Kentucky State Taxes Status

In the United States, state taxes vary significantly across different jurisdictions, impacting residents' financial planning and business operations. This article delves into the specifics of Kentucky's state taxes, exploring its current status, rates, and the various tax laws that shape the state's fiscal landscape.
Understanding Kentucky’s Tax Structure

Kentucky, often praised for its business-friendly environment, boasts a unique tax system that influences its economic growth and resident’s financial obligations. The state’s tax structure is primarily composed of income taxes, sales taxes, and various other levies, each designed to contribute to the state’s revenue stream.
Income Tax in Kentucky
Kentucky operates a progressive income tax system, which means that the tax rate increases as an individual’s income rises. This system is structured to ensure fairness, with higher-income earners contributing a larger proportion of their income to state revenues.
As of the current tax year, Kentucky’s income tax rates range from 5.8% to 6.0%, with an additional 0.15% local tax. This means residents’ effective tax rates can range from 5.95% to 6.15%, depending on their income bracket and the locality they reside in.
It’s worth noting that Kentucky’s income tax rates are relatively moderate compared to other states. For instance, a single filer with an income of 50,000 would fall into the <strong>5.8%</strong> tax bracket, resulting in a tax liability of approximately <strong>2,900, excluding any applicable deductions and credits.
Sales and Use Tax
Kentucky also imposes a sales and use tax, which is a type of consumption tax. This tax is levied on the sale of goods and services within the state and is typically paid by the consumer at the point of purchase. The current sales tax rate in Kentucky is 6%, which is on the lower end of the spectrum when compared to other states.
However, it’s important to recognize that Kentucky allows local jurisdictions to add their own sales tax rates, which can increase the overall sales tax burden. For example, in Louisville, the combined state and local sales tax rate is 6.5%, with an additional 0.5% charged for specific purposes like road improvements.
Other Kentucky Taxes
Beyond income and sales taxes, Kentucky levies various other taxes that contribute to its overall tax revenue. These include:
- Property Tax: Kentucky’s property tax rates vary based on location, with rates ranging from 0.2% to 2.3% of the assessed value. The average effective property tax rate in Kentucky is 0.8%, which is relatively low compared to other states.
- Motor Vehicle Tax: Kentucky imposes a tax on the purchase or transfer of motor vehicles. The tax rate is 6% of the purchase price or the fair market value, whichever is higher.
- Inheritance Tax: Kentucky has an inheritance tax, which is levied on property received by beneficiaries upon the death of the owner. The tax rates depend on the beneficiary’s relationship to the deceased and the value of the property received.
Kentucky’s Tax Incentives and Benefits
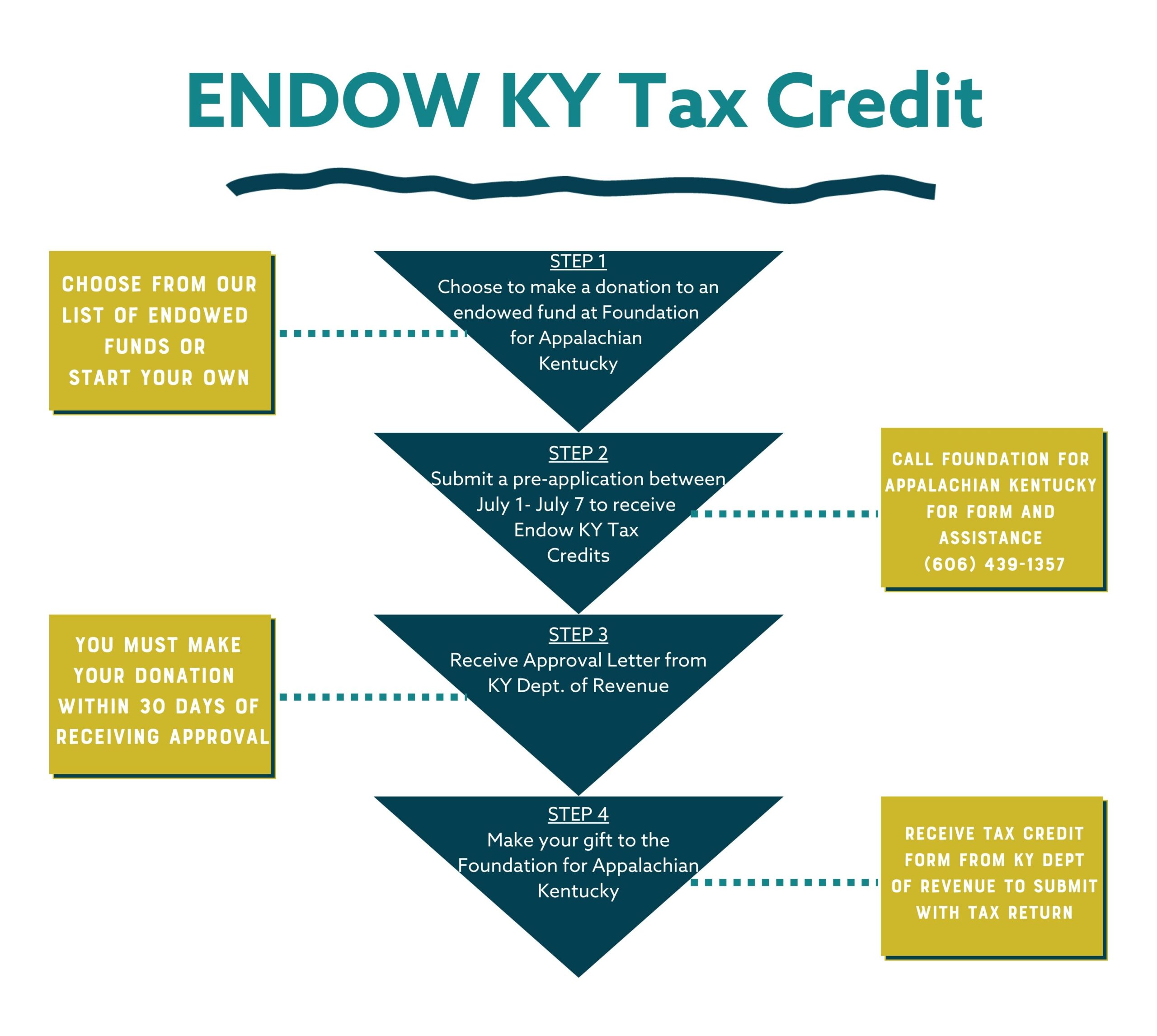
Kentucky is known for its efforts to attract and retain businesses through a range of tax incentives and benefits. These incentives aim to stimulate economic growth and make Kentucky an attractive destination for businesses and investors.
Tax Credits and Incentives
The state offers a variety of tax credits and incentives to encourage business growth and investment. These include:
- Kentucky Business Investment Program: This program offers tax credits to businesses that create new full-time jobs and make significant capital investments in Kentucky. The credits can offset up to 100% of the business’s income tax liability.
- Research and Development Tax Credits: Kentucky provides tax credits for qualified research expenses, encouraging businesses to invest in innovation and technological advancements.
- Film and Entertainment Tax Incentives: To boost the state’s film industry, Kentucky offers tax credits for film production costs incurred within the state.
Low Corporate Tax Rates
Kentucky has a competitive corporate income tax rate, currently set at 6%, which is on the lower end of the national spectrum. This rate applies to corporations, S corporations, and financial institutions. The state also allows for the deduction of federal income taxes, which can further reduce the effective tax rate.
Kentucky’s Tax-Friendly Policies for Retirees
Kentucky is particularly attractive to retirees due to its tax policies. Social Security benefits are exempt from state income tax, and certain pension and retirement plan distributions are also partially exempt.
Tax Compliance and Reporting in Kentucky
Understanding Kentucky’s tax laws and staying compliant is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. Here are some key considerations:
- Individual Income Tax Returns: Kentucky residents must file an individual income tax return annually. The due date is typically April 15th, but it can be extended to October 15th. The Kentucky Department of Revenue provides resources and guidance for tax filing.
- Business Tax Registration: Businesses operating in Kentucky must register with the state and obtain the necessary licenses and permits. This includes registering for sales tax collection if the business sells taxable goods or services.
- Sales Tax Compliance: Businesses collecting sales tax must remit the tax to the state on a regular basis, typically monthly or quarterly. The Kentucky Department of Revenue provides detailed guidelines for sales tax compliance.
Kentucky’s Tax Future: Trends and Projections
Kentucky’s tax landscape is subject to change, influenced by economic trends, legislative decisions, and the state’s overall fiscal health. Here are some key trends and projections:
- Economic Growth: Kentucky’s economy is expected to continue its steady growth, driven by sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and tourism. This growth is likely to result in increased tax revenues, particularly from income and sales taxes.
- Tax Reform: While Kentucky has been relatively stable in its tax policies, there are ongoing discussions about potential tax reforms. These could include changes to the state’s income tax brackets, the introduction of new tax incentives, or adjustments to sales tax rates.
- Population Growth: Kentucky’s population is projected to grow modestly, which could lead to increased demand for public services and, consequently, higher tax revenues. However, population growth can also bring challenges in terms of infrastructure development and the need for additional funding.
Conclusion
Kentucky’s tax system is a nuanced and dynamic framework that shapes the state’s economic landscape. With its progressive income tax, moderate sales tax, and array of targeted incentives, Kentucky offers a competitive and attractive environment for businesses and individuals alike. Understanding Kentucky’s tax status is crucial for effective financial planning and business strategy, ensuring compliance and leveraging the opportunities the state provides.
What is Kentucky’s income tax rate for 2023?
+Kentucky’s income tax rate for the 2023 tax year is 5.8% to 6.0%, with an additional 0.15% local tax. This results in effective tax rates ranging from 5.95% to 6.15%.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in Kentucky?
+Yes, Kentucky offers several tax incentives to businesses, including the Kentucky Business Investment Program, Research and Development Tax Credits, and Film and Entertainment Tax Incentives. These programs aim to encourage investment, job creation, and innovation within the state.
How does Kentucky’s sales tax rate compare to other states?
+Kentucky’s sales tax rate of 6% is on the lower end of the national spectrum. However, it’s important to note that local jurisdictions can add their own sales tax rates, which can increase the overall sales tax burden in certain areas.



