Harvard Tax Exempt Status

The topic of Harvard's tax-exempt status is a fascinating one, delving into the intricate relationship between one of the world's most prestigious educational institutions and its unique tax position. Harvard University, with its rich history spanning over three centuries, has navigated a complex legal and financial landscape to maintain its status as a tax-exempt entity. This article will explore the origins of Harvard's tax exemption, the legal and financial implications, and the ongoing debates and controversies surrounding this topic.
The Historical Perspective: Origins of Harvard’s Tax-Exempt Status

Harvard University, founded in 1636, has been a cornerstone of higher education in the United States and a leader in academic research. Its tax-exempt status, which dates back to the 19th century, is a testament to the institution’s historical significance and its role in promoting education and knowledge. The origins of this status can be traced back to the early days of the United States, when the concept of tax exemption for educational institutions was first introduced.
In the 1800s, the United States was undergoing significant social and economic changes, and the role of education was being re-evaluated. During this period, the federal government began recognizing the importance of educational institutions in fostering societal progress and development. As a result, a series of legal provisions were enacted to grant tax exemptions to certain entities, including educational institutions like Harvard.
The specific legal basis for Harvard's tax-exempt status lies in the Internal Revenue Code (IRC), which defines the criteria for tax-exempt organizations. Under Section 501(c)(3) of the IRC, organizations that are organized and operated exclusively for educational purposes are eligible for tax exemption. This section also covers other charitable purposes, such as religious, scientific, and literary endeavors.
Harvard’s Compliance with 501©(3) Criteria
To maintain its tax-exempt status, Harvard must adhere to the requirements outlined in Section 501©(3). This entails operating exclusively for educational purposes, which encompasses a broad range of activities, including research, teaching, and the dissemination of knowledge. Additionally, Harvard must ensure that its activities are conducted in a manner that does not benefit any private individual or entity.
Harvard's compliance with these criteria is evident in its mission and operational structure. The university's stated mission is to "advance knowledge and educate students in an environment devoted to the highest standards of excellence and learning." This mission aligns closely with the educational purposes outlined in the IRC, ensuring that Harvard's activities are primarily focused on the advancement of education and knowledge.
| Section 501(c)(3) Criteria | Harvard's Compliance |
|---|---|
| Organized and operated exclusively for educational purposes | Harvard's mission and operational structure are focused on education and knowledge advancement. |
| No private benefit to individuals or entities | Harvard ensures that its activities do not benefit private interests, maintaining a public focus. |

Financial Implications: Harvard’s Tax-Exempt Status in Action
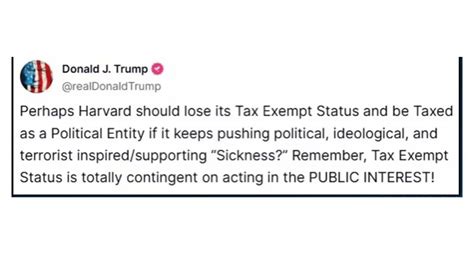
Harvard’s tax-exempt status has significant financial implications for the university and its stakeholders. By being exempt from federal income taxes, Harvard enjoys a competitive advantage over non-exempt institutions, allowing it to direct more resources towards its core mission and objectives.
Revenue Generation and Endowment Management
Harvard’s tax-exempt status enables the university to retain a larger portion of its revenue, which can be reinvested into its operations. This status also provides flexibility in endowment management, allowing Harvard to optimize its investment strategies and maximize returns. The university’s endowment, which is the largest of any academic institution in the world, is a testament to the advantages of tax-exempt status.
As of the 2022 fiscal year, Harvard's endowment stood at approximately $53.2 billion, a significant increase from the previous year. This growth can be attributed, in part, to the university's ability to invest and manage its resources without the burden of taxes. The endowment provides a stable financial foundation for Harvard, enabling it to fund research, support student financial aid, and invest in campus infrastructure.
| Harvard Endowment | Value |
|---|---|
| 2022 Fiscal Year | $53.2 billion |
| 2021 Fiscal Year | $51.3 billion |
Impact on Student Financial Aid and Scholarships
Harvard’s tax-exempt status also benefits students, particularly those who rely on financial aid and scholarships. The university can allocate a larger portion of its resources towards student support, ensuring that financial constraints do not hinder access to education. This is especially crucial given Harvard’s reputation as an elite institution, where the cost of attendance can be a significant barrier for many prospective students.
Harvard's financial aid policies are designed to meet 100% of demonstrated financial need for all admitted students. The university's commitment to need-blind admissions and robust financial aid programs is a direct result of its tax-exempt status, which provides the necessary financial flexibility to support students from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds.
Debates and Controversies: Harvard’s Tax-Exempt Status Under Scrutiny
While Harvard’s tax-exempt status has undeniable benefits, it has also sparked debates and controversies, particularly in the context of growing concerns about income inequality and the role of higher education in society.
Criticisms and Calls for Reform
Critics argue that Harvard’s tax-exempt status, and that of other elite universities, perpetuates a system of privilege and contributes to the widening wealth gap. They question whether institutions like Harvard, with their immense resources and endowments, should continue to benefit from tax exemptions, especially when many Americans struggle to afford higher education.
Calls for reform have gained traction in recent years, with proposals to limit or eliminate tax exemptions for elite universities. These proposals often suggest redirecting the tax revenue generated by these institutions towards more accessible and affordable educational options, such as community colleges or public universities.
Harvard’s Response and Community Engagement
Harvard has actively engaged in these debates, acknowledging the importance of its role in society and the need for a broader discussion on higher education and tax policy. The university has emphasized its commitment to accessibility and has taken steps to address concerns about its tax status.
One notable initiative is Harvard's Financial Aid Initiative, launched in 2004, which significantly expanded the university's financial aid program. This initiative eliminated parental loans for families earning less than $65,000 annually and reduced the expected family contribution for middle-income families. Additionally, Harvard has implemented a number of community-focused programs, such as the Harvard Community Partnership Fund, which supports local non-profit organizations and community development projects.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Harvard’s Tax-Exempt Status
The future of Harvard’s tax-exempt status remains uncertain, as the ongoing debates and changing political landscape shape the higher education sector. While the university has a strong legal basis for its tax exemption, the evolving societal expectations and concerns about income inequality may lead to potential reforms.
Potential Reforms and Policy Changes
Policy makers and legislators are increasingly considering reforms to the tax exemption system for educational institutions. These reforms may include changes to the criteria for tax exemption, increased oversight and accountability measures, or the introduction of a graduated tax system for institutions with large endowments.
For example, some proposals suggest imposing a tax on investment income generated by large endowments, with the revenue directed towards supporting public education initiatives. Others advocate for a more nuanced approach, distinguishing between different types of educational institutions and their tax obligations based on factors such as accessibility, affordability, and community impact.
Harvard’s Adaptability and Long-Term Strategy
Harvard, being a leading institution in higher education, is well-positioned to navigate potential changes to its tax-exempt status. The university’s adaptability and forward-thinking approach are evident in its strategic planning and community engagement initiatives.
Harvard has a long-standing tradition of evolving with the times and adapting to changing societal needs. The university's focus on accessibility, financial aid, and community partnerships demonstrates its commitment to remaining a responsible and impactful institution, regardless of its tax status. By actively engaging in the debates and proactively addressing concerns, Harvard is shaping the future of higher education and ensuring its continued relevance and impact.
How does Harvard’s tax-exempt status benefit the university financially?
+Harvard’s tax-exempt status allows the university to retain a larger portion of its revenue, which can be reinvested into its operations. This status also provides flexibility in endowment management, enabling Harvard to optimize its investment strategies and maximize returns. The tax exemption enables the university to allocate more resources towards its core mission, including research, teaching, and student support.
What are the criticisms of Harvard’s tax-exempt status?
+Critics argue that Harvard’s tax-exempt status, and that of other elite universities, perpetuates a system of privilege and contributes to income inequality. They question whether institutions with large endowments should continue to benefit from tax exemptions when many Americans struggle to afford higher education. Some critics propose redirecting tax revenue from these institutions towards more accessible and affordable educational options.
How has Harvard responded to debates about its tax-exempt status?
+Harvard has actively engaged in these debates, acknowledging the importance of its role in society and the need for a broader discussion on higher education and tax policy. The university has taken steps to address concerns, such as expanding its financial aid program and implementing community-focused initiatives. Harvard emphasizes its commitment to accessibility and community impact.
What potential reforms could impact Harvard’s tax-exempt status in the future?
+Potential reforms include changes to the criteria for tax exemption, increased oversight, and the introduction of a graduated tax system for institutions with large endowments. Some proposals suggest taxing investment income from endowments to support public education initiatives. The future of Harvard’s tax-exempt status will depend on the evolving societal expectations and policy decisions.



