Cigarette Tax
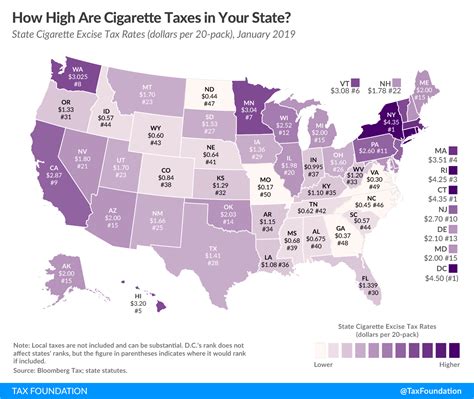
The cigarette tax is a widely implemented levy on the sale of cigarettes and other tobacco products, serving as a significant revenue source for governments worldwide. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the cigarette tax, exploring its history, global variations, economic impact, and future prospects. By examining real-world examples and expert insights, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this critical policy tool.
A Historical Perspective on Cigarette Taxation
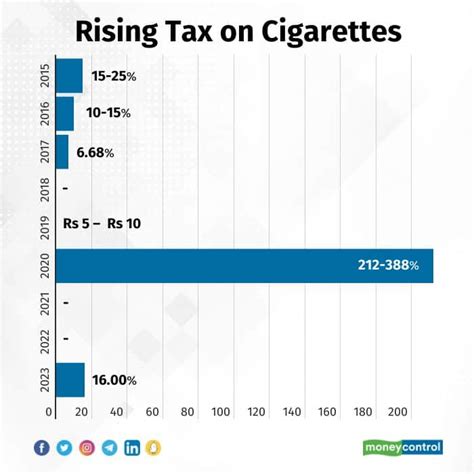
The history of cigarette taxation dates back to the early 20th century when governments began to recognize the potential for generating revenue from the popular tobacco industry. The first recorded instance of a cigarette tax was introduced in the United States in 1864, during the Civil War, as a means to fund the war effort. This tax, known as the “Revenue Act of 1864,” levied a tax of 2 cents per package of 20 cigarettes, marking the beginning of a long-standing relationship between governments and cigarette taxation.
Over the years, cigarette taxes have evolved, driven by various factors such as public health concerns, economic priorities, and political ideologies. In the post-World War II era, as the harmful effects of smoking became more evident, governments began to view cigarette taxes as a tool to discourage tobacco consumption and promote public health. This shift in perspective led to significant increases in cigarette tax rates, particularly in developed nations.
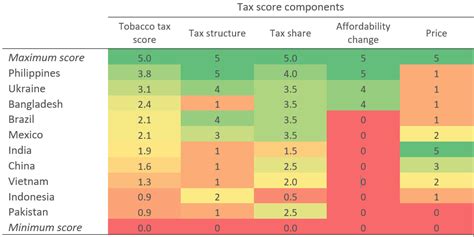
Global Variations in Cigarette Taxation
Today, cigarette taxation varies significantly across countries, reflecting diverse economic, social, and cultural factors. Some nations have implemented high tax rates to curb smoking rates and fund healthcare initiatives, while others maintain lower taxes to support their economies and maintain employment in the tobacco industry.
Case Study: Australia’s Cigarette Tax
Australia stands as a prominent example of a country with a comprehensive and progressive cigarette tax policy. The Australian government has consistently raised cigarette taxes, with the latest increase coming into effect in 2020. The current tax structure includes a base excise tax of AU$0.705 per cigarette, plus a value-based excise tax of 41.5% of the retail price. This approach has resulted in a significant increase in the price of cigarettes, making Australia one of the most expensive places in the world to purchase tobacco products.
The high cigarette tax in Australia has had a profound impact on smoking rates. According to the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, the smoking rate among adults dropped from 24.3% in 1991 to 11.6% in 2020. This decline is attributed not only to the increased tax but also to a comprehensive suite of tobacco control measures, including plain packaging, advertising bans, and public education campaigns.
| Country | Cigarette Tax Rate | Smoking Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | 41.5% of retail price + AU$0.705 per cigarette | 11.6% |
| United Kingdom | 57.7% of retail price | 14.3% |
| France | 82% of retail price | 24.3% |
| China | 25% of retail price | 26.6% |

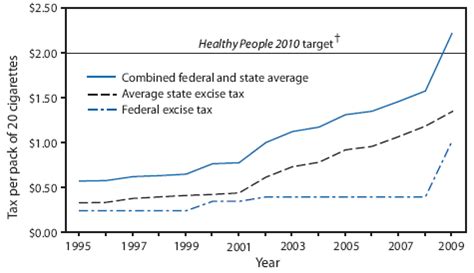
Economic Impact of Cigarette Taxes
The economic implications of cigarette taxes are multifaceted, affecting both governments and consumers. On the government side, cigarette taxes provide a stable source of revenue, contributing to fiscal stability and funding for various public services and healthcare initiatives. For instance, in the United States, cigarette taxes generated approximately $25.6 billion in revenue in 2020, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This revenue is often earmarked for specific programs, such as tobacco prevention and cessation initiatives, as well as general health and education funds.
For consumers, the economic impact of cigarette taxes is primarily felt through increased prices. As tax rates rise, the cost of cigarettes becomes a significant financial burden for smokers, especially those with lower incomes. This can lead to reduced consumption or a shift to cheaper, potentially more harmful tobacco products. However, it is important to note that the economic impact extends beyond the individual smoker. Increased cigarette prices can also lead to a reduction in secondhand smoke exposure, improving public health and reducing healthcare costs associated with smoking-related illnesses.
Tax Evasion and Illicit Trade
High cigarette taxes can also encourage tax evasion and illicit trade. Smokers may turn to the black market to obtain cheaper cigarettes, undermining the effectiveness of the tax and potentially funding organized crime. To combat this, governments often employ a range of measures, including stricter enforcement, tracking systems, and public awareness campaigns. For example, the European Union’s Excise Movement and Control System (EMCS) is designed to monitor the movement of goods subject to excise duty, including cigarettes, to prevent tax evasion and illicit trade.
Future Prospects and Potential Developments
As the world continues to grapple with the public health crisis posed by tobacco use, the future of cigarette taxation remains a critical policy area. Here are some potential developments and trends to watch:
- Global Harmonization of Cigarette Taxes: Efforts to harmonize cigarette taxes globally could reduce price discrepancies and discourage cross-border tobacco trade. This approach aims to create a level playing field for tobacco control measures and make it harder for smokers to access cheaper cigarettes in other countries.
- Innovation in Tobacco Taxation: Governments may explore innovative taxation methods, such as sin taxes or health-related taxes, to further discourage tobacco use. These taxes could be based on the harmfulness of tobacco products or the potential healthcare costs associated with their use.
- Technology-Driven Solutions: The use of technology, such as blockchain and digital tracking systems, could enhance the effectiveness of cigarette taxation. These tools can improve tax collection, reduce tax evasion, and provide real-time data on tobacco consumption patterns.
- Collaboration with the Tobacco Industry: While controversial, some governments may engage with the tobacco industry to find mutually beneficial solutions. This could involve industry-funded tobacco control initiatives or partnerships to reduce the harm caused by tobacco products.
Conclusion
The cigarette tax is a complex policy tool with far-reaching implications for public health, economics, and social welfare. While it has proven effective in reducing smoking rates and generating revenue, its implementation and impact vary significantly across countries. As we move forward, a comprehensive understanding of the historical, economic, and social dimensions of cigarette taxation will be crucial in shaping effective tobacco control strategies.
How do cigarette taxes impact the tobacco industry’s profits?
+Cigarette taxes can significantly impact the tobacco industry’s profits by reducing the demand for their products. Higher taxes lead to increased cigarette prices, making them less affordable for consumers. This, in turn, can result in reduced sales and lower profits for tobacco companies. However, it’s important to note that the industry often adapts to tax increases by adjusting their pricing strategies and exploring alternative revenue streams.
What are the potential health benefits of higher cigarette taxes?
+Higher cigarette taxes are associated with a range of potential health benefits. Firstly, they can discourage smoking initiation among youth and young adults, who are more price-sensitive. Additionally, increased taxes can motivate smokers to quit or reduce their tobacco consumption, leading to improved health outcomes and a reduction in smoking-related diseases. Finally, higher taxes can generate revenue for healthcare initiatives, further promoting public health.
How do cigarette taxes affect employment in the tobacco industry?
+The impact of cigarette taxes on employment in the tobacco industry is a complex issue. While higher taxes may lead to reduced demand for tobacco products, thereby potentially impacting jobs in the industry, it’s important to consider the broader economic context. Some studies suggest that the revenue generated from cigarette taxes can be reinvested in other industries, creating new jobs and promoting economic diversification. Additionally, governments may implement measures to support affected workers through retraining programs or job transition initiatives.



