Hawaii Real Estate Tax
Hawaii, with its stunning natural beauty and vibrant culture, is a desirable location for many individuals seeking a unique lifestyle or investment opportunities. The real estate market in Hawaii is known for its diversity, ranging from luxurious beachfront properties to picturesque mountain retreats. However, when considering a real estate purchase or investment in Hawaii, it is crucial to understand the intricacies of the state's tax system, which can significantly impact the overall cost and financial planning.
Understanding Hawaii's Real Estate Tax Landscape

The real estate tax system in Hawaii operates under a unique set of regulations and guidelines, distinct from many other states in the US. Hawaii imposes a Real Property Tax on both residential and commercial properties, which serves as a significant source of revenue for the state and local governments. This tax is levied on the assessed value of the property, taking into account various factors such as location, improvements, and market trends.
The assessment process in Hawaii is carried out by the County Assessors' offices, with each of the four counties (Hawaii, Honolulu, Kauai, and Maui) responsible for evaluating properties within their respective jurisdictions. The assessed value is then used to calculate the annual real estate tax liability for property owners. It is important to note that Hawaii's real estate tax system operates on a fiscal year basis, which runs from July 1st to June 30th, with taxes typically due in two installments.
Real Property Tax Rates in Hawaii
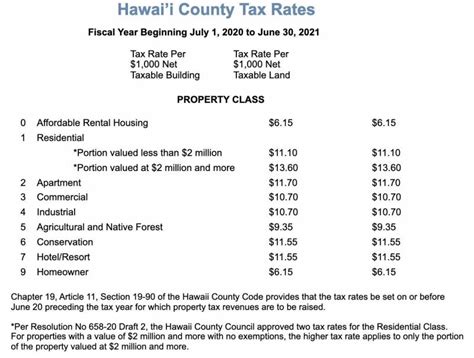
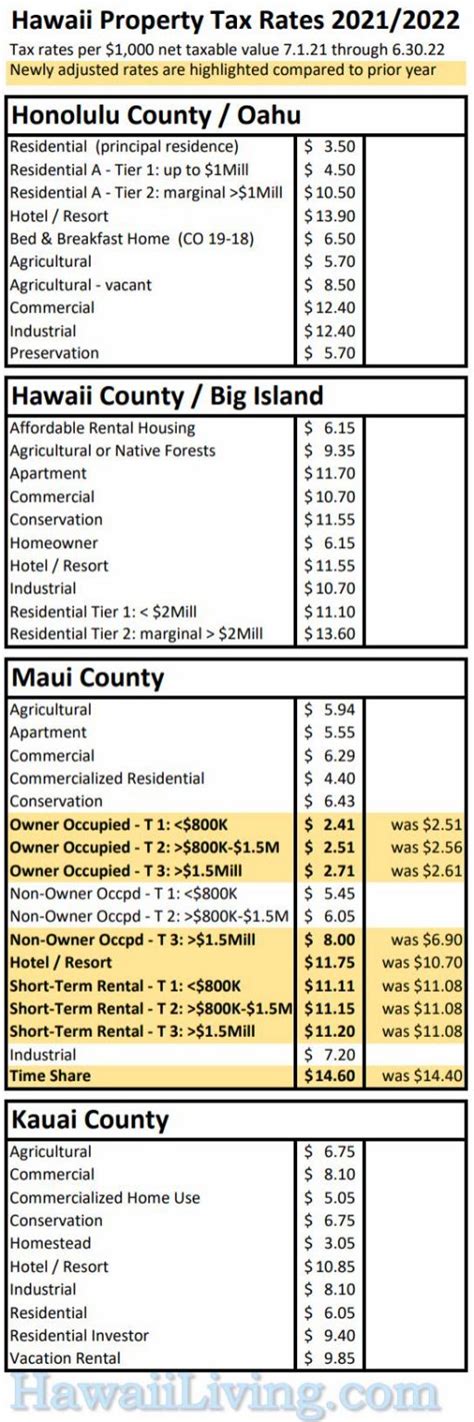
The real property tax rates in Hawaii can vary depending on the specific location and type of property. Generally, Hawaii's tax rates are competitive when compared to other high-cost-of-living states. The tax rates are established by each county and can change annually based on the county's budgetary requirements and property value trends.
As of the most recent data, here is a breakdown of the real property tax rates for the four counties in Hawaii:
| County | Residential Tax Rate | Commercial Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Hawaii County | 0.25% | 0.35% |
| Honolulu County | 0.25% | 0.4% |
| Kauai County | 0.25% | 0.4% |
| Maui County | 0.25% | 0.35% |

It's important to note that these rates are subject to change and are effective for the current fiscal year. Property owners should refer to their county's official website for the most up-to-date tax rate information.
Assessed Value and Tax Calculation
The assessed value of a property in Hawaii is determined through a comprehensive assessment process conducted by the county assessors. This value is typically based on the property's fair market value and may consider factors such as recent sales data, construction costs, and income potential for commercial properties. Once the assessed value is established, it is used to calculate the real estate tax liability.
The tax calculation in Hawaii involves multiplying the assessed value by the applicable tax rate for the property's classification (residential or commercial) and the tax rate set by the county. For example, if a residential property in Honolulu County has an assessed value of $500,000, the tax calculation would be as follows:
$500,000 (assessed value) x 0.25% (residential tax rate) = $1,250 annual real estate tax
It's worth noting that Hawaii also offers certain tax exemptions and credits to eligible property owners, which can further reduce their tax liability. These exemptions include homestead exemptions, military exemptions, and elderly or disabled exemptions. Property owners should consult with their county's tax assessor's office or a tax professional to understand their eligibility for these exemptions.
Real Estate Tax Implications for Buyers and Investors
Understanding the real estate tax implications is crucial for anyone considering a property purchase or investment in Hawaii. Here are some key considerations:
Impact on Property Purchase Costs
The real estate tax in Hawaii directly affects the overall cost of purchasing a property. Prospective buyers should factor in the annual tax liability when calculating their budget for a property purchase. While the tax rates in Hawaii are relatively competitive, the assessed value of properties, especially in desirable locations, can be high, leading to substantial tax obligations.
Long-Term Financial Planning
Real estate investors in Hawaii must consider the ongoing tax obligations associated with their properties. The annual real estate taxes, coupled with other potential tax liabilities such as capital gains tax, can significantly impact the overall return on investment. Investors should carefully evaluate the tax implications and consider strategies to mitigate their tax burden, such as utilizing tax-advantaged investment structures or taking advantage of available tax incentives.
Property Ownership and Transfer
When transferring ownership of a property in Hawaii, whether through a sale or inheritance, the new owner becomes responsible for the real estate taxes. It is important for both buyers and sellers to be aware of the tax implications during the transaction process. Sellers should ensure that any outstanding taxes are settled before the transfer, while buyers should factor in the potential tax liability as part of their due diligence.
Strategies for Managing Real Estate Taxes in Hawaii
Navigating the real estate tax landscape in Hawaii requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some strategies to help manage and optimize your tax obligations:
Utilize Tax Exemptions and Credits
Hawaii offers various tax exemptions and credits that can significantly reduce your tax liability. Property owners should explore their eligibility for these incentives, such as the homestead exemption, which provides a reduction in the assessed value of the property for homeowners who reside in the property as their primary residence. Other exemptions, such as those for veterans or elderly homeowners, can also provide substantial tax savings.
Consider Tax-Efficient Property Types
The tax implications can vary depending on the type of property you own. For example, residential properties in Hawaii may have lower tax rates compared to commercial properties. Additionally, certain types of properties, such as vacation rentals or agricultural lands, may have specific tax considerations or incentives associated with them. Understanding these distinctions can help you make informed decisions when choosing a property type.
Explore Tax-Advantaged Investment Structures
For real estate investors, exploring tax-advantaged investment structures can be beneficial. Entities such as Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) or partnerships may offer certain tax advantages, including pass-through taxation and the ability to deduct business expenses. However, it is crucial to consult with a tax professional to ensure compliance with Hawaii's tax regulations and to determine the most suitable structure for your investment goals.
Stay Informed and Seek Professional Advice
The real estate tax landscape in Hawaii can be complex, and staying informed about changes in tax rates, exemptions, and regulations is essential. Regularly review the tax information provided by your county's assessor's office and keep abreast of any legislative updates that may impact your tax obligations. Additionally, consider seeking guidance from a qualified tax professional who specializes in real estate taxation to ensure you are optimizing your tax strategies and complying with all relevant laws.
Future Implications and Trends in Hawaii's Real Estate Tax
As Hawaii continues to be a desirable destination for residents and investors, the state's real estate market and tax landscape are likely to evolve. Here are some potential future implications and trends to consider:
Increasing Property Values and Tax Revenue
Hawaii's real estate market has experienced significant growth in recent years, with increasing demand and limited supply driving up property values. As property values rise, so does the potential for increased tax revenue for the state and local governments. This trend may lead to more stable funding for public services and infrastructure development, benefiting the community as a whole.
Potential Changes in Tax Rates and Exemptions
The tax rates and exemptions in Hawaii are subject to change based on legislative decisions and budgetary needs. While the current tax rates are relatively stable, future economic conditions, changes in government administration, or shifts in public policy could lead to adjustments in the tax landscape. Prospective buyers and investors should stay informed about any proposed changes and their potential impact on their financial plans.
Technological Advancements in Property Assessment
Advancements in technology and data analytics may play a significant role in the future of property assessment in Hawaii. The use of advanced valuation models, geographic information systems (GIS), and remote sensing technologies could enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the assessment process. These advancements may lead to more equitable assessments and a fairer distribution of the tax burden among property owners.
Community Engagement and Tax Transparency
As Hawaii's communities continue to grow and diversify, there may be increased emphasis on community engagement and tax transparency. County governments may explore initiatives to involve residents in the tax decision-making process, ensuring that tax policies align with the needs and priorities of the community. This could lead to more collaborative approaches to tax planning and a better understanding of the role of real estate taxes in supporting local services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the key factors that determine the assessed value of a property in Hawaii?
+The assessed value of a property in Hawaii is influenced by several factors, including its location, market trends, recent sales data, and improvements made to the property. County assessors consider these factors to determine the fair market value, which forms the basis for the property's assessed value.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any tax incentives or credits available for homeowners in Hawaii?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, Hawaii offers various tax incentives and credits to homeowners. These include the homestead exemption, which provides a reduction in the assessed value of the property for homeowners who reside in it as their primary residence. Additionally, there are exemptions for veterans, elderly homeowners, and disabled individuals, which can further reduce tax liability.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How often are property tax rates reviewed and adjusted in Hawaii?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Property tax rates in Hawaii are typically reviewed annually by each county's Board of Finance or similar governing body. The rates can be adjusted based on the county's budgetary needs and property value trends. It is important for property owners to stay informed about any changes to the tax rates in their respective counties.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What happens if a property owner fails to pay their real estate taxes in Hawaii?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Failure to pay real estate taxes in Hawaii can have serious consequences. The county may place a tax lien on the property, which could lead to penalties, interest charges, and, in some cases, the forced sale of the property to satisfy the outstanding tax debt. It is crucial for property owners to stay current with their tax payments to avoid these potential issues.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can real estate taxes in Hawaii be paid online or through other convenient methods?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, Hawaii counties offer various convenient payment methods for real estate taxes. Many counties provide online payment portals where property owners can pay their taxes securely. Additionally, options such as mail-in payments, in-person payments at county offices, and automatic bank withdrawals are available. It is advisable to check with your county's tax assessor's office for the specific payment methods offered.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>