Ma State Income Tax Percentage

The state of Massachusetts, often referred to as the Bay State, has a robust economic landscape with a diverse tax system that contributes significantly to its overall fiscal health. The state income tax is one of the key revenue streams for Massachusetts, playing a crucial role in funding essential public services and infrastructure development. Understanding the state's income tax structure is essential for both residents and businesses, as it impacts their financial planning and overall cost of living or operation.
Understanding the Massachusetts State Income Tax
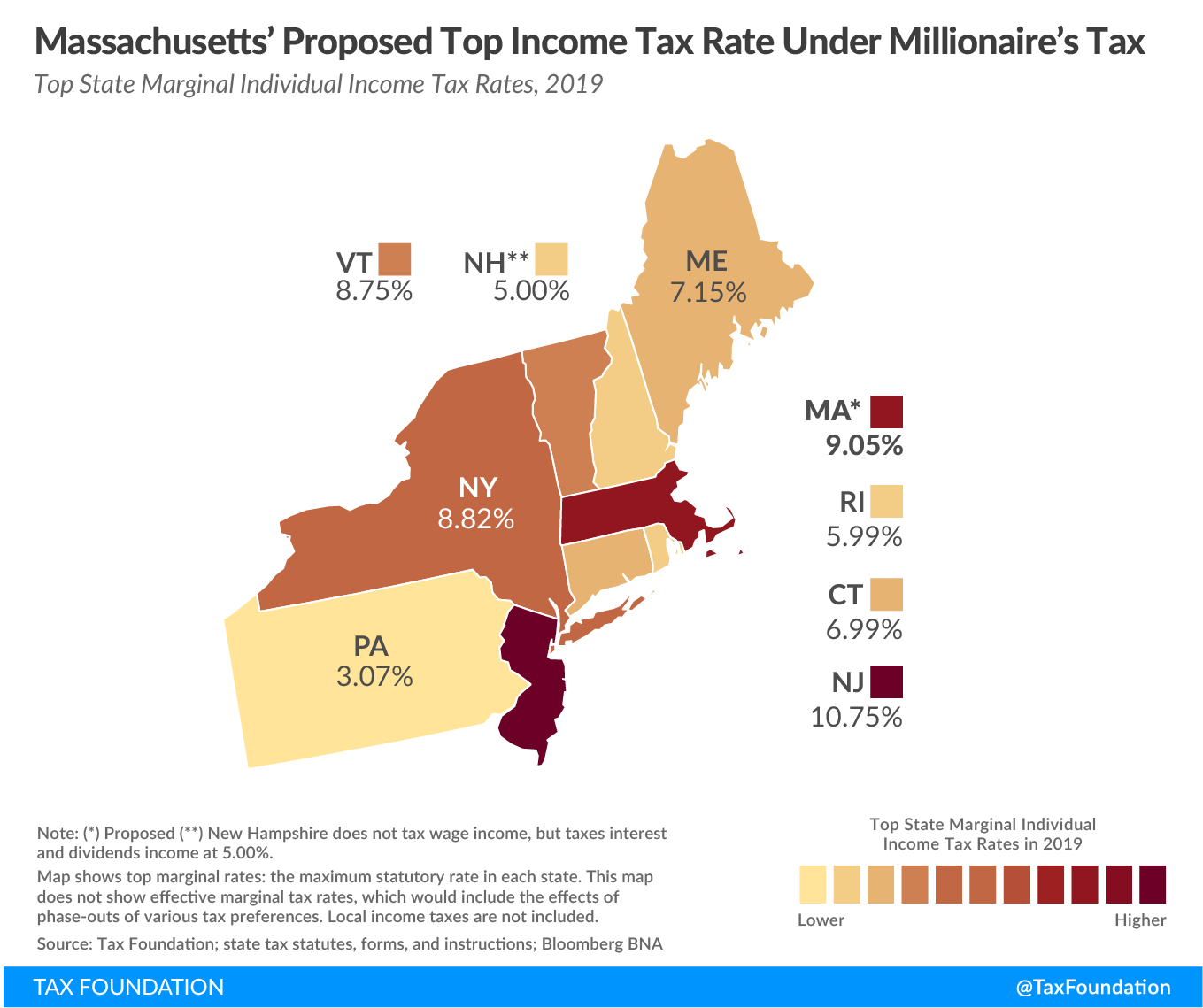
The Massachusetts state income tax is a progressive tax, which means that the tax rate increases as taxable income increases. This system ensures that individuals and entities with higher incomes contribute a larger proportion of their earnings to the state’s revenue. As of my last update in January 2023, the state income tax rates in Massachusetts are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $15,000 | 5.05% |
| $15,001 - $25,000 | 5.05% |
| $25,001 - $49,999 | 5.05% |
| $50,000 - $100,000 | 5.05% |
| $100,001 - $150,000 | 5.05% |
| $150,001 - $300,000 | 5.05% |
| $300,001 and above | 5.05% |

It's important to note that these rates are subject to change, and taxpayers should always refer to the most recent guidelines and regulations issued by the Massachusetts Department of Revenue for accurate and up-to-date information.
Key Considerations for Taxpayers
Massachusetts offers several deductions and credits to reduce the tax burden on individuals and businesses. Some of these include the Personal Exemption, Standard Deduction, and various credits for education, childcare, and healthcare expenses. Additionally, Massachusetts has a separate tax rate for interest and dividends, which is currently set at 12%.
For businesses, the state provides a Corporate Excise Tax, which is calculated based on the business's taxable income. The rate for this tax can vary depending on the type of business entity and other factors. Massachusetts also offers various incentives and tax credits to attract and support businesses, particularly in sectors like renewable energy, research, and development.
The Impact of State Income Tax on Massachusetts’ Economy

The state income tax is a vital component of Massachusetts’ revenue stream, funding various public services and infrastructure projects. It plays a significant role in maintaining the state’s robust economy and high quality of life. The revenue generated from this tax supports education, healthcare, transportation, and other critical sectors, ensuring the state’s continued prosperity and growth.
Moreover, the progressive nature of the state income tax ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a larger share, promoting economic equality and social welfare. This system also incentivizes businesses to create jobs and invest in the state, fostering economic growth and development.
Comparative Analysis
Compared to other states, Massachusetts’ state income tax rates are relatively moderate. Some states, like California and New York, have higher income tax rates, while others, like Florida and Texas, have no state income tax. However, it’s essential to consider the overall tax burden, which includes not just income tax but also sales tax, property tax, and other levies. Massachusetts has a relatively low sales tax rate (6.25%) compared to some other states, which can offset the impact of its state income tax.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
The future of the Massachusetts state income tax is subject to ongoing discussions and potential legislative changes. There have been proposals to reform the tax system, including suggestions to simplify the tax brackets and rates, or even introduce a flat tax rate. These changes could impact the tax burden on individuals and businesses, and it’s crucial for taxpayers to stay informed about any potential shifts in the tax landscape.
Additionally, the economic landscape can influence tax rates. During periods of economic growth, states might consider raising tax rates to capitalize on increased incomes, while during recessions, they might opt for tax cuts to stimulate the economy. Massachusetts, like many other states, has had to navigate these economic cycles, and its tax policies often reflect these fluctuations.
Conclusion
The Massachusetts state income tax is a critical component of the state’s fiscal health, contributing significantly to the funding of essential public services and infrastructure. Its progressive nature ensures a fair distribution of the tax burden, promoting economic equality and growth. While the state income tax rates are relatively moderate compared to some other states, the overall tax landscape in Massachusetts is dynamic and subject to ongoing discussions and potential reforms.
For residents and businesses, understanding the state income tax system is crucial for effective financial planning and contributing to the state's vibrant economy. By staying informed about tax policies and taking advantage of available deductions and credits, taxpayers can navigate the complex tax landscape effectively.
Additional Resources
For more detailed information on Massachusetts’ state income tax, including current rates, deductions, and forms, you can visit the official website of the Massachusetts Department of Revenue: https://www.mass.gov/orgs/department-of-revenue. This resource provides comprehensive guidelines and updates on state tax matters.
Are there any exceptions or special considerations for certain types of income in Massachusetts’ state income tax system?
+
Yes, Massachusetts has specific rules for various types of income. For instance, capital gains are taxed at the same rate as regular income, while Social Security benefits are exempt from state income tax. Additionally, certain types of retirement income may be eligible for deductions or exclusions.
How often are the state income tax rates reviewed and updated in Massachusetts?
+
The state income tax rates in Massachusetts are typically reviewed annually, and any changes are proposed through the state’s legislative process. The rates can be adjusted based on economic conditions, budget requirements, or policy goals.
What are some common deductions or credits that individuals can take advantage of to reduce their state income tax liability in Massachusetts?
+
Common deductions and credits in Massachusetts include the Personal Exemption, Standard Deduction, and credits for education expenses, childcare costs, and healthcare premiums. Additionally, individuals can deduct certain contributions to retirement accounts and claim credits for energy-efficient improvements to their homes.
Are there any specific tax incentives or programs in Massachusetts aimed at attracting and supporting businesses?
+
Absolutely! Massachusetts offers various incentives and programs to encourage business growth and investment. These include tax credits for research and development activities, film and digital media production, and renewable energy projects. There are also programs to support small businesses and startups, such as the Small Business Technical Assistance Program.
How can individuals stay informed about changes to the state income tax laws and regulations in Massachusetts?
+
Individuals can stay informed by regularly checking the official website of the Massachusetts Department of Revenue, which provides the latest updates and announcements. They can also sign up for email notifications or follow the department on social media for timely updates on tax-related matters.



