Georgia County Sales Tax
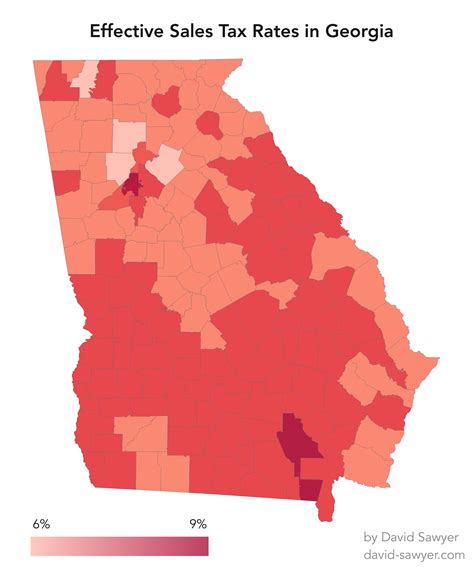
In the state of Georgia, the sales tax is a vital component of the state's revenue generation system, contributing significantly to its overall economic health and stability. The sales tax is a consumption tax that is imposed on the sale of goods and services within the state, with the revenue collected going towards funding essential public services and infrastructure projects. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of the sales tax system in Georgia, focusing on the county-level nuances and the impact it has on local economies.
Understanding Georgia’s Sales Tax Structure
Georgia’s sales tax is a combined state and local tax, which means that the tax rate varies across different counties and even within specific jurisdictions. The state of Georgia imposes a base sales tax rate, currently set at 4%, which is applicable statewide. However, counties and municipalities have the authority to levy additional local sales taxes, creating a unique and diverse tax landscape across the state.
The Georgia Department of Revenue (DOR) is responsible for administering and collecting sales taxes, ensuring compliance with state laws and regulations. The DOR provides comprehensive guidelines and resources to assist businesses and consumers in understanding their sales tax obligations and rights.
Statewide Sales Tax Distribution
The state of Georgia distributes the revenue generated from sales taxes to various funds and programs. A significant portion of the sales tax revenue is allocated to the state’s general fund, which supports a wide range of public services, including education, healthcare, transportation, and public safety. Additionally, specific tax allocations are directed towards targeted initiatives, such as the HOPE Scholarship Program, which provides financial aid to eligible students pursuing higher education.
County-Level Sales Tax Variations

Georgia’s county-level sales tax landscape is diverse and dynamic, with each county possessing the authority to establish its own local sales tax rate. This variability in tax rates can have a substantial impact on the purchasing power of consumers and the financial viability of businesses operating within these counties.
Exploring County-Specific Sales Tax Rates
Let’s delve into some real-world examples of county-level sales tax rates in Georgia:
| County | Local Sales Tax Rate | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Fulton County | 3% | 7% |
| Cobb County | 2.5% | 6.5% |
| Gwinnett County | 2% | 6% |
| Chatham County | 3.5% | 7.5% |
| DeKalb County | 3.5% | 7.5% |

As seen in the table above, the local sales tax rates vary significantly across these counties, resulting in a range of total sales tax rates. These variations can influence consumer behavior, as individuals may choose to shop in counties with lower tax rates, impacting local economies and revenue streams.
Impact on Local Economies
The county-level sales tax variations have a profound impact on the economic landscape of Georgia. Counties with higher sales tax rates may experience a shift in consumer spending patterns, as residents might opt to make larger purchases in neighboring counties with lower tax rates. This phenomenon, often referred to as tax leakage, can result in a loss of revenue for counties with higher tax rates, potentially affecting their ability to fund local services and infrastructure projects.
Conversely, counties with lower sales tax rates may attract more businesses and consumers, leading to increased economic activity and a boost in local tax revenue. This can create a competitive environment among counties, prompting them to strategically adjust their tax rates to attract investment and promote economic growth.
Compliance and Administration
Ensuring compliance with sales tax regulations is crucial for businesses operating in Georgia. The Georgia Department of Revenue provides comprehensive resources and guidance to assist businesses in understanding their sales tax obligations. This includes registering for a sales tax permit, filing regular sales tax returns, and accurately calculating and remitting the applicable sales tax rates.
Sales Tax Registration and Filing
Businesses engaged in taxable sales or services in Georgia are required to register with the DOR and obtain a sales and use tax certificate. This certificate authorizes the business to collect and remit sales taxes on behalf of the state and local governments. The registration process involves completing the necessary forms and providing relevant business information.
Once registered, businesses are obligated to file regular sales tax returns, typically on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, depending on their revenue and sales volume. These returns must accurately report the taxable sales and the applicable tax rates, ensuring timely and accurate remittance of sales tax revenue to the appropriate authorities.
Future Implications and Considerations
The sales tax landscape in Georgia is subject to ongoing evaluation and potential reforms. As the state’s economy evolves and tax policies are reassessed, there may be changes to the sales tax rates, distribution mechanisms, or administrative processes.
Potential Reforms and Initiatives
One area of consideration is the potential for tax reform initiatives aimed at simplifying the sales tax system and reducing administrative burdens on businesses. This could involve streamlining the registration and filing processes, enhancing online resources and portals for tax compliance, and exploring options for uniform tax rates across counties.
Additionally, the state may explore alternative revenue generation methods, such as implementing a broader-based consumption tax or revisiting the allocation of sales tax revenue to ensure it aligns with the evolving needs of the state and its citizens.
The Role of Technology and Data Analytics
Advancements in technology and data analytics offer new opportunities for enhancing sales tax administration and compliance. The DOR can leverage these tools to improve tax collection efficiency, identify potential compliance issues, and provide businesses with real-time guidance and support. By embracing technology, Georgia can streamline its sales tax system, reduce costs, and improve overall tax compliance.
Conclusion

Georgia’s sales tax system, with its county-level variations, plays a pivotal role in the state’s economic landscape. The diverse tax rates across counties influence consumer behavior, business decision-making, and local economic development. Understanding and navigating this complex sales tax environment is crucial for both businesses and consumers alike.
As the state continues to evaluate and refine its sales tax policies, it is essential to strike a balance between revenue generation and the economic well-being of counties and local communities. By embracing technological advancements and exploring innovative tax reforms, Georgia can ensure a robust and sustainable sales tax system that supports its economic growth and prosperity.
How often do businesses need to file sales tax returns in Georgia?
+
The frequency of filing sales tax returns depends on the business’s sales volume and revenue. Generally, businesses with higher sales volumes are required to file monthly returns, while those with lower sales may file on a quarterly or annual basis. The Georgia Department of Revenue provides guidelines and resources to assist businesses in determining their filing frequency.
Are there any exemptions or special considerations for certain types of businesses or products under Georgia’s sales tax laws?
+
Yes, Georgia’s sales tax laws include various exemptions and special considerations. For example, certain agricultural products, prescription medications, and some manufacturing equipment may be exempt from sales tax. Additionally, there are specific rules for online sales and remote sellers, which businesses should be aware of to ensure compliance.
How does Georgia handle sales tax for online transactions?
+
Georgia has implemented a marketplace facilitator law, which requires online marketplaces and remote sellers to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state and local governments. This law ensures that online transactions are subject to the same sales tax obligations as traditional brick-and-mortar businesses.



