California Sales Tax Filing
California's sales tax system is a crucial aspect of the state's revenue generation and plays a significant role in funding public services and infrastructure. Understanding the intricacies of sales tax filing in California is essential for businesses operating within the state's borders. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the specifics of California sales tax filing, providing an in-depth analysis of the process, requirements, and implications for businesses.
Understanding California Sales Tax
Sales tax in California is a consumption tax imposed on the sale of goods and certain services. It is a vital revenue stream for the state, contributing to its economic growth and development. The tax is collected by businesses and remitted to the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA), which oversees sales and use tax regulations.
California's sales tax is unique in its structure and rates, offering a complex yet dynamic system. The state sales tax rate is set at 7.25%, but local jurisdictions, including counties, cities, and special districts, can impose additional sales taxes, resulting in varying rates across the state. These local rates can range from 0% to over 10%, creating a diverse landscape of sales tax obligations.
The Importance of Sales Tax Compliance
Sales tax compliance is critical for businesses in California. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines, interest charges, and even legal consequences. Additionally, accurate sales tax filing ensures businesses maintain a positive relationship with the state and local tax authorities, fostering a conducive environment for growth and expansion.
Compliance with sales tax regulations also contributes to a fair and competitive business landscape. By collecting and remitting sales tax, businesses uphold their legal and ethical responsibilities, ensuring a level playing field for all entities operating within the state.
Sales Tax Registration in California

Before commencing sales tax collection and filing, businesses must first register with the CDTFA. The registration process is straightforward and can be completed online through the California Tax Online Services portal. The registration involves providing essential business information, including the company’s legal name, physical address, and contact details.
Determining Registration Requirements
The necessity for sales tax registration in California depends on several factors, including the nature of the business, the location of operations, and the type of products or services offered. Generally, businesses that sell taxable goods or services within the state must register for sales tax, regardless of their physical presence.
Additionally, out-of-state sellers who make sales into California, even without a physical presence, may be required to register for sales tax if they meet certain thresholds. These thresholds are determined by the volume of sales or the number of transactions conducted within the state.
Online Registration Process
The online registration process is designed to be user-friendly and efficient. Businesses can access the California Tax Online Services portal, select the “Register for a New Account” option, and follow the guided steps. The portal will prompt for essential information, including the business’s federal employer identification number (FEIN) or social security number (SSN) for sole proprietors.
Upon successful registration, businesses will receive a unique California Seller's Permit, which serves as proof of their sales tax registration. This permit should be displayed at all places of business and referenced during sales tax filing.
Calculating Sales Tax Liability
Determining sales tax liability is a critical aspect of the filing process. California’s sales tax calculation involves considering the applicable state and local tax rates, as well as any applicable exemptions or discounts.
Understanding State and Local Tax Rates
As mentioned earlier, California’s sales tax rate consists of a state rate of 7.25% and varying local rates imposed by counties, cities, and special districts. These local rates can significantly impact the total sales tax liability. For instance, in the city of Los Angeles, the total sales tax rate is 9.50%, including the state and local components.
Businesses must research and determine the applicable sales tax rates for their specific locations. The CDTFA provides resources, including a Sales Tax Rate Lookup Tool, to assist businesses in identifying the correct rates for their operations.
Exemptions and Discounts
California offers various sales tax exemptions and discounts for specific goods and services. These exemptions can reduce the overall sales tax liability for businesses. For example, certain food items, prescription medications, and clothing under a certain value are exempt from sales tax.
Businesses should familiarize themselves with the state's exemption guidelines and consult with tax professionals to ensure they are claiming all applicable exemptions accurately.
Sales Tax Filing Requirements
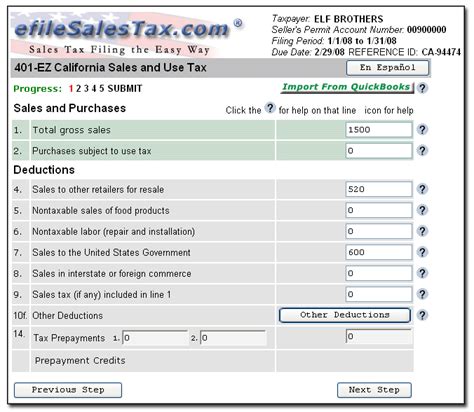
Sales tax filing in California involves submitting periodic returns to the CDTFA, reporting the sales tax collected during a specific period. The filing requirements and deadlines vary based on the business’s sales volume and registration type.
Filing Frequency
California offers businesses flexibility in their sales tax filing frequency. Depending on their sales volume, businesses can choose to file monthly, quarterly, or annually. However, it is essential to note that the filing frequency can impact the timely remittance of sales tax, with more frequent filings generally resulting in more timely payments.
Businesses with higher sales volumes are typically required to file more frequently. For instance, businesses with annual sales exceeding $1 million are mandated to file monthly returns.
Filing Deadlines
Sales tax returns in California are due on specific dates, depending on the filing frequency chosen. Monthly filers must submit their returns by the 20th of the following month, while quarterly filers have deadlines on the 20th of January, April, July, and October. Annual filers have a deadline of the 20th of January each year.
It is crucial for businesses to adhere to these deadlines to avoid late filing penalties. The CDTFA provides a Sales and Use Tax Filing Calendar to assist businesses in staying organized and meeting their filing obligations.
Electronic Filing and Payment
California encourages businesses to utilize electronic filing and payment methods for sales tax returns. The California Tax Online Services portal offers a secure and efficient platform for filing returns and making payments. Electronic filing reduces the risk of errors and provides a convenient, paperless process.
Additionally, the CDTFA offers various payment options, including credit card, debit card, and electronic funds transfer (EFT). Businesses can choose the method that best suits their financial management practices.
Sales Tax Remittance

Remitting sales tax involves transferring the collected tax amounts to the CDTFA. This process is integral to maintaining compliance and ensuring the proper allocation of funds for public services.
Payment Options
As mentioned earlier, California provides a range of payment options for sales tax remittance. Businesses can choose from credit card, debit card, EFT, and traditional check or money order methods. The CDTFA accepts payments through its online portal, ensuring a secure and efficient transaction process.
For businesses with higher sales tax liabilities, the CDTFA recommends utilizing the EFT method, which offers a more streamlined and cost-effective solution.
Penalty and Interest Charges
Failure to remit sales tax on time can result in penalty and interest charges. The CDTFA imposes penalties for late payments, with the penalty amount varying based on the extent of the delay. Additionally, interest accrues on late payments, further increasing the financial burden for non-compliant businesses.
To avoid these charges, businesses should prioritize timely sales tax remittance and maintain accurate records of their sales tax obligations.
Sales Tax Record-Keeping
Maintaining accurate sales tax records is essential for compliance and audit purposes. California requires businesses to retain sales tax records for a minimum of four years, allowing for effective monitoring and potential audits.
Required Records
Sales tax records should include detailed information on sales transactions, including the date, location, and amount of each sale. Additionally, records should indicate the applicable tax rates and any exemptions or discounts applied. These records can be maintained in physical or electronic formats, provided they are easily accessible and searchable.
Businesses should also retain supporting documents, such as invoices, receipts, and purchase orders, to substantiate their sales tax records.
Record Retention Period
California mandates that sales tax records be retained for a minimum of four years from the due date of the corresponding return. This retention period allows the CDTFA to conduct audits and ensure compliance with sales tax regulations.
During an audit, businesses may be required to produce their sales tax records to demonstrate their compliance. Accurate and organized record-keeping is essential to facilitate a smooth audit process.
Sales Tax Audits in California
Sales tax audits are a critical aspect of the CDTFA’s enforcement efforts. These audits are conducted to ensure businesses are accurately calculating and remitting sales tax, contributing to the state’s revenue stream.
Audit Selection Process
The CDTFA employs a risk-based approach to select businesses for sales tax audits. Factors such as sales volume, industry type, and compliance history are considered when determining which businesses to audit. The agency aims to target businesses with a higher likelihood of non-compliance, ensuring efficient use of resources.
Businesses should note that being selected for an audit does not necessarily indicate non-compliance. Audits are a standard part of the tax system, and businesses should cooperate fully with the CDTFA during the audit process.
Audit Procedures
During a sales tax audit, the CDTFA will examine a business’s sales tax records, including returns, payment history, and supporting documentation. The agency may request additional information or conduct onsite visits to verify the accuracy of the records.
Businesses should cooperate with the auditors, providing all necessary documentation and answering any queries promptly. Failure to cooperate can result in penalties and further legal consequences.
Audit Outcomes and Appeals
Upon completion of the audit, the CDTFA will issue a report detailing any adjustments or penalties incurred. If a business disagrees with the audit findings, they have the right to appeal the decision. The appeals process involves submitting a written request to the CDTFA, outlining the reasons for the appeal.
The CDTFA will review the appeal and make a final determination. If the appeal is unsuccessful, businesses may have the option to pursue further legal avenues, but it is recommended to seek professional advice before doing so.
Future Implications and Considerations
California’s sales tax system is dynamic and subject to changes and updates. Businesses should stay informed about any legislative or regulatory changes that may impact their sales tax obligations.
Legislative and Regulatory Changes
The California Legislature and the CDTFA periodically review and amend sales tax regulations. These changes can include alterations to tax rates, exemptions, or filing requirements. Businesses should monitor these changes and adapt their sales tax practices accordingly.
The CDTFA provides resources, including a Sales and Use Tax News section on its website, to keep businesses informed about the latest developments.
Online Sales and Marketplace Facilitator Laws
With the rise of e-commerce, California has implemented laws governing online sales and marketplace facilitators. These laws aim to ensure that sales tax is collected and remitted for online transactions, even when the seller does not have a physical presence in the state.
Businesses engaged in online sales should familiarize themselves with these laws and their obligations. Failure to comply with online sales tax regulations can result in penalties and legal consequences.
Tax Planning and Professional Advice
Navigating California’s sales tax system can be complex, especially for businesses with diverse operations and locations. Engaging the services of tax professionals, such as accountants or tax attorneys, can provide valuable insights and ensure compliance.
Tax professionals can assist with sales tax registration, calculation, and filing, as well as provide guidance on tax planning strategies to optimize the business's financial position.
Conclusion
California sales tax filing is a critical responsibility for businesses operating within the state. By understanding the intricacies of the sales tax system, businesses can ensure compliance, maintain positive relationships with tax authorities, and contribute to the state’s economic growth.
This comprehensive guide has provided an in-depth analysis of California sales tax filing, offering practical insights and guidance. By following the outlined steps and staying informed about sales tax regulations, businesses can effectively manage their sales tax obligations and thrive in California's business landscape.
How often do I need to file sales tax returns in California?
+The frequency of sales tax filing in California depends on your sales volume. Businesses with higher sales volumes are required to file more frequently. Monthly filing is mandatory for businesses with annual sales exceeding $1 million. Quarterly filing is an option for businesses with lower sales volumes, while annual filing is available for the smallest businesses.
What happens if I miss a sales tax filing deadline in California?
+Missing a sales tax filing deadline can result in penalties and interest charges. The CDTFA imposes penalties for late filings, with the amount depending on the extent of the delay. Additionally, interest accrues on the outstanding tax amount. To avoid these charges, it is crucial to prioritize timely filing and payment of sales tax.
Can I register for sales tax online in California?
+Yes, California offers an online registration process through the California Tax Online Services portal. This user-friendly platform allows businesses to register for sales tax, providing a convenient and efficient way to obtain their California Seller’s Permit.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in California?
+Yes, California offers various sales tax exemptions for specific goods and services. These exemptions can reduce your sales tax liability. Examples include exemptions for certain food items, prescription medications, and clothing under a certain value. It is important to consult the CDTFA’s guidelines to ensure you are claiming all applicable exemptions.
How long do I need to keep sales tax records in California?
+California requires businesses to retain sales tax records for a minimum of four years from the due date of the corresponding return. These records should include detailed information on sales transactions, tax rates, and any exemptions applied. Proper record-keeping is essential for compliance and potential audits.