Georgia State Sales Tax

The Georgia State Sales Tax is an essential component of the state's revenue system, impacting both businesses and consumers alike. With a comprehensive understanding of this tax, individuals and companies can navigate their financial obligations and contribute to the economic growth of the state effectively. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the Georgia State Sales Tax, covering its structure, rates, exemptions, and implications for various sectors.
Understanding the Georgia State Sales Tax Structure
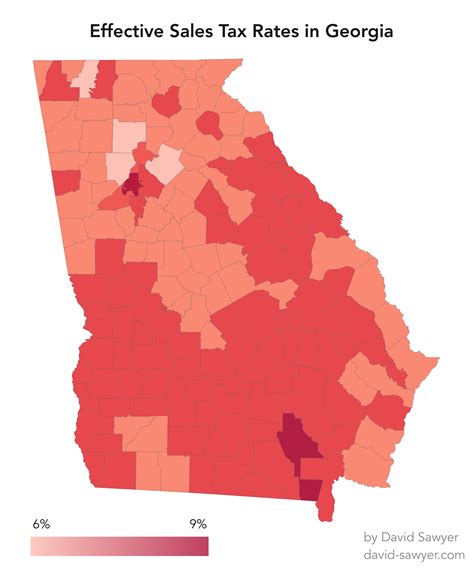
The sales tax system in Georgia is a crucial aspect of the state’s revenue generation, contributing significantly to its economic landscape. This section aims to delve into the intricacies of the Georgia State Sales Tax, offering a comprehensive understanding of its structure, rates, and the impact it has on various sectors within the state.
Statewide Sales Tax Rate
The statewide sales tax rate in Georgia is set at 4%, which serves as a baseline for all taxable goods and services within the state. This rate is applied uniformly across the state, ensuring a consistent approach to taxation. However, it is important to note that this is not the only tax levied on sales in Georgia.
Local Sales Tax Rates
In addition to the statewide sales tax, local governments in Georgia are authorized to impose their own local sales taxes. These local taxes can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another, creating a complex landscape of tax rates across the state. For instance, Atlanta, the state’s capital, has a local sales tax rate of 3.9%, while other cities like Savannah and Augusta have different rates.
This variability in local sales tax rates means that consumers and businesses may encounter different tax burdens depending on their location. For instance, a purchase made in Atlanta would be subject to a total sales tax rate of 7.9% (statewide rate + local rate), whereas the same purchase in Savannah might attract a total tax of 6.5%.
| City | Local Sales Tax Rate | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Atlanta | 3.9% | 7.9% |
| Savannah | 1.6% | 6.5% |
| Augusta | 3.0% | 7.0% |

Special Sales Tax Districts
Georgia also has special sales tax districts that are created to fund specific projects or initiatives. These districts can have additional sales tax rates on top of the statewide and local taxes. For example, a special district might be established to finance transportation infrastructure, with an added 1% sales tax for that specific purpose.
The Impact on Businesses
The complex sales tax structure in Georgia presents a unique challenge for businesses operating within the state. Companies must ensure they are compliant with the various tax rates and rules, which can be a significant administrative burden. Especially for businesses with multiple locations or those selling to customers in different jurisdictions, the task of calculating and remitting the correct sales tax becomes intricate.
Compliance and Software Solutions
To navigate this complex landscape, many businesses turn to sales tax compliance software. These tools help automate the process of calculating sales tax, ensuring accuracy and reducing the risk of errors. They also assist in filing and remitting taxes to the appropriate authorities, a crucial aspect of compliance.
Exemptions and Special Considerations
While the sales tax in Georgia applies to a wide range of goods and services, there are certain exemptions and special considerations that businesses and consumers should be aware of. These exceptions can significantly impact the total tax burden and should be understood to ensure compliance and avoid unnecessary payments.
Food and Groceries
One of the most notable exemptions in Georgia’s sales tax system is for prepared foods and groceries. This exemption extends to a wide range of items, including bread, milk, eggs, fruits, vegetables, meat, and other staples. However, it’s important to note that this exemption does not apply to hot and prepared foods, which are subject to the full sales tax rate.
Prescription Drugs
Another significant exemption is for prescription drugs. All prescription medications, whether purchased at a pharmacy or through a healthcare provider, are exempt from sales tax in Georgia. This exemption is designed to alleviate the financial burden on individuals requiring essential medical treatment.
Manufacturing and Resale
For manufacturers and businesses involved in the resale of goods, there is a special consideration in the sales tax system. These businesses are often eligible for a resale certificate, which allows them to purchase goods without paying sales tax. This exemption is crucial for businesses that will be selling the goods further down the supply chain, as it prevents double taxation.
Remote Sellers and Marketplace Facilitators
With the rise of e-commerce, Georgia has implemented rules for remote sellers and marketplace facilitators. Remote sellers, who do not have a physical presence in the state but sell to Georgia residents, are now required to collect and remit sales tax on their transactions. Similarly, marketplace facilitators, such as large online retailers, are responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax on behalf of the sellers using their platform.
Georgia’s Sales Tax Implications
The Georgia State Sales Tax has wide-ranging implications for various sectors and aspects of the state’s economy. Understanding these implications is crucial for businesses, consumers, and policymakers alike, as it can influence investment decisions, consumer behavior, and the state’s overall fiscal health.
Impact on Retail Sector
The retail sector is directly impacted by the sales tax, as it is responsible for collecting and remitting the tax on all taxable sales. For brick-and-mortar retailers, the sales tax can significantly affect their bottom line, especially in areas with higher tax rates. On the other hand, online retailers, especially those considered marketplace facilitators, now have a more significant role in tax collection, ensuring compliance for sellers on their platforms.
Effect on Consumer Behavior
The sales tax can also influence consumer behavior, particularly in border areas where tax rates differ significantly. Consumers may choose to shop in areas with lower tax rates, leading to a potential loss of revenue for businesses and the state. Conversely, in areas with tax-free shopping events or lower tax rates, retailers may experience increased foot traffic and sales.
Economic Development and Fiscal Health
From an economic development perspective, the sales tax plays a crucial role in funding essential services and infrastructure projects. The revenue generated from sales tax helps support schools, healthcare, public safety, and other critical areas. Additionally, the tax system’s complexity, with its varying rates and exemptions, can influence businesses’ decisions on where to locate and operate within the state.
Future Considerations
Looking ahead, there are several factors that could influence the future of the Georgia State Sales Tax. These include potential changes in consumer behavior, such as increased online shopping, and the continued evolution of e-commerce. Additionally, advancements in technology, particularly in the area of tax compliance software, could streamline the collection and remittance process, making it more efficient and less burdensome for businesses.
What is the current statewide sales tax rate in Georgia?
+
The current statewide sales tax rate in Georgia is 4%.
Are there any exemptions to the sales tax in Georgia?
+
Yes, there are several exemptions, including prepared foods, groceries, and prescription drugs.
How does Georgia handle sales tax for online retailers?
+
Georgia has rules for remote sellers and marketplace facilitators, requiring them to collect and remit sales tax on transactions.



