Does Wyoming Tax Capital Gains
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of Wyoming's tax landscape, specifically focusing on its treatment of capital gains. Wyoming, known for its vast open spaces, diverse industries, and dynamic economy, has a unique approach to taxation, which extends to capital gains.
Wyoming’s Tax Environment: An Overview
Wyoming boasts a tax system designed to foster economic growth and attract businesses. The state’s overall tax burden is among the lowest in the nation, and its tax structure is a key factor in its economic prosperity.
One of the most notable aspects of Wyoming's tax policy is its lack of a personal income tax. This means that residents do not pay state taxes on their wages, salaries, or other income sources. This absence of an income tax has made Wyoming an attractive destination for individuals and businesses seeking tax-friendly environments.
However, Wyoming's tax system is not solely focused on income. The state generates revenue through various other tax streams, including:
- Sales and Use Tax: Wyoming imposes a 4% state sales tax on most goods and services. Local jurisdictions can also add their own sales tax, resulting in a combined rate that varies across the state.
- Property Tax: Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for Wyoming. The state's property tax system is relatively straightforward, with a single assessment date and a fixed mill levy.
- Severance Tax: Wyoming levies a tax on the extraction of natural resources, such as minerals and fossil fuels. This tax is an important revenue stream for the state, particularly in counties with significant mineral production.
Capital Gains Taxation in Wyoming

Now, let’s delve into the heart of our topic: how Wyoming treats capital gains.
In a nutshell, Wyoming does not tax capital gains. This means that individuals and businesses who sell assets for a profit within the state do not owe state taxes on those gains.
The absence of a capital gains tax is a significant advantage for investors and entrepreneurs in Wyoming. It allows them to keep more of their profits, encouraging investment and business growth. This tax-free environment can be particularly beneficial for those involved in real estate, stock market investments, or other asset-based ventures.
However, it's important to note that while Wyoming does not tax capital gains at the state level, federal capital gains taxes still apply. This means that residents of Wyoming still need to comply with federal tax laws when it comes to reporting and paying taxes on their capital gains.
Understanding Capital Gains
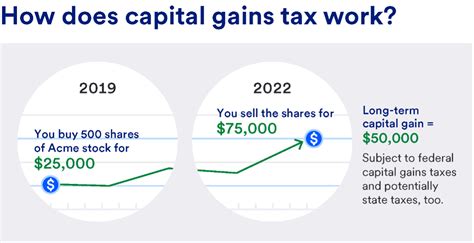
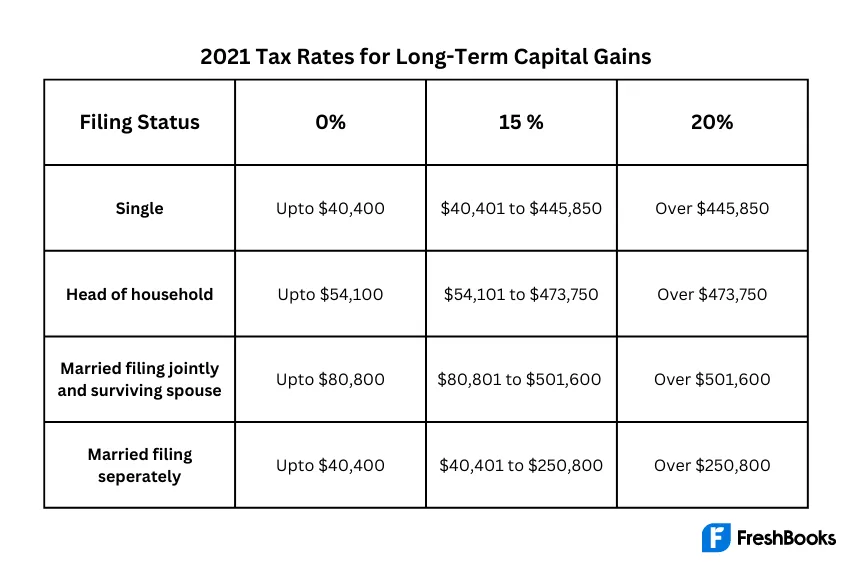
Capital gains are the profits made when selling an asset, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, or other investments. These gains are typically categorized as either short-term (assets held for a year or less) or long-term (assets held for more than a year). The tax treatment of capital gains depends on these categories and can vary based on an individual’s tax bracket.
| Capital Gains Type | Holding Period | Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Short-Term | Up to 1 year | Typically taxed at ordinary income tax rates |
| Long-Term | More than 1 year | Favored tax rates, often lower than ordinary income tax rates |
The Benefits of Wyoming’s Capital Gains Policy
Wyoming’s decision to exempt capital gains from taxation offers several advantages:
- Attracting Investment: By not taxing capital gains, Wyoming becomes an appealing destination for investors and entrepreneurs. This can lead to increased investment in the state's economy, creating jobs and boosting overall economic growth.
- Encouraging Business Growth: Businesses, particularly those in the technology and innovation sectors, often rely on capital gains to fund their operations and expansion. Wyoming's tax-free environment can be a significant incentive for these businesses to establish or expand their presence in the state.
- Promoting Real Estate Development: The absence of a capital gains tax can make Wyoming an attractive market for real estate investors. This can lead to increased property development and revitalization in various parts of the state.
Wyoming’s Tax Strategy: A Balancing Act
Wyoming’s tax policy, including its approach to capital gains, is a carefully crafted strategy aimed at balancing the state’s economic interests with its residents’ needs. By forgoing certain types of taxes, such as personal income tax and capital gains tax, Wyoming creates a competitive advantage that has contributed to its economic success.
However, this strategy also comes with trade-offs. Wyoming relies heavily on its sales and property taxes, which can be less favorable for consumers and homeowners. Additionally, while the absence of a capital gains tax may attract investors, it also means the state misses out on a potential source of revenue.
Comparative Analysis
Let’s take a look at how Wyoming’s tax system compares to other states in the region:
| State | Personal Income Tax | Capital Gains Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Wyoming | None | None |
| Colorado | 4.55% | Varies based on holding period and income level |
| Utah | 4.85% | Varies based on holding period and income level |
| Idaho | 1.6% | None |
As the table illustrates, Wyoming stands out for its absence of both personal income and capital gains taxes. This unique position has helped Wyoming establish itself as a tax haven for certain industries and individuals.
Conclusion: Wyoming’s Tax-Free Capital Gains
Wyoming’s decision to forego taxing capital gains is a strategic move that aligns with its overall tax-friendly environment. This policy attracts investors, encourages business growth, and contributes to the state’s economic prosperity. However, it’s important for residents and businesses to understand the federal tax implications of capital gains, as these still apply.
As Wyoming continues to evolve and adapt its tax policies, the state's unique approach to capital gains will remain a key factor in its economic competitiveness and growth.
Are there any exceptions to Wyoming’s capital gains tax exemption?
+While Wyoming generally does not tax capital gains, there are some exceptions. For instance, gains from the sale of certain types of property, such as timber, may be subject to state taxation. It’s always advisable to consult with a tax professional to understand the specific nuances of Wyoming’s tax laws.
How does Wyoming’s lack of capital gains tax affect its budget and revenue?
+Wyoming’s decision to exempt capital gains from taxation has an impact on its revenue stream. By forgoing this source of income, the state may need to rely more heavily on other tax streams, such as sales and property taxes, to fund its operations and services. This trade-off is a conscious decision by the state’s policymakers.
What are the potential drawbacks of Wyoming’s tax-free capital gains policy?
+While the absence of a capital gains tax has benefits, it also has potential drawbacks. One concern is that it may lead to a concentration of wealth among those who can afford to invest. Additionally, without capital gains tax revenue, the state may face challenges in funding social services and infrastructure projects.



