Does Washington Have Income Tax

When considering the tax landscape of the United States, it is essential to delve into the specific taxation policies of each state. Washington, a state in the Pacific Northwest, presents a unique scenario when it comes to income taxation. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of Washington's income tax system, exploring its intricacies, rates, and the impact it has on its residents and businesses.
The Unique Tax Structure of Washington
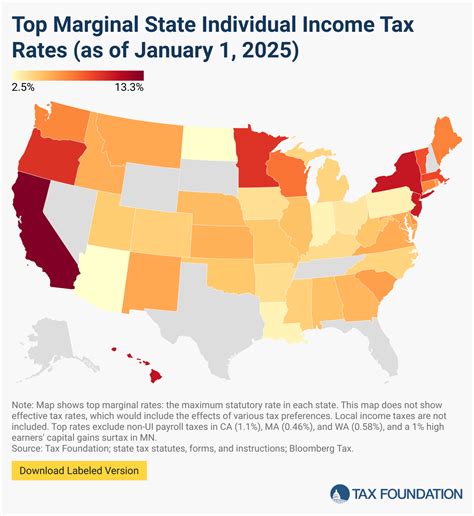
Washington state stands out in the US for its distinctive approach to income taxation. Unlike the majority of states, Washington does not impose a personal income tax on its residents. This means that individuals are not required to pay state income tax on their wages, salaries, or other forms of personal income.
However, this does not mean that Washington residents enjoy a completely tax-free existence. The state still generates revenue through a variety of other tax mechanisms, ensuring its financial stability and the provision of public services.
Business and Corporate Taxation
While individuals may not pay income tax, businesses operating in Washington are subject to a Business and Occupation (B&O) tax. This tax is imposed on the gross income or receipts generated by businesses within the state. The B&O tax rate varies depending on the industry and type of business activity, with rates ranging from 0.16% to 1.5%.
| Business Type | B&O Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 0.484% |
| Wholesale and Distribution | 0.484% |
| Retail Sales | 0.471% |
| Service and Other Activities | 1.5% |

Washington's B&O tax system is designed to be broad-based, applying to a wide range of business activities. This includes manufacturing, wholesale, retail, and service industries. The state also levies additional taxes on specific sectors, such as telecommunications and insurance, to further contribute to its revenue stream.
Sales and Use Tax
Washington imposes a sales tax on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services within the state. The sales tax rate in Washington is 6.5%, with additional local sales taxes varying by jurisdiction, resulting in a combined rate that can exceed 10% in some areas.
In addition to the sales tax, Washington also has a use tax in place. The use tax is applied to the use, storage, or consumption of tangible personal property purchased outside the state and brought into Washington for use. This tax ensures that businesses and individuals pay their fair share, even if they purchase goods online or from out-of-state vendors.
Property Tax
Property owners in Washington are subject to a property tax, which is a significant source of revenue for local governments. The property tax rate is determined by the assessed value of the property and the tax levy set by local jurisdictions, such as counties and school districts. The average effective property tax rate in Washington is approximately 1.15%.
Impact on Residents and Businesses

Washington's unique tax structure has both advantages and drawbacks for its residents and businesses.
Advantages of No Personal Income Tax
- Attracting Businesses and Residents: The absence of a personal income tax makes Washington an attractive destination for businesses and individuals seeking to minimize their tax liabilities. This can lead to increased economic activity and job opportunities within the state.
- Competitive Business Environment: With a focus on business taxes, Washington fosters a competitive environment for businesses, encouraging innovation and growth. The state's B&O tax structure allows for a level playing field, ensuring that all businesses contribute proportionally to the state's revenue.
- Stability and Predictability: Washington's tax system provides a stable and predictable revenue stream for the state government. The reliance on business and sales taxes, which are generally more stable than personal income taxes, ensures consistent funding for public services and infrastructure.
Considerations and Challenges
- Revenue Generation: While Washington's tax system generates substantial revenue, the absence of a personal income tax limits the state's ability to raise funds during economic downturns or in times of fiscal constraint. This can lead to challenges in maintaining public services and infrastructure.
- Inequality Concerns: The reliance on business and sales taxes can disproportionately impact lower-income individuals and small businesses. The sales tax, for instance, is a regressive tax, meaning it affects individuals with lower incomes more significantly.
- Regional Disparities: The varying local sales tax rates across jurisdictions can create regional disparities in the cost of living and business expenses. This can impact the competitiveness of certain areas within the state.
Future Implications and Reforms
As Washington continues to evolve economically and socially, there are ongoing discussions and proposals for tax reforms. Some key considerations include:
- Personal Income Tax Introduction: There have been proposals to introduce a personal income tax in Washington, aiming to address revenue generation concerns and provide a more progressive tax system. However, such proposals often face significant political opposition.
- Tax Reform and Simplification: Efforts are underway to simplify Washington's tax system, making it more transparent and efficient. This includes initiatives to reduce tax complexities and ensure a fair and competitive business environment.
- Tax Incentives and Credits: The state offers various tax incentives and credits to encourage economic development, attract businesses, and support specific industries. These incentives play a crucial role in shaping Washington's economic landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages of Washington’s tax system for businesses?
+
Washington’s tax system, with its focus on business and sales taxes, creates a competitive environment for businesses. The absence of a personal income tax can attract businesses and provide a level playing field for all industries. Additionally, the state offers various tax incentives to support economic development.
How does Washington generate revenue without a personal income tax?
+
Washington generates revenue through a combination of business taxes, sales taxes, and property taxes. The Business and Occupation (B&O) tax applies to various business activities, while the sales tax and use tax contribute to the state’s revenue stream. Additionally, local governments rely on property taxes for funding.
Are there any proposals to introduce a personal income tax in Washington?
+
Yes, there have been ongoing discussions and proposals to introduce a personal income tax in Washington. These proposals aim to address revenue generation concerns and provide a more progressive tax system. However, such proposals often face significant political opposition.
What impact does Washington’s tax system have on lower-income individuals?
+
The reliance on sales taxes can disproportionately affect lower-income individuals, as sales taxes are regressive in nature. However, Washington also offers various tax credits and assistance programs to support low-income residents.
How does Washington compare to other states in terms of tax burden?
+
Washington’s tax system, with its focus on business and sales taxes, places it in a unique position compared to other states. While it lacks a personal income tax, the overall tax burden can vary depending on the specific circumstances and business activities of individuals and businesses.



