Real-World Application of Marginal Tax Rates
Marginal tax rates play a pivotal role in financial planning and investment strategies. For instance, consider an investor who is considering selling a portion of their stock portfolio. By understanding their marginal tax rate, they can estimate the tax liability on the capital gains from the sale. This knowledge can influence their decision-making, especially when considering the potential impact on their tax bracket.
The Concept of Effective Tax Rate
In contrast, the effective tax rate is the actual percentage of income paid in taxes by an individual or entity. It is calculated by dividing the total tax paid by the total income earned. Unlike the marginal tax rate, the effective tax rate provides a more comprehensive view of one’s tax obligation, taking into account all sources of income and deductions.
| Taxpayer | Total Income | Total Tax Paid | Effective Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alice | $50,000 | $7,500 | 15% |
| Bob | $100,000 | $20,000 | 20% |
| Carol | $200,000 | $45,000 | 22.5% |
In the table above, despite having different marginal tax rates based on their income brackets, each taxpayer's effective tax rate varies based on their specific income and tax payments. This showcases the importance of understanding the effective tax rate to gain a clear picture of one's financial obligations.
Implications of Effective Tax Rates
Effective tax rates are particularly relevant when comparing tax burdens across different income levels or entities. They provide a more accurate representation of the impact of tax policies on individuals and businesses. For instance, a business with a high effective tax rate might consider tax planning strategies to reduce its tax liability, which could involve exploring tax-efficient investment options or taking advantage of available deductions and credits.
Key Differences and Considerations
While both marginal and effective tax rates are essential components of tax understanding, they serve different purposes. The marginal tax rate is more focused on the incremental impact of additional income, guiding decisions around earnings and investments. On the other hand, the effective tax rate provides a holistic view of one’s tax obligation, taking into account all income sources and deductions. It is especially useful for understanding the overall tax burden and for comparative analysis.
Furthermore, it's crucial to recognize that tax laws and regulations can vary significantly between jurisdictions. What might be a beneficial tax strategy in one country could have different implications in another. Thus, staying informed about local tax policies and seeking professional advice is essential for making informed financial decisions.
The Impact on Tax Planning
Understanding the distinction between marginal and effective tax rates is crucial for effective tax planning. For instance, an individual with a high marginal tax rate might consider strategies to reduce their taxable income, such as contributing to tax-advantaged retirement accounts or exploring other tax-efficient investment options. On the other hand, understanding one’s effective tax rate can help identify areas where tax liabilities can be minimized through strategic financial planning.
Conclusion
In the complex world of taxation, grasping the nuances of marginal and effective tax rates is vital for individuals and businesses to navigate their financial obligations effectively. These concepts provide critical insights into tax strategies, influencing decisions related to income, investments, and business operations. By understanding these rates, one can make informed choices to optimize their financial position and comply with tax regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between marginal and effective tax rates?
+The marginal tax rate refers to the rate at which the next dollar of income is taxed, while the effective tax rate represents the actual percentage of income paid in taxes. Marginal tax rates guide decisions on incremental income, while effective tax rates provide a holistic view of tax obligations.
How do tax brackets relate to marginal tax rates?
+Tax brackets are income ranges associated with specific tax rates. Your marginal tax rate depends on which bracket your income falls into. As income increases, it may cross into higher tax brackets, resulting in a higher marginal tax rate for that additional income.
Why is understanding effective tax rate important for businesses?
+Effective tax rates provide businesses with a clear picture of their overall tax obligations. This understanding can influence strategic decisions, such as investment choices, expansion plans, and tax-efficient operations.
Can tax planning strategies impact both marginal and effective tax rates?
+Yes, tax planning strategies can aim to reduce both marginal and effective tax rates. Strategies like optimizing deductions, contributing to tax-advantaged accounts, or restructuring business operations can impact both rates, leading to significant tax savings.



