Los Angeles County Sales Tax
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the Los Angeles County Sales Tax, a crucial aspect of the region's economic landscape. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an expert-level understanding of the sales tax system in LA County, offering insights into its rates, applicability, and implications for both businesses and consumers. With a focus on accuracy and depth, we'll delve into the specifics, ensuring you have all the information needed to navigate this essential tax domain.
Understanding the LA County Sales Tax

The Los Angeles County Sales Tax is a tax levied on the sale of goods and certain services within the county. It is an essential revenue source for the local government, contributing significantly to the funding of various public services and infrastructure projects. Understanding this tax is crucial for businesses operating within the county, as it directly impacts their pricing strategies and overall financial operations.
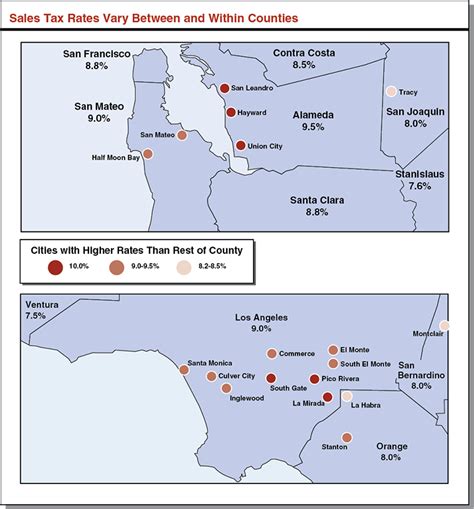
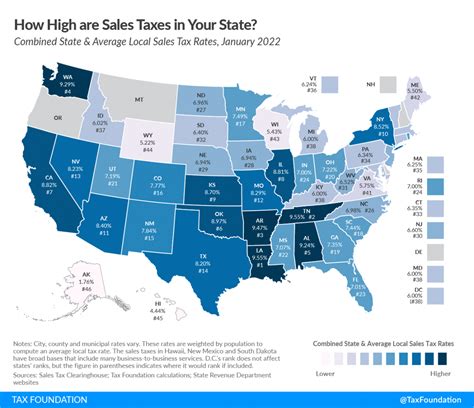
LA County's sales tax is unique in its structure, comprising both a state and a county-level tax. This dual system results in a combined tax rate that can vary depending on the specific location within the county. Additionally, certain jurisdictions within LA County may impose additional taxes, known as district taxes, further complicating the tax landscape.
The sales tax system in LA County is dynamic, with rates subject to change over time. These changes are often influenced by economic conditions, budgetary needs, and legislative decisions. Staying updated on these fluctuations is vital for businesses to ensure compliance and accurate tax collection.
The State and County Tax Components
The state sales tax in California, which applies uniformly across the state, is currently set at 7.25%. This rate is mandated by the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration and is applicable to most tangible personal property and certain services. However, it’s important to note that certain jurisdictions within California, including LA County, have the authority to impose additional local taxes, leading to variations in the overall tax rate.
The LA County sales tax is an additional tax levied on top of the state rate. As of the latest available information, the county tax rate stands at 0.25%. This county tax is collected by the Los Angeles County Office of the Treasurer and Tax Collector and is used to fund various county services and initiatives.
When combined, the state and county sales tax rates result in a total sales tax rate of 7.50% for most transactions within LA County. This rate is a crucial consideration for businesses when setting their pricing strategies and for consumers when making purchasing decisions.
| Tax Component | Rate |
|---|---|
| State Sales Tax | 7.25% |
| LA County Sales Tax | 0.25% |
| Total Sales Tax Rate | 7.50% |
District Taxes and Variations
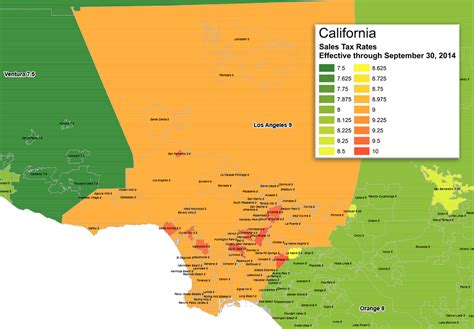
In addition to the state and county sales taxes, certain districts within LA County may impose their own district taxes. These taxes are typically used to fund specific local initiatives or services, such as transportation improvements or community development projects. District taxes can vary significantly, with rates ranging from 0.50% to 2.00% or higher in some cases.
The existence of district taxes adds complexity to the sales tax landscape in LA County. Businesses operating in multiple districts or with customers from different districts need to be aware of these variations to ensure accurate tax collection and compliance. Failure to account for district taxes can lead to financial penalties and legal issues.
| District | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Beverly Hills | 2.00% |
| Burbank | 1.50% |
| Glendale | 0.50% |
| Pasadena | 1.00% |
| Long Beach | 1.50% |
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations

While the general sales tax rate in LA County is 7.50%, it’s important to note that certain transactions and items are exempt from sales tax. Understanding these exemptions is crucial for both businesses and consumers to ensure compliance and take advantage of any applicable tax benefits.
Sales Tax Exemptions
Certain goods and services are exempt from sales tax in LA County, as mandated by state and local laws. These exemptions can vary based on the nature of the transaction and the specific circumstances involved. Here are some key exemptions to be aware of:
- Food for Home Consumption: Most food items purchased for consumption at home are exempt from sales tax. This includes groceries, non-alcoholic beverages, and certain prepared foods intended for off-site consumption.
- Prescription Medications: Sales of prescription drugs and certain medical devices are exempt from sales tax. This exemption extends to both over-the-counter medications and prescription-only items.
- Clothing and Shoes: Clothing and footwear items priced under a certain threshold (currently $110) are exempt from sales tax. This exemption aims to provide relief for essential purchases, especially for lower-income individuals.
- Certain Services: Some services, such as professional services (e.g., legal, accounting), are exempt from sales tax. Additionally, certain services provided by non-profit organizations may also be exempt.
- Real Estate Transactions: Sales of real estate, including residential and commercial properties, are generally exempt from sales tax. However, there may be other taxes and fees associated with these transactions.
It's important to note that while these are common exemptions, the list is not exhaustive. Businesses should consult with tax professionals or refer to official tax guides to ensure they are aware of all applicable exemptions for their specific operations.
Special Considerations for Online Sales
The rise of e-commerce has brought about unique challenges for sales tax collection. In LA County, as in many other jurisdictions, there are specific rules and regulations governing the taxation of online sales. Here are some key considerations for businesses engaged in online commerce:
- Economic Nexus: LA County, along with many other states and counties, has adopted an economic nexus standard. This means that out-of-state sellers with a certain level of economic activity within the county (e.g., exceeding a certain revenue threshold or number of transactions) are required to collect and remit sales tax on their sales to LA County residents.
- Marketplace Facilitator Laws: LA County has implemented marketplace facilitator laws, which hold online marketplaces and third-party sellers accountable for sales tax collection. These laws ensure that sales tax is collected on transactions facilitated through online platforms, regardless of the seller's location.
- Use Tax: In addition to sales tax, LA County residents are also subject to a use tax. This tax applies to purchases made outside of the county, including online purchases from out-of-state sellers. Residents are responsible for self-reporting and paying this tax, which is equal to the sales tax rate in their jurisdiction.
Navigating the complexities of online sales tax can be challenging, but it's essential for businesses to comply with these regulations to avoid penalties and maintain a positive relationship with the tax authorities.
Compliance and Reporting
Ensuring compliance with the Los Angeles County Sales Tax regulations is a critical responsibility for businesses operating within the county. Non-compliance can lead to significant financial penalties, legal issues, and damage to a business’s reputation. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help businesses navigate the compliance and reporting process effectively.
Registering for Sales Tax
To begin collecting and remitting sales tax, businesses must first register with the appropriate tax authorities. In LA County, the registration process involves the following steps:
- Obtain a Seller's Permit: Apply for a Seller's Permit from the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA). This permit authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax in the state.
- Register with the County: Businesses must also register with the Los Angeles County Office of the Treasurer and Tax Collector. This registration ensures that the business is recognized as a tax collector for the county.
- Obtain Necessary Licenses: Depending on the nature of the business, additional licenses or permits may be required. These could include city or county business licenses, health permits, or industry-specific licenses.
The registration process typically involves providing basic business information, such as the legal name, physical address, and contact details. It's important to keep this information up-to-date with the tax authorities to avoid issues with tax filings and communications.
Collecting and Remitting Sales Tax
Once registered, businesses are responsible for collecting sales tax on taxable transactions. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the collection and remittance process:
- Calculate the Tax: For each taxable sale, calculate the sales tax amount by multiplying the sale price by the applicable tax rate. This includes the state sales tax rate, county sales tax rate, and any applicable district taxes.
- Charge the Tax: Add the calculated tax amount to the sale price and charge it to the customer. Ensure that the tax is clearly indicated on the invoice or receipt provided to the customer.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain accurate records of all sales transactions, including the sale price, tax amount, and the tax rate applied. This documentation is crucial for audit purposes and to support the accuracy of tax filings.
- Remit Tax to Authorities: Regularly remit the collected sales tax to the appropriate tax authorities. The frequency of remittance depends on the business's sales volume and the requirements set by the tax authorities. Common remittance frequencies include monthly, quarterly, or annually.
It's important to note that businesses should not commingle the collected sales tax with their own funds. The sales tax collected belongs to the government and must be held in a separate trust account until it is remitted to the tax authorities.
Filing Sales Tax Returns
In addition to collecting and remitting sales tax, businesses must also file sales tax returns with the tax authorities. These returns provide a detailed account of the sales tax collected and paid during a specific period. Here’s an overview of the filing process:
- Determine Filing Frequency: The filing frequency for sales tax returns depends on the business's sales volume. Businesses with higher sales volumes may be required to file more frequently (e.g., monthly or quarterly), while those with lower sales may file annually.
- Prepare the Return: Using the recorded sales transactions and tax amounts, prepare the sales tax return. This involves summarizing the total taxable sales, calculating the total tax due, and providing any necessary supporting documentation.
- File the Return: Submit the completed sales tax return to the appropriate tax authorities by the due date. This can be done online or through traditional mail, depending on the preferences and capabilities of the business and the tax authorities.
- Make Payment: If the tax return indicates that additional tax is due, make the payment to the tax authorities by the due date. This payment can be made electronically or through traditional methods such as checks or money orders.
It's crucial to file sales tax returns accurately and on time to avoid penalties and interest charges. Late or incorrect filings can lead to audits and other enforcement actions by the tax authorities.
Audits and Enforcement
Tax authorities in LA County, like elsewhere, have the authority to conduct audits to ensure compliance with sales tax regulations. Audits can be triggered by various factors, including random selection, risk-based criteria, or in response to tips or complaints.
During an audit, tax authorities will review the business's sales records, tax returns, and other financial documents to verify the accuracy of the reported sales tax. They may also interview employees and customers to gather additional information. It's important for businesses to cooperate fully with the audit process and provide all requested documentation in a timely manner.
If an audit reveals that a business has underreported sales tax or made other errors, the tax authorities may impose penalties and interest on the underpaid tax amount. The severity of the penalties can vary based on the nature and extent of the non-compliance.
To minimize the risk of audits and penalties, businesses should maintain accurate records, stay updated on tax regulations, and seek professional guidance when needed. Regular internal audits can also help identify and correct any potential issues before they become major problems.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The Los Angeles County Sales Tax has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers within the county. Understanding these impacts is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions and for consumers to understand the implications of their purchasing choices.
Impact on Businesses
For businesses operating within LA County, the sales tax system presents both challenges and opportunities. Here’s an overview of the key impacts:
- Revenue Generation: The sales tax is a significant source of revenue for LA County, providing funding for essential public services and infrastructure projects. For businesses, this means that a portion of their sales revenue is dedicated to supporting the local community.
- Pricing Strategies: The sales tax rate directly affects the final price of goods and services. Businesses must consider the tax rate when setting their prices to ensure competitiveness in the market and to cover their costs.
- Compliance and Administration: Compliance with sales tax regulations requires businesses to invest time and resources in training staff, maintaining accurate records, and staying updated on tax law changes. This administrative burden can be significant, especially for small businesses.
- Market Competition: The sales tax rate can influence consumer behavior and market competition. Businesses may need to adjust their strategies to remain competitive, especially when facing online or out-of-state competitors that may not be subject to the same tax rates.
- Tax Exemptions and Benefits: Businesses that qualify for certain sales tax exemptions or tax incentives can benefit from reduced tax liabilities. These benefits can provide a competitive advantage and help support the growth and sustainability of the business.
Overall, businesses in LA County play a vital role in the sales tax system, contributing to the local economy while navigating the complexities of tax compliance.
Impact on Consumers
Consumers in LA County are directly impacted by the sales tax system, as they bear the ultimate responsibility for paying the tax on their purchases. Here’s an overview of the key impacts on consumers:
- Increased Prices: The sales tax adds to the final price of goods and services, resulting in higher prices for consumers. This can affect purchasing decisions, especially for budget-conscious consumers or those with limited disposable income.
- Transparency and Awareness: Consumers have the right to know the sales tax rate and how it affects the prices they pay. Businesses are required to clearly display the tax amount on receipts and invoices, ensuring transparency in the transaction.
- Comparison Shopping: Consumers may engage in comparison shopping, considering not only the base price of goods but also the impact of sales tax on the final cost. This behavior can influence purchasing decisions and market dynamics.
- Exemptions and Savings: Consumers can benefit from sales tax exemptions on certain items, such as groceries, prescription medications, and clothing. These exemptions provide savings and can help stretch budgets, especially for essential purchases.
- Online Shopping Considerations: With the rise of e-commerce, consumers may opt for online shopping to compare prices and take advantage of potential savings. However, they should be aware of the use tax, which applies to out-of-state purchases, to ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Understanding the sales tax system empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions and actively contribute to the local economy through their tax payments.
Future Outlook and Implications
The Los Angeles County Sales Tax system is dynamic and subject to ongoing changes and developments. As economic conditions evolve and legislative priorities shift, the tax landscape can undergo significant transformations. Here’s an analysis of the future outlook and potential implications for businesses and consumers.
Potential Rate Changes
Sales tax rates in LA County, like in many other jurisdictions, are not static. They can be subject to adjustments based on various factors, including economic conditions,



