Is Life Insurance Taxed
Understanding the tax implications of life insurance is crucial for anyone considering this financial product. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of how life insurance policies are taxed, exploring the various aspects that impact policyholders and beneficiaries. From the different types of life insurance to the tax treatment of premiums and payouts, we will provide a detailed analysis to help you navigate this complex landscape.
The Taxation Landscape of Life Insurance Policies

Life insurance is an essential financial tool that provides security and peace of mind to policyholders and their loved ones. However, the tax treatment of these policies can be a complex and often confusing matter. In this section, we will provide an overview of the key concepts and considerations regarding the taxation of life insurance.
Understanding Life Insurance Types and Their Tax Treatment
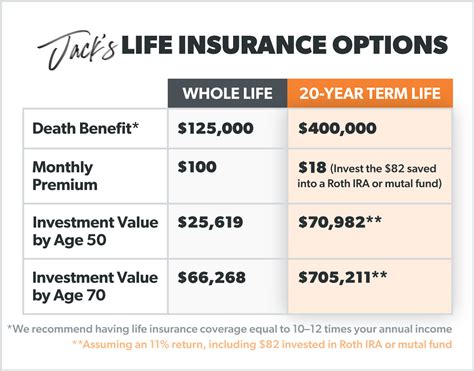
Life insurance policies come in various forms, each with its own set of features and tax implications. The two primary types are term life insurance and permanent life insurance, which encompass further subtypes. Term life insurance offers coverage for a specific period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years, and is generally more affordable. On the other hand, permanent life insurance, including whole life and universal life policies, provides lifelong coverage and often includes a cash value component. The tax treatment of these policies differs significantly, as we will explore below.
| Life Insurance Type | Tax Treatment |
|---|---|
| Term Life Insurance | Premiums paid are generally not tax-deductible, and death benefits received by beneficiaries are typically tax-free. |
| Whole Life Insurance | Premiums paid may be partially tax-deductible, and the cash value within the policy may be subject to taxation if withdrawn or used as collateral. |
| Universal Life Insurance | Similar to whole life, premiums may be tax-deductible, and the cash value component is taxable if accessed. |

It's important to note that the tax treatment of life insurance policies can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific features of the policy. Therefore, consulting with a tax professional is highly recommended to ensure a thorough understanding of the tax implications relevant to your circumstances.
Premiums, Payouts, and Tax Liability
When it comes to life insurance, both the premiums paid and the payouts received can have tax consequences. Let’s explore these aspects in detail.
Premiums and Tax Deductibility
The tax treatment of life insurance premiums depends on the type of policy and the purpose for which it is held. Generally, premiums for term life insurance are not tax-deductible, as they are considered a personal expense. However, premiums for business-owned life insurance policies, often used as a form of employee benefit or key person insurance, may be tax-deductible as a business expense.
For permanent life insurance policies with a cash value component, the tax treatment becomes more complex. The premium payments may be partially tax-deductible if the policy qualifies as a qualified plan, such as a cash value life insurance plan or a whole life insurance plan. These plans have specific guidelines and limitations set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to ensure they maintain their tax-advantaged status.
Death Benefits and Tax-Free Status
One of the primary benefits of life insurance is the tax-free status of the death benefit payouts. In most cases, the proceeds received by the beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s death are not subject to federal income tax. This applies to both term life and permanent life insurance policies, providing a valuable financial safety net for loved ones.
However, it's important to note that there are certain situations where the death benefit may be taxable. For instance, if the policyholder is the beneficiary of their own policy and receives the death benefit while alive, this could be considered a taxable event. Additionally, if the policy has been in force for less than two years at the time of death, the IRS may treat the death benefit as a modified endowment contract (MEC), subjecting it to ordinary income tax.
Cash Value Withdrawals and Loans
Permanent life insurance policies, particularly those with a cash value component, offer policyholders the flexibility to access their cash value through withdrawals or loans. While this can be a valuable feature, it also carries tax implications.
When a policyholder takes a loan against the cash value of their permanent life insurance policy, the loan is not considered taxable income. However, if the policy lapses or is surrendered while the loan is outstanding, the outstanding loan amount may be subject to taxation as ordinary income. Additionally, if the policyholder chooses to withdraw funds from the cash value, the taxable portion of the withdrawal is generally the amount that exceeds the total premiums paid into the policy.
Tax Considerations for Business-Owned Life Insurance
Business-owned life insurance (BOLI) is a specialized form of life insurance that businesses use for various purposes, such as funding employee benefits, executive compensation, or as a source of capital. The tax treatment of BOLI policies differs from personal life insurance and requires careful consideration.
Tax Deductibility of BOLI Premiums
BOLI policies allow businesses to deduct the premiums paid as a business expense, providing a valuable tax benefit. This deduction is available as long as the policy is owned by the business and the premiums are reasonable and customary for the coverage provided. However, it’s important to note that there are specific guidelines and limitations set by the IRS to ensure that BOLI policies are not abused for tax avoidance purposes.
Taxation of BOLI Death Benefits
The death benefits received by the business from a BOLI policy are generally taxable as ordinary income. This is because the business is considered the beneficiary of the policy and the death benefit is seen as compensation for the loss of the insured individual’s services. However, there are certain exceptions and limitations to this taxation, and businesses should consult with tax professionals to understand the specific implications for their circumstances.
Life Insurance and Estate Planning
Life insurance plays a crucial role in estate planning, providing a way to transfer wealth to heirs and beneficiaries while minimizing tax liability. Let’s explore how life insurance fits into the estate planning landscape.
Using Life Insurance to Fund Estate Taxes
One of the primary benefits of life insurance in estate planning is its ability to provide liquidity to pay for estate taxes and other expenses associated with settling an estate. By purchasing a life insurance policy with a death benefit sufficient to cover these costs, individuals can ensure that their heirs receive the full value of the estate without having to sell assets or incur significant tax burdens.
Life Insurance and Gift Tax Exclusion
Life insurance policies can also be used strategically to take advantage of the annual gift tax exclusion. Policyholders can gift a certain amount of the policy’s death benefit to their beneficiaries each year without triggering gift taxes. This allows for the transfer of wealth while minimizing tax liability.
Trust-Owned Life Insurance (TOLI)
Trust-owned life insurance (TOLI) is a specialized arrangement where a trust owns the life insurance policy on behalf of the insured individual. TOLI policies can provide significant tax advantages and flexibility in estate planning. The trust can be structured to minimize estate and income taxes, and the death benefit can be used to fund various estate planning objectives, such as charitable donations or providing for heirs.
The Impact of Life Insurance on Medicare and Medicaid
Life insurance policies can also have implications for individuals receiving Medicare or Medicaid benefits. It’s important to understand how these programs interact with life insurance to avoid any potential complications.
Medicare and Life Insurance
For individuals on Medicare, life insurance policies do not typically impact their benefits. However, it’s crucial to disclose any life insurance policies when applying for Medicare Savings Programs or other Medicare-related assistance. Failure to disclose such information could result in penalties or repayment of benefits.
Medicaid and Life Insurance
Medicaid, on the other hand, has more stringent rules regarding life insurance. Medicaid considers life insurance policies as an asset when determining eligibility for benefits. If the policy’s cash value exceeds the Medicaid asset limit, it could impact an individual’s eligibility. However, there are strategies, such as using an irrevocable life insurance trust (ILIT), that can help protect the policy’s value while maintaining Medicaid eligibility.
Navigating the Complexities: Expert Insights

The tax landscape surrounding life insurance policies can be intricate and challenging to navigate. Here, we provide expert insights and considerations to help you make informed decisions regarding the tax implications of your life insurance policy.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Given the complexity of tax laws and the potential consequences of missteps, it is highly recommended to seek professional advice when dealing with life insurance and taxes. Tax professionals, such as Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) or Enrolled Agents (EAs), can provide valuable guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
These experts can help you understand the tax implications of your life insurance policy, including the deductibility of premiums, the tax treatment of cash value withdrawals or loans, and the potential tax consequences of death benefit payouts. They can also assist in optimizing your tax strategy and ensuring compliance with applicable regulations.
Regular Policy Review and Updates
Life insurance policies and tax laws are not static; they can change over time. Therefore, it is essential to regularly review and update your policy to ensure it aligns with your financial goals and the current tax landscape. Changes in your personal or financial situation, such as marriage, divorce, birth of a child, or career transitions, may impact the tax treatment of your policy.
Staying informed about any changes in tax laws and consulting with your financial advisor or tax professional can help you make necessary adjustments to your policy. This proactive approach can ensure that your life insurance remains an effective tool for financial protection and tax planning.
Understanding Tax-Advantaged Life Insurance Strategies
Certain life insurance strategies can offer significant tax advantages, such as tax-deferred growth of cash value and tax-free death benefits. One such strategy is the use of permanent life insurance, which, when properly structured, can provide tax-efficient wealth accumulation and preservation.
Additionally, life insurance can be a powerful tool in estate planning, allowing for the transfer of wealth to heirs while minimizing tax liability. Strategies like irrevocable life insurance trusts (ILITs) and gifting of life insurance policies can help ensure that your beneficiaries receive the full value of your estate, free from excessive taxes.
The Role of Life Insurance in Business Succession Planning
For business owners, life insurance plays a crucial role in business succession planning. Business-owned life insurance (BOLI) policies can provide the necessary funds to buy out a deceased owner’s interest, ensuring the business’s continuity and protecting the interests of remaining owners and employees.
Furthermore, BOLI policies can be structured to provide key employees with additional financial security, enhancing employee retention and loyalty. The tax-deductible premiums and tax-free death benefits of BOLI policies make them an attractive option for business owners looking to protect their businesses and employees.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Financial Decisions
In conclusion, understanding the tax implications of life insurance is a critical aspect of financial planning. By familiarizing yourself with the tax treatment of different types of life insurance policies, premiums, and payouts, you can make informed decisions to maximize the benefits of your policy while minimizing tax liability.
Remember, the tax landscape is dynamic, and it's essential to stay informed and seek professional guidance to navigate this complex terrain. Whether you're an individual, a business owner, or a beneficiary, life insurance can be a powerful tool for financial security and wealth transfer, but it requires careful consideration of its tax implications.
Are life insurance premiums tax-deductible for individuals?
+For most individuals, life insurance premiums are not tax-deductible. However, there are certain situations where premiums may be deductible, such as when the policy is held by a business as a form of employee benefit or key person insurance.
What is the tax treatment of life insurance death benefits?
+In most cases, the death benefits received by beneficiaries from a life insurance policy are not subject to federal income tax. However, there are exceptions, such as when the policy has been in force for less than two years or when the beneficiary is the policyholder.
How are cash value withdrawals from life insurance policies taxed?
+When withdrawing funds from the cash value of a life insurance policy, the taxable portion is generally the amount that exceeds the total premiums paid into the policy. This taxable amount is considered ordinary income and is subject to income tax.
Can life insurance be used to minimize estate taxes?
+Yes, life insurance can be a valuable tool in estate planning to minimize estate taxes. By purchasing a life insurance policy with a sufficient death benefit, individuals can ensure that their heirs receive the full value of the estate without incurring significant tax burdens.
What are the tax implications of business-owned life insurance (BOLI)?
+BOLI policies offer tax advantages to businesses, as the premiums paid are generally tax-deductible. However, the death benefits received by the business are taxable as ordinary income. Businesses should consult tax professionals to understand the specific implications of BOLI policies.