Marginal Tax Rate Formula
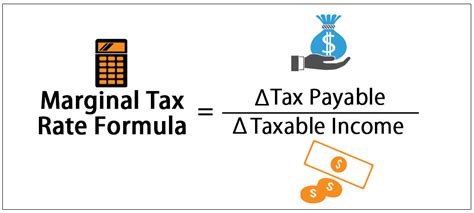
Taxation is a complex system that impacts individuals and businesses worldwide, and understanding the marginal tax rate is crucial for financial planning and decision-making. The marginal tax rate formula plays a pivotal role in determining the tax liability for each additional dollar earned, and it varies based on factors such as income level, tax brackets, and the specific tax system in a given jurisdiction.
Unraveling the Marginal Tax Rate Formula
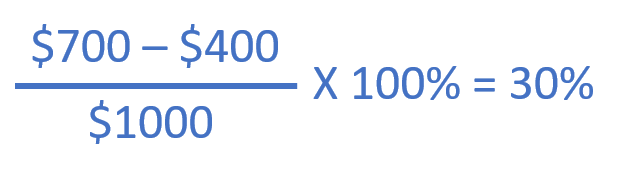
The marginal tax rate formula is a fundamental concept in tax systems, and its understanding is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the financial landscape effectively. This formula, often a source of curiosity and sometimes confusion, provides insight into how tax obligations increase or decrease as income levels fluctuate. Let's delve into the intricacies of this formula and explore its significance in the world of taxation.
At its core, the marginal tax rate formula represents the rate at which an individual or entity is taxed on each additional dollar of income. It is a progressive tax structure, meaning that as income increases, the tax rate also increases, resulting in a higher tax liability for those with higher earnings. This progressive nature aims to ensure fairness and redistribute wealth within a society.
The formula itself is relatively straightforward. It calculates the tax liability for a specific income bracket by applying the corresponding tax rate to that income range. The marginal tax rate, however, is the rate applied to the next dollar earned, which can be different from the average tax rate.
The Progressive Nature of Tax Brackets
Tax systems typically divide income into different brackets, each with its own tax rate. As income increases, it moves through these brackets, and the applicable tax rate changes accordingly. This progressive structure means that individuals pay a higher tax rate as their income surpasses the threshold for each subsequent bracket.
For example, in a hypothetical tax system with three brackets: 10%, 20%, and 30%, an individual's income of $50,000 would be taxed at 10% for the first bracket, 20% for the portion exceeding that bracket's threshold, and so on. The marginal tax rate, in this case, would be the rate applied to the income just above the highest bracket's threshold.
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $20,000 | 10% |
| $20,001 - $40,000 | 20% |
| $40,001 and above | 30% |

Calculating Marginal Tax Rate: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating the marginal tax rate involves a few simple steps. Let's walk through an example to illustrate the process.
Suppose an individual's income is $60,000, and the tax system has the following brackets:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $20,000 | 10% |
| $20,001 - $40,000 | 20% |
| $40,001 and above | 30% |
To calculate the marginal tax rate:
- Identify the income bracket where the income falls: In this case, it's the third bracket ($40,001 and above)
- Apply the corresponding tax rate to the income: 30% of $60,000 = $18,000
- The marginal tax rate is the rate applied to the income just above the threshold. In this example, the marginal tax rate is 30%, as the income of $60,000 falls within the third bracket.
Real-World Implications and Strategies
Understanding the marginal tax rate is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications for individuals and businesses. It influences financial decisions, investment strategies, and even career choices.
Financial Planning and Investment Strategies
For individuals, knowing the marginal tax rate can guide financial planning. It helps in deciding when to take on additional income-generating activities, such as consulting work or investments. Understanding the tax implications of these activities can lead to more informed and tax-efficient decisions.
Additionally, it plays a role in investment strategies. Certain investment vehicles offer tax advantages, and by understanding the marginal tax rate, individuals can optimize their portfolios to minimize tax liabilities.
Business Strategies and Tax Planning
Businesses also leverage the knowledge of marginal tax rates for strategic decision-making. They can structure their operations to take advantage of tax incentives and optimize their tax positions. This may involve strategic planning for capital investments, research and development expenditures, or even employee compensation strategies.
Avoiding the "Income Cliff"
One common concern related to the marginal tax rate is the potential "income cliff." This occurs when an individual's income increases just enough to push them into a higher tax bracket, resulting in a significant increase in tax liability. To avoid this, individuals may consider strategies like tax-deferred savings or income-smoothing techniques to ensure they don't inadvertently cross into a higher tax bracket.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Relationship with Taxation
The marginal tax rate formula is a dynamic and ever-evolving concept in the world of taxation. As tax systems adapt to economic realities and societal needs, the brackets and rates can change, impacting the financial landscape. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for effective financial planning.
Whether for personal financial management or business strategy, understanding the marginal tax rate is a fundamental step towards optimizing tax positions and making informed decisions. It empowers individuals and businesses to navigate the complexities of taxation and make the most of their financial resources.
How does the marginal tax rate affect tax planning strategies for individuals?
+The marginal tax rate is a critical factor in tax planning. It guides individuals on when to take on additional income and how to structure their finances to minimize tax liabilities. For example, individuals may consider deferring income to a lower tax year or investing in tax-advantaged accounts to reduce their overall tax burden.
What are some common strategies businesses employ to optimize their tax positions based on marginal tax rates?
+Businesses often use strategies like tax-efficient investment decisions, optimizing depreciation schedules, and utilizing tax credits and incentives to reduce their overall tax liability. They may also consider the tax implications of business structures and ownership arrangements to minimize their tax burden.
How often do tax brackets and rates change, and what impact does this have on taxpayers?
+Tax brackets and rates can change annually or over longer periods, depending on economic conditions and government policies. These changes can significantly impact taxpayers, as they may find themselves in a different tax bracket with different tax rates, affecting their overall tax liability. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for effective tax planning.



