La Ca Tax Rate
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of the California State Tax Rate, a crucial aspect of understanding the financial landscape for residents and businesses within the Golden State. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the CA tax system, shedding light on the rates, structures, and implications for taxpayers. Join us as we navigate through the complexities of California's tax regime, providing you with valuable insights and a thorough understanding of this essential topic.
Unraveling the California Tax Landscape
California, renowned for its vibrant economy and diverse population, boasts a robust tax system that plays a pivotal role in funding essential public services and infrastructure. The state’s tax policies are designed to balance revenue generation with economic growth, impacting individuals, businesses, and investors alike. As we embark on this journey, we aim to demystify the CA tax rate, offering a comprehensive overview that will empower readers with the knowledge needed to navigate their tax obligations confidently.
Understanding the CA Income Tax Structure
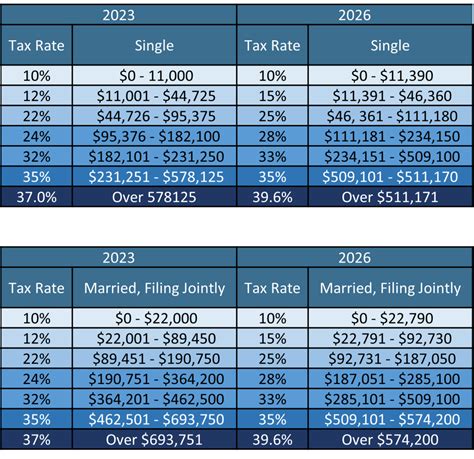
At the heart of California’s tax system lies its progressive income tax structure, which means that higher income earners contribute a larger proportion of their income towards state revenue. This structure is designed to promote fairness and ensure that those with greater financial means contribute accordingly. The CA income tax is levied on various sources of income, including wages, salaries, investments, and business profits.
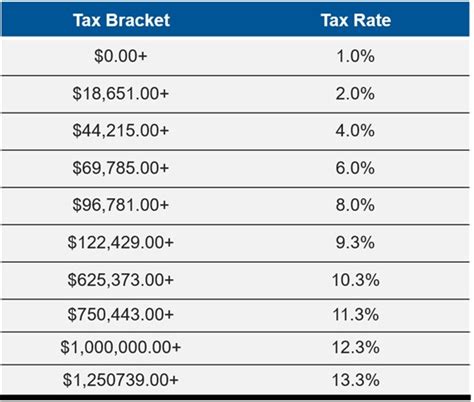
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $9,738 | 1% |
| $9,739 - $40,967 | 2% |
| $40,968 - $81,935 | 4% |
| $81,936 - $274,499 | 6% |
| $274,500 - $548,999 | 8% |
| $549,000 - $1,098,999 | 9.3% |
| $1,099,000 and above | 10.3% |
Sales and Use Taxes: Impact on Daily Life
California also imposes a state sales and use tax on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services. This tax is typically added to the purchase price, making it a visible component of the cost of goods and services for consumers. Additionally, the state allows local jurisdictions to levy their own sales taxes, resulting in varying rates across different regions.
The sales tax rate in California can range from approximately 7.25% to over 10%, depending on the location. This variability is a result of local add-on taxes that municipalities or counties may implement to fund specific projects or services. For instance, a city might add a 0.5% tax to fund public transportation improvements, resulting in a higher overall sales tax rate for its residents.
| City | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Los Angeles | 9.5% |
| San Francisco | 8.75% |
| San Diego | 8.0% |
| Sacramento | 8.75% |
| Oakland | 9.25% |
Property Taxes: A Major Revenue Source
California’s property tax system, governed by Proposition 13, is a significant revenue generator for the state and local governments. This system, while relatively straightforward, has a profound impact on homeowners and property investors.
Under Proposition 13, the property tax rate is set at 1% of the assessed value of the property, with an annual inflation adjustment limit of 2%. This means that, in theory, a property's assessed value should only increase by a maximum of 2% each year, ensuring that property taxes remain relatively stable for long-term homeowners. However, when a property is sold or undergoes a significant change, its assessed value is reset to its current market value, which can lead to a substantial increase in property taxes for new owners.
The assessed value is determined by the county assessor and is based on factors such as the property's location, size, and market conditions. It's important to note that California's property tax system also allows for various exemptions and deductions, such as the Homeowner's Exemption, which reduces the assessed value of a primary residence by up to $7,000.
Corporate and Business Taxes: Supporting Economic Growth
California’s tax regime also extends to businesses and corporations, playing a crucial role in fostering economic development and supporting local communities. The state imposes a corporate income tax on business profits, which varies depending on the entity’s structure and revenue.
For C Corporations, the corporate tax rate is a flat 8.84%, while S Corporations and Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) are taxed at the individual member level, with rates aligned with the personal income tax brackets mentioned earlier. This means that business owners and investors must carefully consider the tax implications of their business structure to optimize their tax liability.
In addition to the income tax, businesses in California are subject to various other taxes and fees, including the Franchise Tax, Sales and Use Tax, and Employment Taxes. These taxes contribute to the state's revenue stream and help fund essential services, infrastructure projects, and public benefits.
Tax Incentives and Credits: Encouraging Investment
To attract and retain businesses, California offers a range of tax incentives and credits aimed at stimulating economic growth and job creation. These incentives can significantly reduce a company’s tax liability and make the state more competitive in the global business landscape.
One notable example is the Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit, which provides a credit of up to 17% of qualified research expenses for businesses conducting innovative research activities in California. This credit can be carried forward for up to five years, offering long-term benefits for companies investing in research and development.
Additionally, California offers tax credits for hiring veterans, investing in renewable energy, and supporting low-income communities. These incentives not only benefit businesses but also contribute to the state's overall social and economic development goals.
The Future of California’s Tax System
As California continues to evolve, its tax system is likely to undergo changes and reforms to adapt to the evolving economic landscape. The state’s commitment to fairness, sustainability, and economic growth will shape the future of its tax policies, impacting taxpayers and businesses alike.
One area of potential focus is tax reform aimed at simplifying the tax code, reducing complexity, and minimizing compliance burdens for taxpayers. This could involve consolidating tax brackets, streamlining tax forms, and enhancing tax administration to make the system more efficient and user-friendly.
Additionally, as the state explores ways to enhance its revenue base and support public services, it may consider expanding its tax base, exploring new revenue streams, or adjusting existing tax rates. These changes could impact individuals and businesses, necessitating a proactive approach to tax planning and compliance.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of CA Taxes
California’s tax system is a multifaceted and dynamic entity, playing a critical role in the state’s economic prosperity and public welfare. By understanding the various tax rates, structures, and incentives, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions, optimize their tax liability, and contribute effectively to the state’s fiscal health.
As we've explored in this comprehensive guide, the CA tax rate encompasses a range of taxes, from income and sales to property and corporate taxes. Each of these taxes has unique characteristics and implications, requiring a thoughtful approach to compliance and planning. By staying informed and seeking professional guidance when needed, taxpayers can navigate the complexities of California's tax landscape with confidence and ensure they meet their obligations accurately and efficiently.
How often are tax rates adjusted in California?
+Tax rates in California are typically adjusted annually to account for inflation and economic changes. The state legislature and tax authorities review and approve these adjustments to ensure the tax system remains fair and up-to-date.
Are there any tax breaks or incentives for first-time homebuyers in California?
+Yes, California offers several tax benefits for first-time homebuyers, including the Homeowner’s Exemption, which reduces the assessed value of a primary residence by up to $7,000. Additionally, there are tax credits and deductions available for mortgage interest and property taxes.
How does California’s tax system compare to other states in terms of overall tax burden?
+California’s tax system is considered relatively high in terms of overall tax burden, primarily due to its progressive income tax rates and the inclusion of local sales and use taxes. However, the state also offers a range of tax incentives and credits that can offset some of this burden for businesses and individuals.
What are the key factors to consider when choosing a business entity for tax purposes in California?
+When selecting a business entity, consider factors such as tax liability, ownership structure, and potential tax incentives. C Corporations have a flat tax rate, while S Corporations and LLCs are taxed at the individual member level. Additionally, research tax credits and other incentives specific to your industry or business activities.
How can I stay updated on changes to California’s tax laws and regulations?
+To stay informed, regularly visit the official websites of the California Franchise Tax Board and the State Board of Equalization. These agencies provide updates, news releases, and guidance on tax-related matters. Additionally, consider subscribing to tax newsletters or seeking advice from tax professionals to ensure you’re aware of any changes that may impact your tax obligations.