Does Indiana Have State Taxes
When it comes to taxes, Indiana follows a unique approach, and its tax system is an interesting topic for exploration. Indiana's tax structure differs from many other states in the United States, offering both advantages and considerations for residents and businesses alike. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the specifics of Indiana's tax landscape, exploring the state's tax policies, rates, and their impact on various aspects of life and business within the Hoosier State.
Understanding Indiana’s Tax System

Indiana, known for its vibrant cities, diverse industries, and rich history, has developed a tax system that reflects its economic goals and values. The state’s tax structure is designed to support its thriving economy while providing essential services to its residents. Let’s uncover the intricacies of Indiana’s tax landscape.
State Income Tax: A Key Component
Indiana imposes a progressive income tax, meaning the tax rate increases as income levels rise. This approach ensures fairness and contributes to the state’s revenue generation. Here’s a breakdown of Indiana’s income tax brackets for the current tax year:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to 3,750</td> <td>2.43%</td> </tr> <tr> <td>3,751 - 11,250</td> <td>3.23%</td> </tr> <tr> <td>11,251 - 27,500</td> <td>3.3%</td> </tr> <tr> <td>27,501 - 125,000</td> <td>3.23%</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Over 125,000 | 3.23% |

These rates are applicable to both individual and corporate tax returns, ensuring consistency and simplicity in the tax filing process.
Sales and Use Tax: A Significant Revenue Source
Indiana levies a sales and use tax on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services within the state. The standard sales tax rate in Indiana is 7%, which includes both the state and local sales tax rates. However, it’s important to note that certain jurisdictions within Indiana may have slightly different sales tax rates due to local additions.
For instance, the city of Indianapolis has a 1% local sales tax in addition to the state sales tax, resulting in a combined sales tax rate of 8% for purchases made within the city limits. These variations in sales tax rates across different areas of the state provide a fascinating insight into the regional dynamics of Indiana's tax landscape.
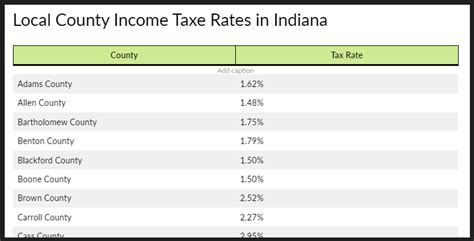
Property Tax: Assessing Real Estate
Property taxes in Indiana are assessed at the local level, primarily by counties and municipalities. The property tax rates can vary significantly depending on the location and the specific taxing district. These rates are typically expressed as a percentage of the property’s assessed value, and they contribute to funding local services such as schools, fire protection, and infrastructure maintenance.
To provide a clearer picture, let's consider an example. In a hypothetical scenario, a residential property located in the city of Evansville might be subject to a 1.5% property tax rate, while a similar property in the town of Seymour could face a 1.2% property tax rate. These variations reflect the unique needs and funding requirements of different communities within Indiana.
Other Taxes: A Diverse Revenue Stream
Indiana’s tax system extends beyond income, sales, and property taxes. The state also imposes various other taxes to support its operations and initiatives. These include:
- Motor Vehicle Excise Tax: A tax levied on the purchase or lease of motor vehicles, varying by the vehicle’s cost and type.
- Inheritance Tax: A tax applied to assets inherited from a deceased individual, with rates based on the relationship between the deceased and the beneficiary.
- Gaming Taxes: Taxes imposed on various forms of gaming activities, including casinos and lottery winnings.
- Alcohol and Tobacco Taxes: Excise taxes on the sale of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products.
The Impact of Indiana’s Tax System

Indiana’s tax policies have a profound influence on various aspects of life and business within the state. Let’s explore some key areas where the tax system plays a significant role.
Economic Development and Business Climate
Indiana’s tax system aims to create an attractive environment for businesses, fostering economic growth and job creation. The state’s competitive tax rates, especially in comparison to neighboring states, make it an appealing destination for companies considering expansion or relocation.
For instance, Indiana's corporate income tax rate is 6.5%, which is notably lower than many other states. This rate, combined with other business-friendly initiatives, has contributed to Indiana's reputation as a hub for manufacturing, logistics, and technology industries.
Education and Infrastructure Funding
Tax revenues play a vital role in funding essential services, including education and infrastructure development. Property taxes, in particular, are a significant source of revenue for local school districts, ensuring that Indiana’s youth receive quality education.
Additionally, the state's sales and use tax revenues contribute to various infrastructure projects, such as road maintenance, public transportation initiatives, and the development of recreational facilities. These investments not only enhance the quality of life for residents but also attract tourists and businesses, further bolstering the state's economy.
Tax Incentives and Economic Growth
Indiana actively promotes economic growth through various tax incentives and programs. The state offers a range of tax credits and deductions aimed at encouraging business investment, job creation, and innovation.
For example, the Hoosier Business Investment Tax Credit provides incentives for businesses that invest in capital improvements or create new jobs within the state. This credit can significantly reduce a company's tax liability, making it an attractive incentive for businesses considering expansion or relocation to Indiana.
Taxation and Social Services
Tax revenues also fund critical social services, ensuring the well-being of Indiana’s residents. These services include healthcare initiatives, social welfare programs, and support for vulnerable populations.
For instance, the state's Medicaid program, funded in part by tax revenues, provides healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families. Similarly, tax-funded initiatives support senior care, disability services, and programs aimed at improving the overall health and quality of life for Hoosiers across the state.
Conclusion: Navigating Indiana’s Tax Landscape
Indiana’s tax system is a carefully crafted framework that balances revenue generation with the needs of its residents and businesses. The state’s tax policies contribute to a vibrant economy, support essential services, and foster economic growth and development.
As we've explored, Indiana's tax landscape is diverse and dynamic, offering both advantages and considerations for individuals and businesses alike. Whether you're a resident navigating your tax obligations or a business exploring opportunities within the state, understanding Indiana's tax system is key to making informed decisions and contributing to the continued prosperity of the Hoosier State.
How do Indiana’s tax rates compare to other states?
+Indiana’s tax rates are generally competitive when compared to other states. For instance, its corporate income tax rate is lower than many neighboring states, making it an attractive destination for businesses. However, it’s important to consider the overall tax burden, which includes factors like sales tax and property tax rates.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in Indiana?
+Yes, Indiana offers a range of tax incentives to encourage business investment and job creation. These include tax credits for capital investments, job creation, and innovation. The Hoosier Business Investment Tax Credit is a notable example of such incentives.
How does Indiana’s sales tax compare to other states?
+Indiana’s standard sales tax rate of 7% is on the lower end of the spectrum when compared to other states. However, it’s important to note that local sales tax rates can vary, resulting in slightly higher combined rates in certain areas of the state.



