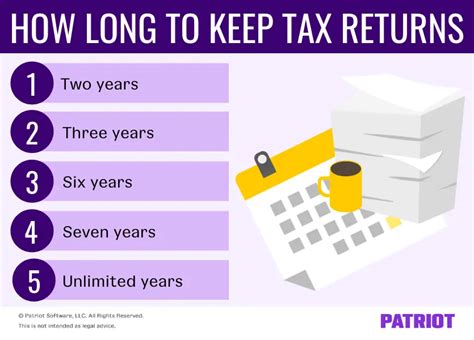
How Many Years To Keep Tax Returns
When it comes to tax returns, determining how long to retain them is a crucial aspect of financial record-keeping. Tax returns contain sensitive information and serve as vital documents for various purposes, including tax audits, financial planning, and historical reference. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the recommended practices for retaining tax returns, exploring the optimal duration, the factors that influence this decision, and the best practices for tax return storage.
The Importance of Tax Return Retention

Tax returns are more than just a record of your financial activities; they are a legal document that can impact your financial well-being for years to come. Here are some key reasons why retaining tax returns is essential:
- IRS Audits and Reviews: In the event of an IRS audit, your tax returns are the primary source of information for both you and the IRS. Audits can occur years after filing, so having accessible records is crucial.
- Amendments and Corrections: Mistakes happen, and sometimes tax returns need amendments. Retaining your records allows you to identify and correct errors promptly.
- Financial Planning and Historical Analysis: Tax returns provide a detailed financial snapshot of your life at a particular moment. They can be invaluable for long-term financial planning, retirement strategies, and understanding your financial history.
- Legal and Estate Matters: Tax returns are often required for legal proceedings, estate settlements, and insurance claims. They can also be essential for proving income, assets, and liabilities.
- Charitable Contributions and Deductions: If you make charitable contributions or claim tax deductions, having tax returns as proof can be beneficial for future planning and tax strategies.
Recommended Retention Periods

The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides guidelines on how long taxpayers should keep their tax returns and related documents. However, it’s important to note that these guidelines are not set in stone and may vary based on individual circumstances and the type of tax return.
Basic Rule: Three to Seven Years
The general recommendation is to retain tax returns and supporting documents for at least three to seven years after the tax filing deadline or the due date of the return, whichever is later. This period is based on the IRS’s statute of limitations for auditing tax returns.
During this time, the IRS can initiate an audit or review your tax returns for potential errors or discrepancies. By keeping your records for this duration, you ensure that you have the necessary documentation to address any inquiries or challenges from the IRS.
Extended Retention for Certain Scenarios
In some cases, it may be prudent to keep tax returns and related records for an extended period, especially if you anticipate the need for them in the future.
- Unreported Income: If you have unreported income, such as from a forgotten investment or a one-time windfall, consider keeping tax returns indefinitely. This can protect you in case the IRS discovers the income and requests additional information.
- Business Owners: Business owners, especially those with complex financial structures or multiple entities, may benefit from retaining tax returns and related documents indefinitely. This ensures access to historical financial data for strategic planning and tax optimization.
- Legal or Estate Matters: If you anticipate legal proceedings, estate planning, or complex financial transactions, it's advisable to keep tax returns for an extended period, potentially up to ten years or more. These records can be vital for verifying financial information.
Special Circumstances
Certain tax situations may require additional consideration when determining the retention period.
- Amended Returns: If you've filed an amended return, keep the original return and all supporting documents indefinitely. Amended returns can trigger additional IRS scrutiny, so having these records is essential.
- Foreign Income and Assets: If you have foreign income or assets, the IRS has a longer statute of limitations for auditing these returns. Consider retaining these tax returns and related documents for up to six years.
- Fraud or Substantial Errors: In cases of fraud or substantial errors, the IRS has an unlimited period to audit your tax returns. If you suspect or have knowledge of such issues, it's best to keep your records indefinitely.
Best Practices for Tax Return Storage
Once you’ve determined the appropriate retention period for your tax returns, the next step is to implement effective storage practices to ensure the safety and accessibility of your records.
Digital Storage
With the advent of digital technology, many taxpayers opt for digital storage solutions for their tax returns. Here are some tips for secure digital storage:
- Use Cloud Storage: Cloud-based storage platforms offer a secure and accessible way to store tax returns. Ensure you choose a reputable provider and implement strong passwords and two-factor authentication for added security.
- Backup Your Data: Always maintain multiple backups of your digital tax records. Consider using external hard drives, USB drives, or even physical copies (printed or scanned) for added protection against data loss.
- Encrypt Sensitive Information: If you're storing tax returns on your personal devices, consider using encryption software to protect sensitive financial data.
- Organize Your Files: Create a well-organized digital filing system with clear folder structures and naming conventions. This makes it easier to locate specific tax returns when needed.
Physical Storage
For those who prefer physical copies of their tax returns, here are some best practices:
- Secure Storage Location: Store your tax returns in a secure location, such as a fireproof safe or a locked cabinet. Avoid leaving them in easily accessible places like drawers or desks.
- Use Acid-Free Paper: If you're printing tax returns, use acid-free paper to prevent yellowing and deterioration over time.
- Consider Scanning: Scanning your physical tax returns and supporting documents allows you to create digital backups. This provides an additional layer of protection against loss or damage.
- Label and Organize: Create a clear labeling system for your tax returns, including the tax year and any relevant details. This simplifies the process of retrieving specific records when needed.
The Benefits of Proactive Record-Keeping
Proactively managing your tax return retention and storage can offer several advantages:
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that you have well-organized and accessible tax records provides peace of mind, especially in the event of an audit or financial inquiry.
- Efficient Tax Preparation: Having your past tax returns readily available can streamline the tax preparation process, making it easier to identify deductions, credits, and potential errors.
- Historical Perspective: Tax returns serve as a financial timeline, allowing you to track your financial progress and make informed decisions for the future.
- Legal and Estate Planning: Proper tax return retention can simplify legal proceedings, estate settlements, and the transfer of assets.
Conclusion: A Customized Approach

The optimal duration for keeping tax returns depends on individual circumstances and the complexity of your financial situation. While the IRS provides general guidelines, it’s essential to tailor your retention practices to your specific needs.
By understanding the factors that influence tax return retention and implementing effective storage strategies, you can ensure that your financial records are secure, accessible, and ready to serve you when needed. Whether you opt for digital or physical storage, a well-organized system is the key to peace of mind and efficient financial management.
How often should I review my tax returns?
+It’s a good practice to review your tax returns annually to ensure accuracy and identify any potential issues. This review can help you catch errors, adjust your financial strategies, and stay prepared for future tax obligations.
Can I shred my tax returns after the retention period?
+Yes, once you’ve determined that the tax return and related documents are no longer needed, you can shred them to ensure the privacy and security of your financial information. However, it’s essential to verify that you have digital backups or physical copies in a secure location before discarding original documents.
What happens if I don’t keep my tax returns for the recommended period?
+Failing to retain tax returns for the recommended period can lead to complications if the IRS requests documentation for an audit or if you need to prove income or deductions for legal or financial purposes. It’s always advisable to follow the recommended retention guidelines to avoid potential issues.