Illinois Real Estate Taxes

Illinois, known for its vibrant cities, diverse landscapes, and rich history, is a state that attracts residents and investors alike. Among the many considerations when buying property in Illinois, understanding the real estate tax system is crucial. Real estate taxes play a significant role in the state's economy and are a key factor in property ownership. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Illinois real estate taxes, exploring the rates, assessments, exemptions, and the overall impact on homeowners and investors.
Understanding Illinois Real Estate Tax Rates

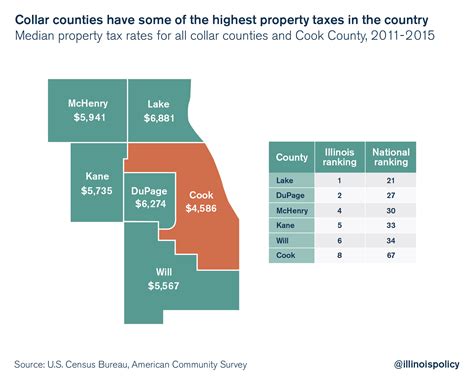
Illinois real estate taxes are levied on both residential and commercial properties and are primarily used to fund local government services, including schools, fire departments, and infrastructure development. The tax rates can vary significantly depending on the location within the state, with different counties and municipalities setting their own tax rates.
The tax rate is typically expressed as a percentage of the property's assessed value. For instance, if a property is assessed at $200,000 and the tax rate is 2%, the annual real estate tax due would be $4,000. However, it's important to note that this is a simplified example, and the actual calculation involves several factors.
One key factor influencing the tax rate is the taxing district. Illinois is divided into various taxing districts, each with its own set of tax rates. These districts can include counties, townships, municipalities, and special purpose districts like school districts or fire protection districts. Each of these entities has the authority to levy taxes on properties within their jurisdiction, leading to a complex web of tax rates.
| Taxing District | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Cook County | 1.85% |
| DuPage County | 1.70% |
| Lake County | 1.55% |
| Will County | 1.60% |
| McHenry County | 1.40% |

The table above provides a glimpse into the varying tax rates across different counties in Illinois. It's important to note that these rates are subject to change annually, and they can also differ within a county, depending on the specific municipality or taxing district.
Factors Influencing Tax Rates
The tax rates in Illinois are influenced by a variety of factors, including the cost of living, property values, and the demand for local services. For instance, areas with higher property values and a greater demand for services, such as schools and public safety, often have higher tax rates. On the other hand, rural areas with lower property values and fewer service requirements may have lower tax rates.
Additionally, the state's budget and economic conditions play a role in tax rates. During times of economic prosperity, tax rates may remain stable or even decrease, while economic downturns can lead to increased tax rates to compensate for reduced revenue.
Real Estate Tax Assessments in Illinois

Understanding the assessment process is essential when navigating Illinois real estate taxes. Property assessments are conducted to determine the value of a property, which forms the basis for calculating the real estate taxes due.
In Illinois, the assessment process is typically handled by the county assessor's office. Assessors are responsible for evaluating properties within their jurisdiction and assigning a fair market value. This value is then used to calculate the property's taxable value, which is what determines the real estate tax bill.
The assessment process involves various methods, including analyzing recent sales of comparable properties, evaluating the property's physical characteristics, and considering any improvements or modifications made to the property. Assessors aim to ensure that properties are valued fairly and accurately, taking into account factors like location, size, and condition.
Assessment Frequency and Appeals
The frequency of property assessments varies across Illinois. In some counties, assessments are conducted annually, while in others, they may occur every few years. This variation is influenced by factors such as the county’s budget and the availability of resources for conducting assessments.
Property owners have the right to appeal their assessed value if they believe it is inaccurate or unfair. The appeals process involves submitting evidence and documentation to support the claim that the assessed value should be adjusted. It's important for property owners to be aware of the assessment schedule and their rights regarding appeals.
| County | Assessment Frequency |
|---|---|
| Cook County | Every 3 years |
| DuPage County | Every 4 years |
| Lake County | Every 3 years |
| Will County | Every 3 years |
| McHenry County | Every 4 years |
The table above provides an overview of the assessment frequencies in some of the major counties in Illinois. It's important to consult the relevant county assessor's office for specific details and timelines regarding assessments and appeals.
Exemptions and Reductions in Illinois Real Estate Taxes
Illinois offers various exemptions and tax reduction programs to ease the financial burden of real estate taxes for eligible property owners. These exemptions can significantly reduce the taxable value of a property, leading to lower tax bills.
Homestead Exemptions
One of the most common exemptions in Illinois is the homestead exemption, which provides a reduction in the assessed value of a property that is the primary residence of the owner. This exemption aims to provide relief to homeowners, making homeownership more affordable.
The homestead exemption varies in value across the state, with some counties offering a fixed dollar amount reduction, while others provide a percentage reduction based on the assessed value. For instance, Cook County offers a homestead exemption of up to $6,000, while DuPage County provides a reduction of 4% on the assessed value.
| County | Homestead Exemption |
|---|---|
| Cook County | $6,000 |
| DuPage County | 4% of assessed value |
| Lake County | $6,000 |
| Will County | $6,000 |
| McHenry County | $5,000 |
The table above showcases the homestead exemptions in some of the major counties in Illinois. These exemptions can provide significant savings on real estate taxes for eligible homeowners.
Other Exemptions and Reductions
In addition to the homestead exemption, Illinois offers a range of other exemptions and tax reduction programs. These include:
- Senior Citizen Exemption: Provides a reduction in assessed value for eligible senior citizens, typically based on age and income criteria.
- Veteran's Exemption: Offers a tax reduction for eligible veterans or their surviving spouses, honoring their service to the country.
- Disabled Persons Exemption: Provides a tax break for individuals with disabilities, helping them afford homeownership.
- Farmland Assessment: Offers a lower assessment rate for agricultural properties, encouraging farmland preservation.
- Historical Property Tax Relief: Provides tax relief for properties of historical significance, promoting their preservation.
These exemptions and reductions demonstrate Illinois' commitment to making real estate ownership more accessible and affordable for various segments of its population.
Impact of Real Estate Taxes on Homeownership and Investment
Real estate taxes in Illinois have a significant impact on both homeowners and investors. For homeowners, these taxes are a recurring expense that must be factored into the overall cost of owning a home. While exemptions and reductions can provide some relief, the tax burden can still be substantial, especially in areas with high property values and tax rates.
Investors, on the other hand, must consider real estate taxes as a part of their investment strategy. The tax burden can influence investment decisions, particularly when comparing investment properties in different locations or when evaluating the financial feasibility of a potential investment.
Strategies for Managing Real Estate Taxes
To effectively manage real estate taxes in Illinois, both homeowners and investors can employ various strategies. These include:
- Understanding Local Tax Rates: Staying informed about local tax rates and their potential fluctuations is crucial for budgeting and financial planning.
- Exploring Exemptions: Researching and applying for applicable exemptions can provide significant tax savings, especially for eligible homeowners.
- Appealing Assessments: If an assessment is believed to be inaccurate, property owners can appeal to ensure a fair and accurate valuation, potentially reducing the tax burden.
- Tax Planning: Working with financial advisors or tax professionals can help in developing strategies to minimize the tax impact, especially for investors with multiple properties.
- Long-Term Considerations: When purchasing a property, considering the long-term tax implications, including potential increases in tax rates or assessments, is essential for financial planning.
Conclusion
Illinois real estate taxes are a complex but essential aspect of property ownership and investment in the state. Understanding the tax rates, assessments, and exemptions is crucial for both homeowners and investors. By staying informed, exploring available tax relief programs, and employing effective tax management strategies, property owners can navigate the real estate tax landscape successfully.
As Illinois continues to evolve, with its vibrant cities and diverse communities, real estate taxes will remain a key consideration for those looking to invest in the state's property market. By providing a comprehensive understanding of the tax system, this guide aims to empower property owners and investors with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions and navigate the financial aspects of real estate ownership in Illinois.
How often are property taxes paid in Illinois?
+In Illinois, property taxes are typically paid twice a year, with the due dates varying by county. It’s important to check with the local county treasurer’s office for the specific payment schedule.
Can I deduct my Illinois real estate taxes on my federal tax return?
+Yes, Illinois real estate taxes are generally deductible on federal tax returns. However, there are limits and restrictions, especially with the recent changes in tax laws. It’s recommended to consult with a tax professional for specific guidance.
How can I estimate my real estate taxes before buying a property in Illinois?
+You can estimate your real estate taxes by multiplying the assessed value of the property by the tax rate. However, this is a rough estimate, and it’s advisable to consult with a real estate professional or the county assessor’s office for a more accurate calculation.
Are there any online tools to help me calculate my real estate taxes in Illinois?
+Yes, many counties in Illinois provide online tax estimators or calculators on their websites. These tools can help you estimate your real estate taxes based on the property’s assessed value and the applicable tax rate.
What happens if I don’t pay my real estate taxes in Illinois?
+Unpaid real estate taxes can lead to penalties, interest, and, in extreme cases, the loss of the property through a tax sale. It’s crucial to stay current with your tax payments to avoid these consequences.