Does Washington Have State Tax
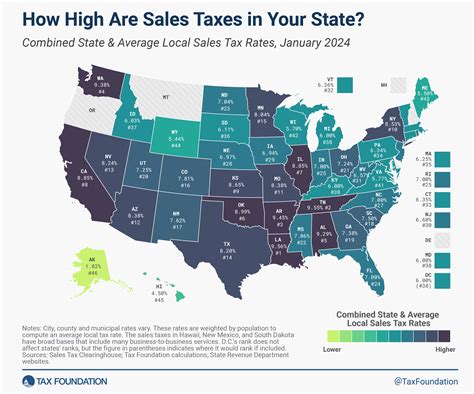
Yes, the state of Washington does indeed have a state tax system in place, which plays a significant role in funding various public services and initiatives. The tax structure in Washington is unique compared to many other states, as it primarily relies on sales and business taxes, while notably absent is a personal income tax.
Understanding Washington’s Tax Structure

Washington’s tax system is designed to support the state’s infrastructure, education, healthcare, and other essential services. The absence of a personal income tax is a distinguishing feature, setting it apart from most other states in the US.
Sales Tax
The sales tax is a significant revenue generator for the state. As of 2023, the state sales tax rate in Washington stands at 6.5%, which is applied to the sale of most goods and some services. However, it’s important to note that local jurisdictions can also levy additional sales taxes, resulting in a combined sales tax rate that can vary from one area to another.
| Sales Tax Rate | Description |
|---|---|
| 6.5% | State Sales Tax Rate |
| Varies | Local Sales Tax Rates (up to 3.9% additional) |

Business and Occupation (B&O) Tax
Washington also imposes a Business and Occupation (B&O) tax on businesses operating within the state. This tax is unique in that it’s a gross receipts tax, meaning it’s based on the total revenue generated by a business, rather than its profit. The B&O tax rate varies depending on the type of business activity, ranging from 0.471% to 1.5%.
| B&O Tax Rate | Business Activity |
|---|---|
| 0.471% | Manufacturing and wholesale |
| 0.484% | Retail sales |
| 1.5% | Service and other business activities |
Other Taxes
In addition to the sales and B&O taxes, Washington also levies other taxes, including a real estate excise tax on property transactions, a motor vehicle excise tax, and various license and permit fees.
The Impact of Washington’s Tax System
Washington’s tax system has both advantages and disadvantages. On the one hand, the absence of a personal income tax makes the state more attractive to individuals and businesses, as it eliminates the burden of income tax filings and potentially high tax rates. This has contributed to a thriving business environment and economic growth.
However, the reliance on sales and business taxes can place a heavier burden on lower-income individuals and small businesses. Sales taxes are regressive in nature, meaning they impact lower-income individuals more significantly as a percentage of their income. Additionally, the variability of tax rates across the state can create complexities for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Advantages
- Attractive to businesses and individuals due to the absence of personal income tax.
- Encourages economic growth and business development.
- Simplifies tax filings for individuals and certain businesses.
Disadvantages
- Regressive nature of sales taxes can disproportionately affect lower-income individuals.
- Complexity for businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions due to varying tax rates.
- Potential strain on certain industries, such as small businesses, due to the B&O tax structure.
Comparison with Other States
When compared to other states, Washington’s tax system is quite unique. Most states in the US have a personal income tax, making Washington one of the few that do not. This distinction has significant implications for both residents and businesses, influencing factors such as cost of living, business competitiveness, and tax policy.
Tax Policy Implications
The absence of a personal income tax in Washington means that the state relies more heavily on other forms of taxation, particularly sales and business taxes. This tax policy decision has wide-ranging effects on the state’s budget, economic development, and social services.
Resident Perspective
For residents, the lack of a personal income tax can be seen as a significant benefit, as it eliminates the complexity and potential financial burden associated with filing income taxes. However, it’s important to consider the trade-offs, such as the impact of sales taxes on daily purchases and the potential for higher property taxes or other fees to make up for the lack of income tax revenue.
Future Outlook
The future of Washington’s tax system is an ongoing topic of discussion and debate. As the state’s economy and population continue to grow, the tax structure will need to adapt to meet changing needs and demands. Proposals for tax reforms, including the potential introduction of a personal income tax, are periodically put forth, reflecting the dynamic nature of tax policy.
Potential Reforms
Proponents of tax reform argue that a personal income tax could provide a more progressive and stable source of revenue, reducing the reliance on sales and business taxes. However, such proposals often face strong opposition, as they can be seen as a burden on individuals and businesses that have grown accustomed to the current tax system.
Regardless of the specific reforms proposed, the ongoing discussion around Washington's tax system highlights the importance of a robust and sustainable tax base for funding essential public services and maintaining a competitive business environment.
What is the state sales tax rate in Washington for 2023?
+The state sales tax rate in Washington for 2023 is 6.5%.
Are there any other taxes besides sales and B&O taxes in Washington?
+Yes, Washington also levies real estate excise taxes, motor vehicle excise taxes, and various license and permit fees.
How does Washington’s tax system compare to other states without personal income tax?
+Washington’s tax system, particularly its reliance on sales and business taxes, is similar to other states without personal income tax, such as Texas and Florida. However, the specific tax rates and structures can vary significantly between states.



