California Payroll Tax

The complexities of payroll taxes are a significant challenge for businesses, especially in a state as diverse and economically vibrant as California. The Golden State, with its diverse workforce and unique tax regulations, presents a complex landscape for employers to navigate. This article aims to demystify the intricacies of California payroll taxes, offering a comprehensive guide to help businesses comply with the state's regulations and efficiently manage their payroll processes.
Understanding California Payroll Tax: A Comprehensive Overview

California’s payroll tax system is a multifaceted regulatory framework that encompasses various taxes and contributions. At its core, payroll taxes in California are designed to fund essential state services, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure development. These taxes are levied on employers based on their payroll and are an essential source of revenue for the state.
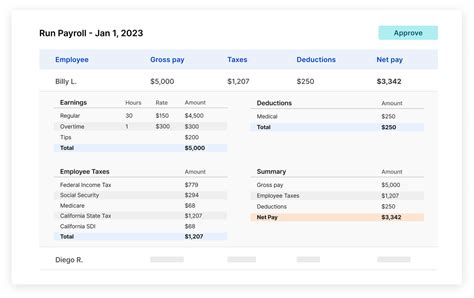
One of the primary components of California's payroll tax is the State Disability Insurance (SDI) tax. SDI provides short-term disability benefits to employees who are unable to work due to non-work-related illnesses or injuries. Employers are required to withhold SDI contributions from their employees' wages and remit them to the state. The current SDI tax rate for 2023 is 1.1% of the first $147,000 of an employee's earnings.
Another critical aspect of California payroll taxes is the State Unemployment Insurance (SUI) tax. SUI is designed to provide financial support to employees who lose their jobs through no fault of their own. Like SDI, SUI taxes are withheld from employees' wages and remitted to the state. The SUI tax rate for 2023 is 1.5% of the first $7,000 of an employee's earnings.
In addition to SDI and SUI, California employers must also navigate the Employment Training Tax (ETT). ETT funds the state's Employment Training Panel, which provides workforce development programs to enhance the skills of California's workforce. The ETT rate is 0.1% of the first $7,000 of an employee's earnings, making it a relatively small but essential component of the payroll tax landscape.
Furthermore, California employers must also consider Federal Unemployment Tax (FUTA), which is a federal tax levied on employers to fund unemployment benefits at the national level. While the FUTA rate is typically 6%, California employers may be eligible for a credit that reduces the effective rate to 0.6%. This credit is subject to certain conditions, such as timely payment of state unemployment taxes.
Registration and Compliance
To comply with California’s payroll tax regulations, employers must register with the Employment Development Department (EDD). The EDD is the state agency responsible for administering payroll taxes, including SDI, SUI, and ETT. Registration involves providing detailed information about the business, its employees, and its payroll operations. This process ensures that the EDD has the necessary data to accurately calculate and collect the appropriate taxes.
Once registered, employers must comply with various reporting and payment requirements. This includes quarterly reporting of wages and taxes using forms such as DE 9 or DE 9C, depending on the size of the business. Late or inaccurate filings can result in penalties, so it's crucial for employers to stay organized and maintain accurate records.
To simplify the process, the EDD offers an online payroll tax filing system called e-Services for Business. This platform allows employers to register, file returns, and make payments electronically, providing a convenient and efficient way to manage their payroll tax obligations.
| Payroll Tax | Rate | Tax Year |
|---|---|---|
| State Disability Insurance (SDI) | 1.1% (on first $147,000 of earnings) | 2023 |
| State Unemployment Insurance (SUI) | 1.5% (on first $7,000 of earnings) | 2023 |
| Employment Training Tax (ETT) | 0.1% (on first $7,000 of earnings) | 2023 |
| Federal Unemployment Tax (FUTA) | Effective rate: 0.6% (credit may apply) | 2023 |

Navigating California’s Unique Payroll Tax Challenges
California’s diverse economy and complex tax regulations present unique challenges for businesses when it comes to payroll taxes. One of the primary challenges is the variety of tax rates applicable to different categories of employees and earnings. For instance, the SDI tax rate varies based on the employee’s earnings, with a maximum tax amount applicable to earnings above a certain threshold.
Another complexity arises from the differing tax rates between various counties and cities within California. Some local jurisdictions impose additional taxes on employers, such as the Los Angeles County Employee Relations Ordinance or the San Francisco Health Service Surcharge. These local taxes can further complicate the payroll tax landscape, requiring employers to carefully consider their specific regional obligations.
Moreover, California's dynamic workforce, characterized by a high rate of job turnover and a diverse range of employment types, presents its own set of challenges. Employers must accurately categorize employees as exempt or non-exempt for overtime purposes, classify independent contractors correctly, and ensure compliance with various employment laws, such as the California Minimum Wage Law and the California Overtime Law.
Employment Classification and Wage Laws
Correctly classifying employees is crucial for payroll tax purposes. Misclassification can lead to significant legal and financial consequences. California law defines an employee as someone who is under the control and direction of an employer in performing services and is not free from the employer’s direction and control. This definition is critical for determining tax obligations and eligibility for various benefits.
California also has strict wage laws, including regulations on minimum wage, overtime pay, and meal and rest breaks. Employers must ensure they are compliant with these laws, as non-compliance can result in costly penalties and legal repercussions. For instance, the state's minimum wage has been increasing gradually and is set to reach $15.50 per hour for employers with 26 or more employees by January 1, 2023.
Furthermore, California's AB 5 legislation, which came into effect in 2020, has significantly impacted the classification of independent contractors. The law establishes a strict ABC test for determining independent contractor status, making it more challenging for businesses to classify workers as contractors rather than employees. This has implications for payroll taxes, as employees are subject to a wider range of taxes and contributions compared to independent contractors.
Best Practices for California Payroll Tax Management
Effective management of California payroll taxes is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance and avoid costly penalties. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of any changes in payroll tax laws and regulations. California's tax landscape is dynamic, and staying informed can help businesses adapt to new requirements.
- Accurate Record-Keeping: Maintain detailed and accurate records of all payroll transactions, including wages, taxes withheld, and contributions made. This ensures compliance and facilitates easy reference during audits.
- Timely Filing: Ensure that all payroll tax returns are filed on time. Late filings can result in penalties and interest charges, which can be avoided with timely compliance.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage payroll software and online tools to streamline the payroll process. These tools can automate tax calculations, ensure compliance, and provide real-time insights into payroll activities.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to identify and correct any errors or discrepancies in payroll tax calculations. This proactive approach can help businesses avoid potential issues and maintain compliance.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consider engaging the services of a payroll tax professional or outsourcing payroll functions to a specialized firm. These experts can provide valuable guidance and ensure that businesses meet their payroll tax obligations accurately and efficiently.
Future Implications and Emerging Trends in California Payroll Taxes
California’s payroll tax landscape is constantly evolving, driven by changing economic conditions, legislative updates, and emerging trends. One of the key future implications is the continued emphasis on compliance. As the state strives to maintain a robust revenue stream, it is likely to increase its focus on payroll tax compliance, potentially leading to more stringent enforcement measures and increased audits.
Additionally, the digitization of payroll processes is expected to play a significant role in the future of California payroll taxes. The state is likely to encourage and even mandate the use of digital platforms and technologies for payroll management and tax compliance. This shift towards digital payroll could enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and improve overall compliance.
Furthermore, the ongoing debate around tax fairness is likely to influence future payroll tax policies in California. As the state seeks to balance its budget and provide essential services, it may explore options to increase tax revenue from higher-income earners or larger businesses. This could potentially lead to changes in tax rates or the introduction of new taxes targeted at specific industries or high-earning individuals.
Potential Impact of Legislative Changes
California’s legislature is constantly evaluating and proposing new laws and regulations, which can have a significant impact on payroll taxes. For instance, recent discussions around the California Fair Pay to Play Act have raised questions about how employee compensation related to brand endorsements and sponsorships might be treated for tax purposes. If such laws are enacted, they could lead to new reporting requirements and tax obligations for employers.
Additionally, the state's ongoing efforts to address income inequality could result in changes to payroll tax structures. Potential measures include increasing tax rates for higher-income earners or introducing new taxes on specific types of income, such as capital gains or stock options. These changes could significantly impact payroll tax calculations and compliance requirements.
Finally, California's commitment to environmental sustainability could lead to the introduction of green taxes or carbon pricing mechanisms. While these taxes may not directly impact payroll, they could affect business operations and, consequently, payroll costs. For example, a carbon tax could increase the cost of energy, which could be passed on to employees in the form of reduced benefits or increased payroll deductions.
Conclusion: Navigating California’s Payroll Tax Landscape

California’s payroll tax system is a complex but critical component of the state’s economic infrastructure. For businesses operating in the Golden State, understanding and effectively managing payroll taxes is essential to ensure compliance and maintain a healthy relationship with the state’s tax authorities.
By staying informed about the latest regulations, utilizing technology to streamline processes, and seeking professional guidance when needed, businesses can navigate California's payroll tax landscape with confidence. As the state continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic conditions, staying ahead of payroll tax requirements will remain a key priority for businesses seeking long-term success in California.
What is the difference between SDI and SUI in California payroll taxes?
+SDI (State Disability Insurance) provides short-term disability benefits to employees, while SUI (State Unemployment Insurance) provides financial support to employees who lose their jobs through no fault of their own. SDI is funded by contributions from employers and employees, while SUI is primarily funded by employers.
How often do California employers need to file payroll tax returns?
+California employers typically file payroll tax returns on a quarterly basis, using forms such as DE 9 or DE 9C. However, certain employers with higher payroll tax obligations may be required to file monthly.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with California payroll tax regulations?
+Non-compliance with California payroll tax regulations can result in penalties, interest charges, and even legal action. The state’s Employment Development Department (EDD) has the authority to assess penalties for late filings, underreporting of wages, or failure to withhold and remit taxes.
How can businesses stay updated on changes to California payroll tax laws and regulations?
+Businesses can stay informed about changes to California payroll tax laws and regulations by regularly checking the official website of the Employment Development Department (EDD) and subscribing to their newsletters or alerts. Additionally, engaging the services of a payroll tax professional or consulting firm can provide valuable insights and updates.
What resources are available to help businesses manage California payroll taxes effectively?
+The Employment Development Department (EDD) provides a wealth of resources on its website, including guides, tutorials, and frequently asked questions. Additionally, businesses can consider using payroll software or outsourcing payroll functions to specialized firms to ensure accurate and compliant payroll tax management.