Colorado Taxes Calculator

Colorado, known for its stunning natural landscapes and vibrant cities, offers a unique tax landscape for residents and businesses alike. The state's tax system is designed to support essential services and infrastructure while also promoting economic growth. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of Colorado's tax structure, providing a detailed analysis of its impact on individuals and businesses.
Understanding Colorado’s Tax Landscape

Colorado’s tax system is a multifaceted framework, encompassing various tax types and rates. From income taxes to sales and use taxes, property taxes, and more, each component plays a vital role in funding state initiatives and services. Let’s explore these taxes in detail.
Income Taxes
Colorado imposes a progressive income tax system, meaning tax rates increase as taxable income rises. The state’s income tax rates range from 4.55% to 6.9%, with five tax brackets based on taxable income. For instance, single taxpayers with taxable income between 50,000</strong> and <strong>150,000 fall into the 5.45% tax bracket. It’s worth noting that Colorado’s income tax rates are relatively competitive compared to other states.
Additionally, Colorado allows taxpayers to claim various deductions and credits, reducing their taxable income and overall tax liability. Common deductions include federal income tax paid, mortgage interest, and charitable contributions. Moreover, Colorado offers tax credits for low- and moderate-income taxpayers, providing a valuable financial boost for eligible residents.
| Tax Rate | Taxable Income Range |
|---|---|
| 4.55% | $0 - $5,000 |
| 5.00% | $5,000 - $20,000 |
| 5.45% | $20,000 - $50,000 |
| 5.45% | $50,000 - $150,000 |
| 6.90% | $150,000 and above |
Sales and Use Taxes
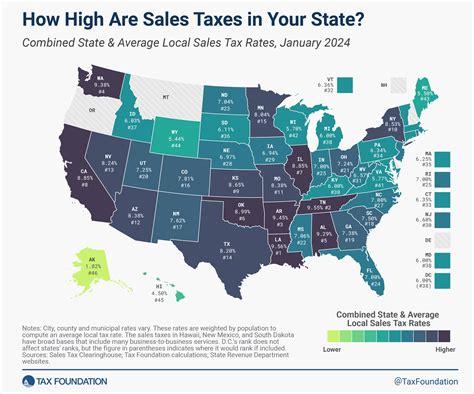
Colorado’s sales and use tax system is a significant revenue generator for the state. The statewide sales tax rate stands at 2.9%, while local sales tax rates vary across jurisdictions, ranging from 0% to 7.45%. This variability in local sales tax rates means that the total sales tax rate can differ significantly from one city or county to another. For instance, the combined sales tax rate in Denver is 7.62%, while it’s 8.31% in Boulder.
Use taxes are applied to purchases made outside of Colorado but used within the state. This ensures that residents and businesses pay taxes on goods and services, regardless of where they are purchased. The use tax rate is the same as the sales tax rate in the jurisdiction where the item is used.
Property Taxes
Colorado’s property tax system is designed to fund local government services, including schools, roads, and public safety. The average effective property tax rate in Colorado is 0.58%, which is slightly below the national average. Property taxes are assessed based on the assessed value of the property, which is typically a percentage of the fair market value.
The assessed value of residential properties is capped at 7% of the actual value for the first $300,000 and 10% for the remainder. This ensures that property owners are not burdened with excessive tax liabilities. Moreover, Colorado offers property tax exemptions for certain categories, such as veterans, seniors, and disabled individuals.
Other Taxes
Colorado imposes additional taxes on specific industries and activities to generate revenue and support state initiatives. These include:
- Corporate Income Tax: Colorado levies a 4.63% corporate income tax rate on business profits. This tax is applied to both C-corporations and S-corporations.
- Motor Vehicle Taxes: The state charges a 2.9% sales tax on vehicle purchases, in addition to a 1% to 3% registration fee based on the vehicle's value. This fee supports transportation infrastructure.
- Tobacco and Alcohol Taxes: Colorado imposes excise taxes on tobacco products and alcoholic beverages. These taxes fund healthcare programs and substance abuse prevention efforts.
The Impact of Colorado’s Tax System
Colorado’s tax system has a significant impact on both individuals and businesses operating within the state. Let’s explore these impacts in more detail.
Impact on Individuals
For individuals, Colorado’s tax system offers a balanced approach. The progressive income tax structure ensures that higher-income earners contribute a larger share of their income to the state’s revenue. This helps fund essential services and infrastructure projects, benefiting all residents.
Moreover, the availability of deductions and credits provides taxpayers with opportunities to reduce their tax liability. This can be especially beneficial for low- and moderate-income households, as they can access tax relief through targeted credits.
However, it's important to note that Colorado's sales tax system can impact individuals differently based on their spending habits. Residents who purchase goods and services within the state will contribute to the sales tax revenue, while those who primarily shop online or out of state may pay less.
Impact on Businesses
Colorado’s tax system provides a competitive environment for businesses. The relatively low corporate income tax rate and the absence of a state-level personal property tax make the state attractive for business owners. Additionally, the varying local sales tax rates allow businesses to consider their location strategically, depending on their target market and tax implications.
However, businesses must also consider the impact of Colorado's sales and use tax system. With the state's emphasis on sales taxes, businesses must ensure they are compliant with the complex tax regulations. This includes properly registering, collecting, and remitting sales taxes, which can be a significant administrative burden.
Furthermore, businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions within Colorado must navigate the varying tax rates and regulations, ensuring they are compliant with each locality's requirements.
Future Implications and Considerations
Colorado’s tax system is dynamic and subject to change, influenced by economic trends, legislative decisions, and the state’s evolving needs. Here are some key considerations for the future:
Economic Growth and Tax Revenue
Colorado’s robust economy and thriving industries, such as tourism, outdoor recreation, and technology, contribute significantly to the state’s tax revenue. As the state continues to attract businesses and residents, it’s crucial to balance the need for economic growth with sustainable tax policies.
The state must carefully manage its tax structure to ensure it remains competitive, encourages investment, and supports economic development. This includes regularly reviewing and adjusting tax rates and incentives to remain aligned with market trends and industry demands.
Tax Reform and Equity
Colorado’s tax system has faced calls for reform to address concerns about fairness and equity. Some argue that the state’s reliance on sales taxes disproportionately impacts lower-income residents, as they tend to spend a larger portion of their income on taxable goods and services.
Future tax reforms may focus on redistributing the tax burden more equitably, potentially through adjustments to income tax brackets or the introduction of new tax measures. This could help ensure that all residents contribute to the state's revenue in a manner that reflects their ability to pay.
Infrastructure and Service Funding
Colorado’s tax revenue is vital for funding essential services and infrastructure projects. As the state continues to grow, the demand for services such as education, healthcare, and transportation will increase. Ensuring that the tax system generates sufficient revenue to support these services is crucial for the state’s long-term prosperity.
The state may need to explore innovative funding mechanisms or partnerships to address infrastructure needs, especially in areas such as transportation and water management, which are critical for Colorado's economic growth and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
Colorado’s tax system is a complex but essential component of the state’s economy and governance. By understanding the various tax types, rates, and their impact on individuals and businesses, residents and stakeholders can make informed decisions about their financial strategies and contributions to the state.
As Colorado continues to evolve, its tax landscape will play a pivotal role in shaping the state's future. By staying informed and engaged, residents can ensure that their voices are heard in the ongoing discussions about tax policy and its impact on the community.
How does Colorado’s income tax system compare to other states?
+
Colorado’s income tax system is relatively competitive compared to other states. While it has a progressive structure with higher tax rates for higher incomes, the top tax bracket of 6.9% is lower than many other states. This makes Colorado an attractive option for high-income earners seeking a more favorable tax environment.
What are the key differences in sales tax rates across Colorado’s cities and counties?
+
Sales tax rates vary significantly across Colorado’s cities and counties. The statewide sales tax rate is 2.9%, but local sales tax rates can range from 0% to 7.45%. This means that the total sales tax rate can differ substantially from one place to another. For example, Denver has a combined sales tax rate of 7.62%, while Boulder’s rate is 8.31%.
How can businesses ensure they are compliant with Colorado’s sales and use tax regulations?
+
Businesses operating in Colorado must register with the state to collect and remit sales taxes. They should stay informed about the varying sales tax rates across jurisdictions and ensure they collect the correct amount of tax based on the location of the sale. Additionally, businesses should keep accurate records and regularly file sales tax returns to avoid penalties.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available for businesses in Colorado?
+
Yes, Colorado offers various tax incentives and credits to attract and support businesses. These include tax credits for research and development, job creation, and capital investment. Additionally, the state provides tax incentives for specific industries, such as renewable energy and film production. Businesses should consult with tax professionals to explore these opportunities.
How does Colorado’s tax system impact the state’s overall economic growth and development?
+
Colorado’s tax system plays a crucial role in supporting the state’s economic growth and development. The state’s competitive tax rates, especially in corporate income taxes, make it an attractive destination for businesses. Additionally, the revenue generated from taxes funds essential services and infrastructure projects, contributing to a robust economy and high quality of life for residents.



