How Is Severance Taxed

Severance tax is a crucial aspect of taxation that pertains to the extraction of natural resources. It is an essential revenue stream for governments, particularly in regions rich in natural resources such as oil, gas, coal, minerals, and timber. This tax is levied on the value of the resources extracted, often by companies engaged in the extraction process. Understanding how severance tax is imposed and the implications it carries is vital for businesses and individuals alike.
Understanding Severance Tax
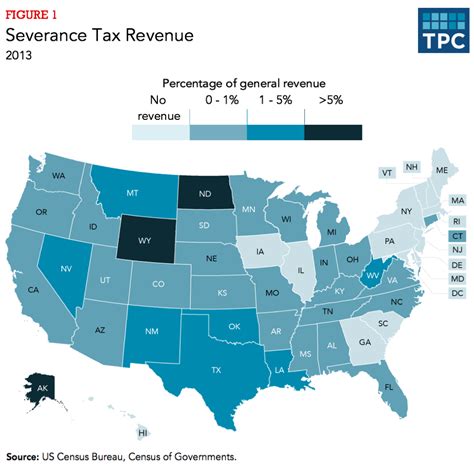
Severance tax, in its essence, is a form of excise tax. It is distinct from income tax as it is not calculated based on the profits or earnings of the extraction companies. Instead, it is a direct tax on the value of the resources extracted from the earth. This tax is typically imposed on a per-unit basis, such as per barrel of oil, per cubic foot of gas, or per ton of coal.
The purpose of severance tax is twofold. Firstly, it serves as a means for governments to capture some of the value created by the extraction of natural resources, which are often considered common property. Secondly, it acts as a regulatory tool, encouraging sustainable extraction practices and discouraging over-exploitation.
The tax rate for severance tax can vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction and the specific resource being extracted. For instance, in the United States, the severance tax rate for oil and gas can range from 0% to over 12%, with states like Alaska and North Dakota imposing higher rates.
Calculation and Assessment

The calculation of severance tax involves several steps. Firstly, the value of the extracted resources needs to be determined. This valuation can be based on market prices, wellhead or mine-mouth prices, or even a percentage of the downstream sales price.
Once the value is established, the applicable tax rate is applied. The tax rate can be a flat rate, a progressive rate (where the rate increases as the value of the resource increases), or a sliding scale based on various factors such as the depth of the well, the age of the field, or the level of production.
In some cases, there may be exemptions or deductions available to reduce the tax liability. For instance, some jurisdictions offer deductions for transportation costs, processing costs, or even a percentage of the total investment in the extraction project. These deductions can significantly impact the final tax bill.
Payment and Compliance
Severance tax is typically payable to the relevant government authority, often at regular intervals such as monthly or quarterly. The tax payment process usually involves filing a tax return or report detailing the volume and value of the extracted resources. The return may also require additional information such as the method of valuation, production costs, and any deductions claimed.
Compliance with severance tax regulations is critical. Failure to pay or underpayment of severance tax can result in penalties, interest charges, and even legal action. Therefore, it is essential for extraction companies to maintain accurate records, ensure timely payments, and stay updated with any changes in the tax laws and regulations.
To assist with compliance, many governments provide guidance and resources. This may include publication of tax rates, valuation methods, and deduction rules. Some jurisdictions even offer online tools and calculators to help taxpayers estimate their severance tax liability.
Impact on Businesses and the Economy
Severance tax has a significant impact on the businesses involved in resource extraction. It can influence the profitability of extraction projects, particularly those with lower margins. Higher severance tax rates can make certain projects economically unviable, leading to potential job losses and reduced investment in the industry.
However, from a broader economic perspective, severance tax can bring numerous benefits. The revenue generated from this tax can be used to fund essential public services, infrastructure development, and environmental protection measures. It can also contribute to the diversification of the economy, reducing reliance on a single industry.
Furthermore, severance tax can promote responsible resource management. By discouraging over-extraction and encouraging sustainable practices, it can help preserve natural resources for future generations.
Future Trends and Considerations
The future of severance tax is likely to be influenced by several factors. As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, the demand for traditional fossil fuels may decrease, potentially impacting the revenue generated from severance tax.
However, with the increasing focus on sustainability and environmental concerns, there may be a shift towards taxing resources based on their environmental impact. For instance, carbon taxes or emission-based severance taxes could become more prevalent. These taxes would aim to discourage the extraction and use of high-emission resources, encouraging a transition to cleaner alternatives.
Additionally, the rise of data-driven technologies and blockchain could revolutionize the severance tax landscape. These technologies can enhance transparency, streamline the tax payment process, and reduce the potential for tax evasion. They can also provide governments with more accurate and real-time data on resource extraction, aiding in better tax policy formulation and enforcement.
Key Takeaways
In summary, severance tax is a critical component of the taxation system for governments with abundant natural resources. It is a direct tax on the value of extracted resources, serving both revenue-generating and regulatory purposes. The calculation and assessment of severance tax involve determining the value of the resources and applying the appropriate tax rate, with potential deductions and exemptions.
Compliance with severance tax regulations is essential for businesses involved in resource extraction. The impact of severance tax extends beyond the extraction industry, influencing the economy, public services, and environmental sustainability. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the role and nature of severance tax are likely to evolve, potentially incorporating environmental considerations and benefiting from technological advancements.
How is the value of extracted resources determined for severance tax calculation?
+
The value of extracted resources is typically determined based on market prices, wellhead or mine-mouth prices, or a percentage of the downstream sales price. This valuation method can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific resource being extracted.
Are there any deductions or exemptions available for severance tax?
+
Yes, some jurisdictions offer deductions or exemptions for severance tax. These may include deductions for transportation costs, processing costs, or a percentage of the total investment in the extraction project. However, the availability and specifics of these deductions can vary widely.
What happens if a business fails to pay or underpays severance tax?
+
Failure to pay or underpayment of severance tax can result in severe consequences. Businesses may face penalties, interest charges, and even legal action. It is crucial for extraction companies to maintain accurate records, ensure timely payments, and stay updated with tax regulations to avoid such issues.
How does severance tax impact the economy and public services?
+
Severance tax generates significant revenue for governments, which can be used to fund public services, infrastructure development, and environmental protection measures. It can also contribute to economic diversification, reducing reliance on a single industry. However, high severance tax rates can impact the profitability of extraction projects and potential job losses.
What are some future trends in severance tax?
+
The future of severance tax is likely to be influenced by the transition to cleaner energy sources and increasing environmental concerns. This may lead to the implementation of carbon taxes or emission-based severance taxes. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as blockchain, can enhance transparency and streamline the tax payment process.



