Is Tax Evasion A Felony

Tax evasion, a term that often sparks intrigue and raises important legal questions, is a complex issue with far-reaching implications. In the realm of financial and legal matters, understanding the intricacies of tax evasion and its potential consequences is crucial. This comprehensive exploration delves into the definition, common practices, and legal repercussions of tax evasion, shedding light on a topic that impacts individuals, businesses, and governments alike.
Understanding Tax Evasion
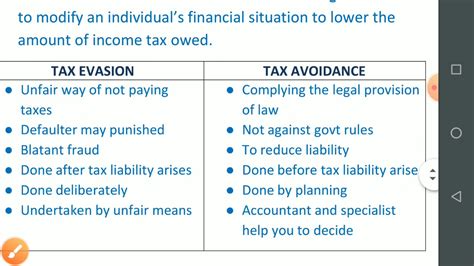
Tax evasion is a deliberate act of avoiding or underreporting one's financial obligations to the government, specifically regarding taxes. It is a serious offense that undermines the fairness and integrity of the tax system, impacting revenue collection and, consequently, the provision of public services.
The practice of tax evasion takes various forms, each with its own degree of complexity and potential consequences. Common methods include:
- Underreporting Income: This involves intentionally failing to report all income earned, whether from business activities, investments, or other sources. It is one of the most prevalent forms of tax evasion, as it allows individuals or entities to pay less tax than they actually owe.
- Overstating Expenses: Another common tactic is inflating expenses on tax returns, which reduces taxable income and, consequently, the amount of tax owed. This method often involves claiming false or exaggerated business expenses.
- Offshore Accounts and Tax Havens: The use of offshore bank accounts or tax havens is a sophisticated method of tax evasion. Individuals or corporations may transfer funds to these locations to avoid domestic taxation, taking advantage of lenient tax laws and privacy protections.
- False Deductions: Some individuals or businesses claim false deductions on their tax returns, such as non-existent charitable donations or inflated medical expenses, to reduce their taxable income.
- Structuring Transactions: This practice involves structuring financial transactions in a way that avoids reporting requirements. For instance, making multiple cash deposits just below the reporting threshold to evade detection.
The Legal Implications of Tax Evasion
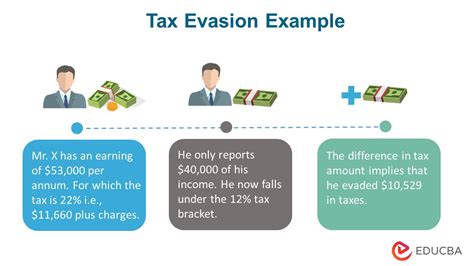
Tax evasion is not merely a financial misstep but a serious legal offense. The legal repercussions can be severe and far-reaching, impacting not only the individual or entity involved but also their financial standing and reputation.
Is Tax Evasion a Felony?
In many jurisdictions, including the United States, tax evasion is considered a felony offense. A felony is a serious crime that is typically punishable by imprisonment for a year or more. The specific definition and penalties for tax evasion can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the severity of the offense.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States plays a pivotal role in investigating and prosecuting tax evasion cases. The IRS has a dedicated Criminal Investigation division that focuses on identifying and bringing tax evaders to justice. The penalties for tax evasion can include significant fines, imprisonment, or both.
| Jurisdiction | Penalty |
|---|---|
| United States | Fines up to $100,000 for individuals and $500,000 for corporations, plus imprisonment of up to 5 years |
| United Kingdom | Unlimited fines and imprisonment of up to 7 years |
| Canada | Fines up to $250,000 and imprisonment of up to 2 years for individuals, and fines up to $1 million and imprisonment of up to 5 years for corporations |
| Australia | Fines up to $1.1 million and imprisonment of up to 10 years |

It's important to note that while these are common penalties, the actual sentence can vary based on the specific circumstances of the case, including the amount of tax evaded, the intent, and any mitigating factors.
The Impact of Tax Evasion
Tax evasion has wide-ranging consequences that extend beyond the individual or entity involved. It undermines the fairness of the tax system, as it allows some individuals or businesses to avoid their fair share of taxes, shifting the burden onto others. This can lead to reduced government revenue, impacting the funding of public services, infrastructure, and social programs.
Moreover, tax evasion can distort market competition, as businesses that evade taxes gain an unfair advantage over those who comply with tax laws. This unfair competition can harm the overall business environment and economic growth.
Prevention and Compliance
Preventing tax evasion and promoting compliance with tax laws is a collective effort involving governments, tax authorities, and individuals or businesses.
Measures for Prevention
Governments and tax authorities employ various strategies to deter tax evasion, including:
- Enhanced Enforcement: Tax authorities conduct audits and investigations to identify potential cases of tax evasion. These efforts can lead to the discovery of hidden assets, offshore accounts, and other tax evasion schemes.
- Whistleblower Programs: Many jurisdictions have implemented whistleblower programs that encourage individuals to report suspected tax evasion. These programs often offer rewards or incentives to whistleblowers.
- International Cooperation: In an era of globalization, tax authorities collaborate across borders to combat tax evasion. This includes sharing information and working together to track down individuals or entities that evade taxes by utilizing offshore accounts or tax havens.
Compliance Strategies for Individuals and Businesses
For individuals and businesses, maintaining compliance with tax laws is essential to avoid legal troubles and maintain a positive reputation. Here are some strategies to ensure compliance:
- Keep Accurate Records: Maintain detailed and organized financial records, including income, expenses, and transactions. This practice not only simplifies tax preparation but also provides a clear audit trail in case of an investigation.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with tax professionals, such as accountants or tax attorneys, to ensure compliance with tax laws. They can provide guidance on tax planning, deductions, and reporting requirements.
- Understand Tax Laws: Stay informed about tax laws and regulations that apply to your situation. This includes being aware of changes in tax codes, reporting requirements, and deadlines.
- Report Truthfully: When filing tax returns, ensure that all information is accurate and complete. Avoid the temptation to underreport income or overstate expenses to reduce tax liability.
Conclusion
Tax evasion is a serious offense with significant legal and financial consequences. It undermines the fairness of the tax system and can have a detrimental impact on society as a whole. By understanding the definition, practices, and legal implications of tax evasion, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid the pitfalls of tax evasion.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are the signs of tax evasion?
+Signs of tax evasion can include consistently underreporting income, claiming excessive or false deductions, using offshore accounts without disclosure, or failing to file tax returns altogether.
What happens if I am accused of tax evasion?
+If accused of tax evasion, it is crucial to seek legal advice immediately. You may be subject to an investigation by tax authorities, and a conviction can result in significant fines and imprisonment. Consulting with a tax attorney can help navigate the legal process and potentially mitigate the consequences.
Can tax evasion charges be reduced or dismissed?
+In some cases, tax evasion charges can be reduced or dismissed. This may occur if there is a valid defense, such as an honest mistake or if the tax authorities made procedural errors. However, it is essential to have a strong legal strategy and evidence to support your case.
Are there any tax evasion cases that carry lesser penalties?
+Yes, in certain circumstances, tax evasion cases may result in lesser penalties. For instance, if the amount of tax evaded is relatively small or if the individual or entity voluntarily discloses the evasion and cooperates with tax authorities, the penalties may be reduced.
How can I ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid tax evasion charges?
+To ensure compliance and avoid tax evasion charges, it is crucial to maintain accurate financial records, seek professional tax advice, understand your tax obligations, and report your income and expenses truthfully. Regularly reviewing tax laws and staying updated on any changes can also help prevent unintentional violations.