Corporate Income Tax By State
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of corporate income tax in the United States, a complex yet crucial aspect of doing business in the country. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the varying corporate tax landscapes across different states, offering valuable insights for businesses and investors alike.
Unraveling the Corporate Income Tax Landscape
The United States boasts a diverse fiscal system, with each state possessing the autonomy to establish its own corporate tax policies. This results in a unique and intricate corporate income tax landscape, posing both opportunities and challenges for businesses aiming to optimize their tax strategies.
Tax Rates and Structures: A Varied Approach
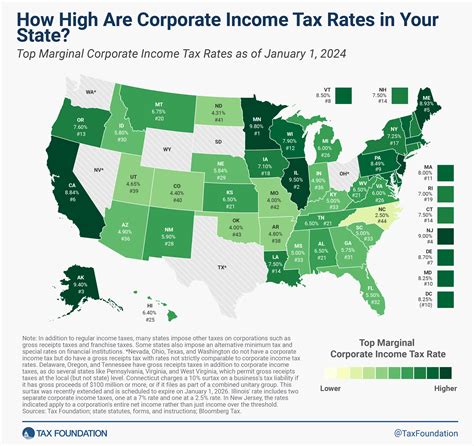
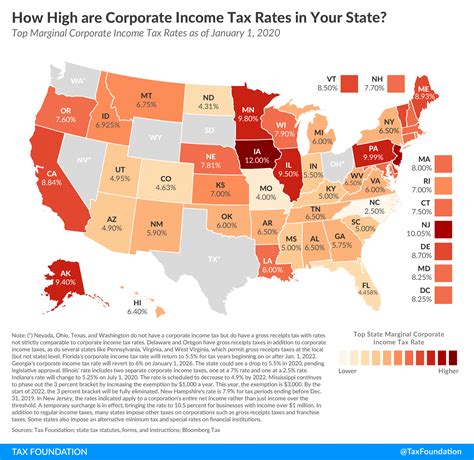
One of the most striking aspects of corporate taxation in the US is the diversity of tax rates and structures across states. While some states opt for a flat tax rate, others implement progressive systems with multiple tax brackets. For instance, Delaware is renowned for its 8.7% flat tax rate, offering a straightforward and predictable tax environment for businesses. Conversely, California employs a progressive tax structure with four tax brackets, ranging from 1.0% to 12.3%, catering to varying corporate income levels.
| State | Corporate Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Delaware | 8.7% |
| California | 1.0% - 12.3% (Progressive) |
| Texas | 0.475% - 10.0% |
| New York | 4.0% - 6.5% |
This variance in tax rates and structures can significantly impact a business's overall tax liability, underscoring the importance of careful consideration when selecting a state for operations.
Tax Incentives and Credits: Attracting Businesses
Many states utilize tax incentives and credits as a strategic tool to attract and retain businesses. These incentives can take various forms, including tax holidays, tax credits for specific industries or investments, and deductions for research and development expenses. For example, North Carolina offers a 25% tax credit for film and television production, fostering the state’s burgeoning film industry.
Similarly, Massachusetts provides a 2.5% tax credit for research and development expenses, encouraging innovation and technological advancement within the state. Such incentives can prove highly beneficial for businesses, significantly reducing their tax burden and enhancing their profitability.
Tax Compliance and Administrative Burdens
Navigating the complex web of state-specific tax regulations can be a daunting task for businesses, particularly those operating across multiple states. The varying tax forms, deadlines, and compliance requirements can add significant administrative burdens, potentially impacting a business’s operational efficiency and profitability.
For instance, New Jersey requires businesses to file a Corporate Business Tax (CBT) return, annual report, and payment, adding to the administrative load. Similarly, Illinois mandates the filing of a Franchise Tax Return, further complicating the tax compliance process.
Impact on Business Decisions
The intricate corporate tax landscape across states significantly influences business decisions, from initial setup to ongoing operations. Here’s a deeper dive into some key considerations:
Business Setup and Location
When deciding on a state for business setup, corporate tax rates and structures play a pivotal role. States with lower tax rates or more favorable tax structures may be more appealing to businesses, offering reduced tax burdens and increased profitability.
For instance, Wyoming, with its zero corporate income tax policy, has emerged as a popular choice for businesses seeking tax-friendly environments. Similarly, Nevada and South Dakota are known for their lack of corporate income tax, making them attractive destinations for business operations.
Tax Planning and Strategy
Effective tax planning is crucial for businesses to optimize their tax liability and enhance profitability. Understanding the unique tax landscapes of different states allows businesses to strategically allocate resources, make informed investment decisions, and leverage tax incentives to their advantage.
For instance, a business operating in Michigan, which offers a 1.9% corporate income tax rate, may choose to locate its headquarters there to benefit from the lower tax rate. Simultaneously, the business could leverage tax incentives in other states for specific operations, such as manufacturing or research and development, optimizing its tax strategy.
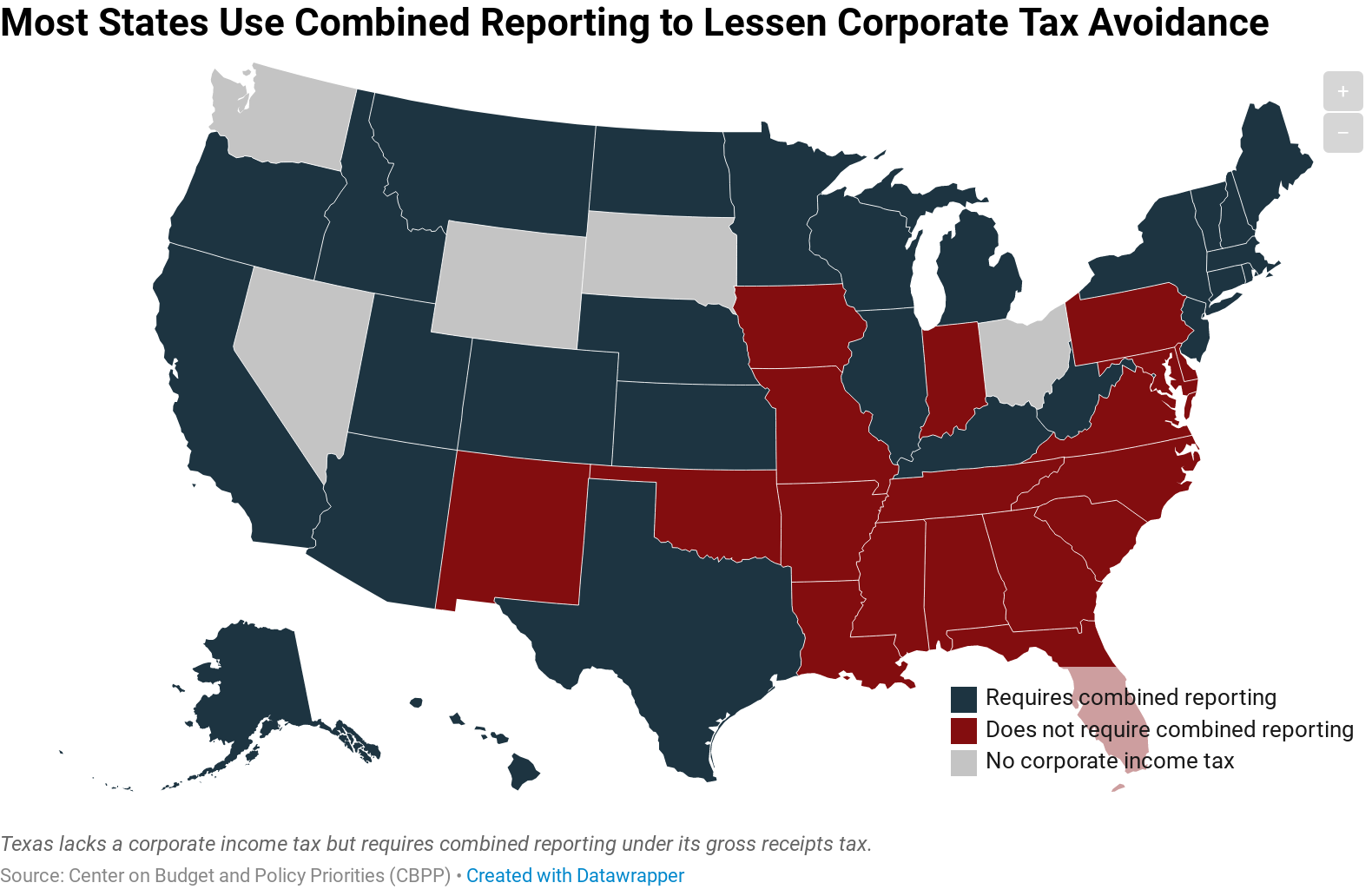
Inter-State Operations and Tax Compliance
Businesses operating across multiple states face the challenge of complying with diverse tax regulations. This includes registering with state tax authorities, filing tax returns, and paying taxes in each state, often with varying deadlines and requirements.
To illustrate, a business with operations in both Pennsylvania and Ohio would need to navigate two distinct tax systems. While Pennsylvania imposes a 9.99% corporate net income tax, Ohio has a flat rate of 4.75%, requiring the business to manage these differences effectively.
Future Implications and Trends
The corporate income tax landscape in the US is dynamic and ever-evolving, influenced by economic, political, and societal factors. Here’s a glimpse into some potential future developments and their implications.
Tax Reform and Policy Changes
Tax reforms and policy changes at the federal and state levels can significantly impact corporate taxation. Recent federal tax reforms, such as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), have altered the corporate tax landscape, introducing new considerations for businesses.
At the state level, ongoing debates around tax policies, such as the introduction of new tax brackets or changes to tax rates, can shape the future tax environment. Businesses need to stay abreast of these developments to adapt their tax strategies accordingly.
Economic and Market Dynamics
Economic and market dynamics play a pivotal role in shaping corporate tax landscapes. Factors such as economic growth, inflation, and industry trends can influence tax policies and business operations.
For instance, during economic downturns, states may opt to increase corporate tax rates to bolster revenue. Conversely, in periods of economic growth, states may implement tax incentives to attract businesses and foster economic development.
Technological Advancements and Tax Administration
Technological advancements are revolutionizing tax administration, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. States are increasingly adopting digital platforms and tools to streamline tax filing and payment processes, improving compliance and reducing administrative burdens for businesses.
For example, California has implemented an online tax filing system, e-file, allowing businesses to file their tax returns electronically, making the process more convenient and efficient.
How do state tax rates impact a business’s bottom line?
+State tax rates directly affect a business’s profitability. Lower tax rates can lead to increased profits, while higher rates can reduce a business’s net income. It’s crucial for businesses to consider tax rates when making location decisions.
What are the key differences in tax compliance between states?
+Tax compliance varies widely between states. Differences include tax forms, deadlines, and specific requirements. For instance, some states may require additional forms or documentation, adding to the complexity of compliance.
How can businesses stay updated on state tax reforms and policy changes?
+Businesses can stay informed by subscribing to tax newsletters, following industry associations, and utilizing tax research tools. Regularly reviewing state tax websites and consulting with tax professionals is also recommended.



