How To Add Sales Tax

Implementing sales tax accurately is crucial for businesses, especially when operating in multiple jurisdictions with varying tax rates and regulations. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps and considerations for adding sales tax to your business operations, ensuring compliance and accurate tax collection.
Understanding Sales Tax Basics

Sales tax is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services. It is a vital revenue source for governments, funding public services and infrastructure. Businesses act as tax collectors, remitting the collected tax to the appropriate tax authorities. Understanding sales tax involves grasping its fundamental concepts, such as tax rates, taxability rules, and exemptions.
Tax Rates and Jurisdictions
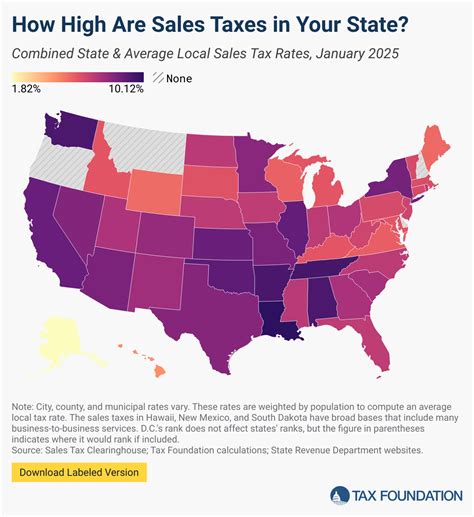
Sales tax rates vary across different jurisdictions, including countries, states, provinces, or even cities. These rates can be flat or tiered, depending on the jurisdiction’s tax laws. For instance, in the United States, sales tax rates can range from 0% to over 10%, with variations at the state, county, and city levels. Businesses must be aware of these rates and ensure they apply the correct tax rate based on the customer’s location.
| Jurisdiction | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| California | 7.25% |
| New York City | 8.875% |
| Texas | 6.25% |
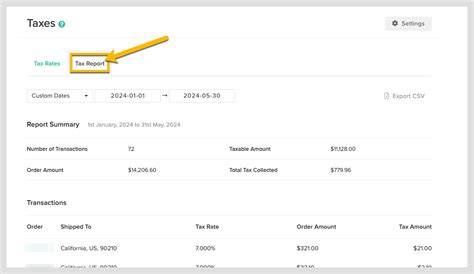
It's important to note that sales tax rates can change periodically, so businesses should stay updated with the latest tax laws and regulations to avoid compliance issues.
Taxability Rules and Exemptions
Not all goods and services are subject to sales tax. Taxability rules define which items are taxable and which are exempt. These rules can vary widely, depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the product or service. For example, certain food items, prescription drugs, and educational materials may be exempt from sales tax in some regions.
Businesses must be well-versed in the taxability rules applicable to their industry and products to avoid overcharging or undercharging sales tax. Misapplication of tax rates or exempt status can lead to legal and financial repercussions.
Assessing Your Business’s Tax Obligations
Before adding sales tax to your business operations, it’s essential to evaluate your tax obligations. This involves understanding your business’s tax registration requirements, sales tax collection responsibilities, and the tax authorities you need to interact with.
Tax Registration and Permits
To collect and remit sales tax, businesses typically need to obtain tax registration permits from the relevant tax authorities. These permits authorize the business to operate within a specific jurisdiction and collect sales tax. The registration process varies by jurisdiction and may involve completing applications, providing business information, and paying registration fees.
Some jurisdictions may have specific requirements for certain industries or business types. For instance, online businesses may need to register for sales tax permits in multiple states if they have a significant customer base across different regions.
Sales Tax Collection Responsibilities
Businesses are responsible for collecting sales tax from customers at the point of sale. This involves calculating the applicable tax rate, adding it to the sale price, and ensuring accurate tax calculation. The collected sales tax must be remitted to the appropriate tax authority at regular intervals, such as monthly or quarterly.
To ensure accurate tax collection, businesses should consider using tax calculation tools or software that can automatically apply the correct tax rates based on the customer's location. This reduces the risk of errors and ensures compliance with tax laws.
Implementing Sales Tax Collection
Adding sales tax to your business operations requires careful planning and the implementation of robust systems and processes. This section provides a step-by-step guide to help you set up sales tax collection efficiently.
Step 1: Determine Taxable Sales
The first step is to identify which sales are subject to sales tax. This involves reviewing your product catalog and understanding which items are taxable and which are exempt. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of the taxability rules specific to your industry and jurisdiction.
Create a comprehensive list of taxable and exempt items, and assign the correct tax rates to each. This list will serve as a reference for your sales tax calculation process.
Step 2: Integrate Sales Tax Calculation
Integrating sales tax calculation into your sales process is crucial for accuracy and efficiency. You can choose from various sales tax calculation tools and software solutions available in the market.
These tools can automatically calculate the applicable tax rate based on the customer's shipping address or billing location. They consider factors such as tax jurisdictions, tax rates, and taxability rules to provide accurate tax calculations. By integrating these tools into your sales platform, you can streamline the tax calculation process and reduce the risk of errors.
Step 3: Display Tax Information Clearly
Transparency is essential when it comes to sales tax. Ensure that your customers are aware of the sales tax they will be charged before completing a purchase. Display the tax information clearly on your website or point-of-sale systems, including the tax rate and the total tax amount.
Providing tax information upfront helps build trust with your customers and ensures they understand the final cost of their purchase. It also minimizes the chances of disputes or surprises at the checkout stage.
Step 4: Collect and Store Sales Tax Data
As you collect sales tax from customers, it’s crucial to maintain accurate records of the collected amounts. Develop a robust system for tracking and storing sales tax data. This includes capturing customer information, such as shipping addresses and billing details, to determine the applicable tax jurisdiction.
Store the collected sales tax data securely and ensure it is easily accessible for tax reporting purposes. Regularly reconcile your sales tax records with your accounting system to ensure accuracy and detect any discrepancies early on.
Compliance and Reporting
Compliance with sales tax regulations is non-negotiable for businesses. This section outlines the key aspects of sales tax compliance and reporting, including tax remittance, record-keeping, and audits.
Tax Remittance
Tax remittance is the process of sending the collected sales tax to the appropriate tax authority. Businesses are typically required to remit sales tax on a regular basis, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the jurisdiction’s requirements.
Ensure that you understand the remittance schedule and deadlines for your business. Late or incorrect remittance can result in penalties and interest charges. Use reliable accounting software or systems to track and manage your sales tax remittances, ensuring timely and accurate payments.
Record-Keeping and Documentation
Maintaining accurate records is vital for sales tax compliance. Keep detailed records of all sales transactions, including the date, amount, tax rate applied, and customer information. These records should be easily accessible and organized for audit purposes.
Consider implementing a robust sales tax record-keeping system that integrates with your accounting software. This will streamline the process of retrieving sales tax data and generating tax reports when needed.
Audits and Tax Examinations
Tax authorities may conduct audits or examinations to ensure businesses are compliant with sales tax regulations. During an audit, tax officials will review your sales tax records, transactions, and tax remittances. It’s crucial to be prepared for such audits and have your sales tax processes and records in order.
Stay updated with the latest sales tax regulations and any changes that may impact your business. Regularly review your sales tax practices and seek professional advice if needed. By maintaining accurate records and adhering to tax laws, you can mitigate the risks associated with audits and ensure smooth compliance.
Future of Sales Tax

The landscape of sales tax is constantly evolving, with technological advancements and changing tax laws. Businesses need to stay informed about the latest trends and developments to adapt their sales tax strategies accordingly.
Technology and Automation
The use of technology and automation in sales tax management is on the rise. Advanced tax calculation software and platforms can automate tax calculations, ensuring accuracy and efficiency. These tools can integrate with e-commerce platforms, accounting software, and point-of-sale systems, providing a seamless tax management experience.
By leveraging technology, businesses can stay up-to-date with tax rate changes, taxability rules, and exemption updates. This minimizes the risk of errors and ensures compliance with the latest tax regulations.
Tax Reform and Regulatory Changes
Tax laws and regulations are subject to change, and businesses must be aware of any upcoming reforms or amendments. Stay informed about proposed changes in sales tax laws, such as new tax rates, expanded taxability rules, or revised exemption criteria.
Monitor industry publications, government websites, and tax authority communications for updates. Being proactive in understanding and adapting to these changes will help your business maintain compliance and avoid potential penalties.
Conclusion
Adding sales tax to your business operations is a complex but essential process. By understanding the basics of sales tax, assessing your tax obligations, implementing robust sales tax collection systems, and staying compliant with tax regulations, you can ensure accurate tax collection and reporting.
Stay informed, leverage technology, and seek professional guidance when needed. By adopting a proactive approach to sales tax management, your business can operate efficiently and maintain its reputation as a tax-compliant entity.
How often should I update my sales tax rates and rules?
+Sales tax rates and rules can change periodically, so it’s essential to stay updated. Set up notifications or alerts from tax authorities or subscribe to tax newsletters to receive updates on any changes. Additionally, regularly review your sales tax calculation processes to ensure they align with the latest regulations.
What happens if I overcharge or undercharge sales tax by mistake?
+Mistakes can happen, but it’s important to rectify them promptly. If you overcharge sales tax, issue a refund to the customer and adjust your records accordingly. If you undercharge, calculate the difference and add it to the next sales tax remittance. It’s crucial to keep accurate records and inform the tax authorities about any corrections made.
Are there any sales tax exemptions for specific industries or products?
+Yes, sales tax exemptions vary by jurisdiction and industry. Certain industries, such as healthcare or education, may have specific exemptions for certain products or services. It’s crucial to research and understand the taxability rules applicable to your industry to ensure you correctly apply exemptions and avoid non-compliance.
How can I stay updated with the latest sales tax regulations and changes?
+Staying informed about sales tax regulations is crucial. Subscribe to tax newsletters, follow tax authority websites and social media accounts, and join industry associations or forums where tax-related discussions take place. Regularly review tax publications and attend webinars or workshops to stay updated with the latest developments.
What should I do if I receive a sales tax audit notice?
+If you receive a sales tax audit notice, it’s important to respond promptly and cooperate with the tax authorities. Gather all relevant sales tax records, including transaction details, tax calculations, and remittance reports. Engage a tax professional or legal advisor to guide you through the audit process and ensure compliance.