Does Sc Have State Income Tax
In the United States, each state has its own unique tax system, and understanding these differences is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. When it comes to the state of South Carolina, or SC, the question of income tax is an important one, as it directly impacts the financial obligations and planning of its residents.
This comprehensive article will delve into the intricacies of SC's income tax system, shedding light on its structure, rates, exemptions, and the overall impact it has on the state's economy and its citizens.
The South Carolina Income Tax System
South Carolina, like many other states, imposes an income tax on its residents and businesses. The SC Department of Revenue is responsible for administering and enforcing the state’s tax laws, ensuring compliance, and providing guidance to taxpayers.
The income tax system in SC is designed to generate revenue for the state, which is then allocated towards various public services, infrastructure development, and other government expenditures.
Taxable Income and Rates
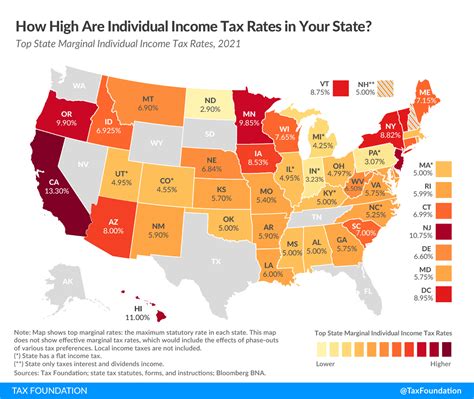
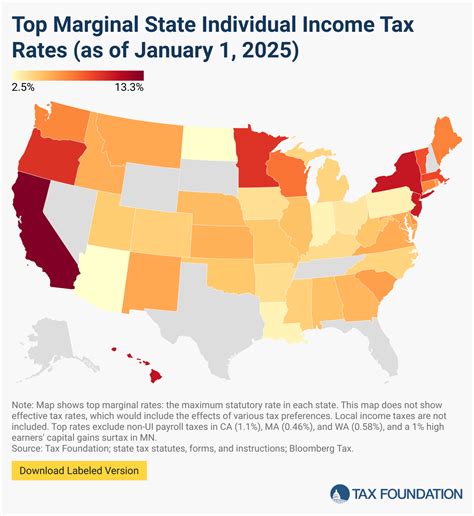
SC’s income tax system operates on a marginal bracket system, which means that different income levels are taxed at varying rates. As of the 2023 tax year, the state has six tax brackets, ranging from 0% to 7%.
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Income Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0% | Up to $2,999 |
| 2 | 3% | $3,000 - $5,999 |
| 3 | 4% | $6,000 - $9,999 |
| 4 | 5% | $10,000 - $14,999 |
| 5 | 6% | $15,000 - $22,999 |
| 6 | 7% | $23,000 and above |
These tax brackets apply to both single and married filers. It's important to note that South Carolina's income tax system is separate from federal income taxes, and residents must file both state and federal tax returns.
Exemptions and Deductions
SC offers several exemptions and deductions to help reduce the tax burden on its residents. These include:
- Standard Deduction: Taxpayers can choose to take the standard deduction, which reduces taxable income by a fixed amount. For the 2023 tax year, the standard deduction is $4,200 for single filers and $8,400 for married couples filing jointly.
- Personal Exemptions: SC allows personal exemptions for each dependent, reducing taxable income. However, the personal exemption amount is subject to change annually.
- Itemized Deductions: Taxpayers can opt for itemized deductions instead of the standard deduction. This allows for the reduction of taxable income based on eligible expenses such as medical costs, charitable contributions, and certain tax-deductible interest payments.
Additionally, SC offers tax credits for various purposes, including education, low-income individuals, and those with disabilities. These credits can further reduce the tax liability of eligible taxpayers.
Taxable Sources of Income
South Carolina imposes income tax on various sources of income, including:
- Wages and salaries earned within the state
- Business income generated within SC
- Investment income, such as dividends, interest, and capital gains
- Retirement income, including pensions and annuities
- Gambling and lottery winnings
It's important for residents to understand the specific rules and regulations surrounding each type of income to ensure accurate reporting and compliance.
Filing and Payment Options
Taxpayers in SC have several options for filing their income tax returns. They can choose to file electronically through the SC Department of Revenue’s online portal, or they can opt for traditional paper filing. The department also provides guidance on various payment methods, including direct debit, credit card payments, and electronic funds transfer.
The deadline for filing SC income tax returns typically aligns with the federal tax deadline, which is usually April 15th of each year. However, it's crucial to stay updated on any changes or extensions announced by the state's tax authorities.
Impact on the State’s Economy

The income tax system in SC plays a significant role in shaping the state’s economy. The revenue generated through income taxes is a vital source of funding for essential public services, infrastructure projects, and social programs.
Revenue Allocation
A portion of the income tax revenue collected by SC is allocated to the General Fund, which supports various state agencies and programs. These include education, healthcare, public safety, transportation, and economic development initiatives.
Additionally, a percentage of the income tax revenue is directed towards specific funds, such as the Education Improvement Act Fund, which aims to enhance educational opportunities and infrastructure in the state.
Economic Growth and Business Climate
The income tax structure in SC is designed to encourage economic growth and attract businesses. The state offers various incentives and tax credits to businesses, promoting investment, job creation, and economic development.
SC's competitive tax rates and a range of business-friendly initiatives have contributed to its reputation as a desirable location for companies, fostering a positive business climate and supporting the growth of diverse industries.
Resident Impact
For residents, the income tax system in SC has both benefits and considerations. While it provides funding for essential services and infrastructure, it also impacts their disposable income and financial planning.
The availability of exemptions, deductions, and tax credits can significantly reduce the tax burden for many residents, making it an important factor in their overall financial well-being.
Comparative Analysis
When comparing SC’s income tax system to other states, it’s evident that the structure and rates vary significantly. Some states, like Alaska, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Texas, Washington, and Wyoming, have no income tax, offering a distinct advantage to taxpayers.
On the other hand, states like California and New York have higher income tax rates, which can impact individuals and businesses considering relocation.
SC's income tax system falls somewhere in the middle, offering a balanced approach that generates revenue for essential services while maintaining competitiveness in the regional economic landscape.
Future Implications and Considerations
The income tax system in SC is subject to ongoing evaluation and potential reforms. As economic conditions and tax policies evolve, the state may consider adjustments to its tax brackets, exemptions, and deductions to ensure fairness and competitiveness.
Additionally, the impact of federal tax reforms, such as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, may influence SC's tax policies and the overall tax landscape in the state. It's crucial for taxpayers and businesses to stay informed about any changes that may affect their tax obligations and planning.
Furthermore, the digital transformation of tax systems and the rise of remote work present new challenges and opportunities for states like SC. The state may explore innovative solutions to adapt to these changes and ensure a fair and efficient tax system for its residents and businesses.
What is the tax rate for SC’s highest income bracket in 2023?
+
The highest income tax rate in SC for the 2023 tax year is 7%.
Are there any tax credits available for SC residents?
+
Yes, SC offers various tax credits, including education, low-income, and disability credits.
When is the deadline for filing SC income tax returns?
+
The deadline for filing SC income tax returns typically aligns with the federal tax deadline, which is usually April 15th of each year. However, it’s advisable to stay updated on any extensions or changes announced by the state’s tax authorities.



