Auto Sales Tax Calculator
Calculating auto sales tax is an essential aspect of purchasing a vehicle, as it directly impacts the overall cost and financial planning involved. While sales tax rates and regulations can vary significantly across different regions, understanding the process and potential costs is crucial for informed decision-making. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of auto sales tax calculations, exploring real-world examples and providing valuable insights to assist buyers in navigating this critical financial consideration.
Understanding Auto Sales Tax Fundamentals
Auto sales tax is a levy imposed on the purchase of motor vehicles, typically by state or local governments. It is calculated as a percentage of the vehicle’s sale price and is an additional cost on top of the base price, dealer fees, and other applicable charges. The purpose of this tax is to generate revenue for government entities, which can be used for various public services and infrastructure projects.
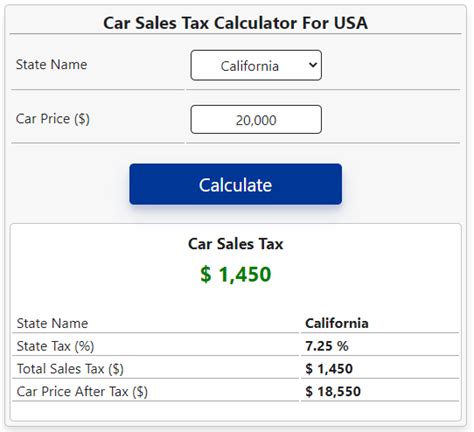
The sales tax rate for vehicles can vary significantly, ranging from single-digit percentages in some states to over 10% in others. This variation is primarily influenced by the specific tax policies and financial needs of each jurisdiction. For instance, in California, the state sales tax rate is set at 7.25%, but local jurisdictions can add their own taxes, resulting in a cumulative rate that can exceed 10% in certain areas. On the other hand, states like Delaware and Montana do not impose a statewide sales tax on vehicles, making them attractive destinations for car buyers seeking to minimize tax burdens.
Factors Influencing Sales Tax Calculation
The calculation of auto sales tax involves several key factors that can impact the final amount. Firstly, the purchase price of the vehicle is a crucial determinant. Higher-priced vehicles will generally incur higher sales taxes. Additionally, some jurisdictions may offer sales tax exemptions or reduced rates for specific vehicle types, such as electric or hybrid cars, which can significantly reduce the tax burden for environmentally conscious buyers.
Furthermore, certain states implement a vehicle registration fee that is tied to the sales tax calculation. This fee, often based on the vehicle's value, is collected by the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) and used to maintain and improve transportation infrastructure. For example, in New York, the registration fee is calculated as a percentage of the vehicle's suggested retail price (SRP), with rates varying based on the vehicle's weight and usage classification.
| State | Sales Tax Rate (%) | Vehicle Registration Fee |
|---|---|---|
| California | 7.25% (state) + up to 2% (local) | Varies based on vehicle type and weight |
| Texas | 6.25% (state) + up to 2% (local) | 6.25% of the vehicle's sales price |
| Florida | 6% | Varies based on county of registration |

Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Auto Sales Tax

Calculating auto sales tax is a straightforward process once you have the necessary information. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you compute the sales tax on your vehicle purchase:
Step 1: Determine the Purchase Price
Start by identifying the actual purchase price of the vehicle. This should include the base price, any dealer-installed options or add-ons, and applicable fees, but exclude taxes and registration costs. For instance, if you’re purchasing a 2023 Toyota Camry with a base price of 25,000 and add 2,000 worth of dealer-installed accessories, your total purchase price would be $27,000.
Step 2: Identify the Applicable Sales Tax Rate
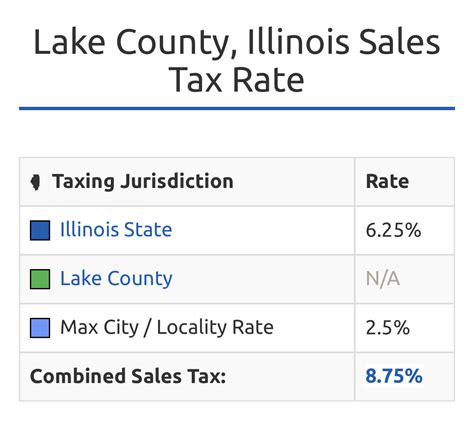
Research and identify the sales tax rate for your specific jurisdiction. This information is typically available on the website of your state’s Department of Revenue or Taxation. For example, in Illinois, the statewide sales tax rate is 6.25%, but local taxes can add up to an additional 3.75%, resulting in a combined rate of up to 10%.
Step 3: Calculate the Sales Tax
Multiply the purchase price by the applicable sales tax rate to determine the sales tax amount. Using our previous example, if the total purchase price of the Toyota Camry is $27,000 and the combined sales tax rate in your jurisdiction is 10%, the sales tax calculation would be as follows:
Sales Tax = Purchase Price * Sales Tax Rate
Sales Tax = $27,000 * 0.10 = $2,700
So, in this case, the sales tax on the Toyota Camry purchase would amount to $2,700.
Step 4: Factor in Additional Fees and Costs
Remember that sales tax is just one component of the overall costs associated with purchasing a vehicle. You’ll also need to consider other fees and expenses, such as:
- Title and Registration Fees: These fees vary by state and are typically paid to the DMV to officially register your vehicle.
- Document Fees: Dealers often charge a document fee to process the necessary paperwork for the sale.
- Destination Fees: Manufacturers may charge a destination or delivery fee to cover the cost of transporting the vehicle from the factory to the dealership.
- Insurance Costs: Don't forget to factor in the cost of insuring your new vehicle.
Strategies for Minimizing Auto Sales Tax
While sales tax is a necessary component of vehicle purchases, there are strategies you can employ to potentially minimize the tax burden. Here are some tips to consider:
Explore Tax-Free States
Certain states, like Alaska, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon, do not impose a sales tax on vehicles. If you live near one of these states, purchasing your vehicle there could result in significant savings. However, keep in mind that you may need to pay use tax when registering the vehicle in your home state.
Utilize Tax Incentives
Many states offer tax incentives or rebates for purchasing certain types of vehicles, such as electric or hybrid cars. These incentives can significantly reduce the sales tax burden. For instance, California provides an EV rebate of up to $7,000 for the purchase of a new electric vehicle.
Negotiate the Price
While sales tax is based on the purchase price, negotiating a lower price can indirectly reduce the sales tax amount. Aim to secure a competitive deal on the vehicle’s price to minimize the overall cost, including sales tax.
Timing Your Purchase
Some states offer tax holidays or reduced sales tax rates during specific periods, often around major holidays like Independence Day or Labor Day. Planning your purchase during these periods can result in substantial savings. Additionally, consider purchasing a vehicle at the end of the model year, as dealers may offer incentives to clear out inventory.
Real-World Examples: Auto Sales Tax Calculations
To further illustrate the auto sales tax calculation process, let’s explore some real-world examples. These examples will help you understand how sales tax is applied in different scenarios and jurisdictions.
Example 1: Vehicle Purchase in New York
Suppose you’re purchasing a 2023 Ford Mustang in New York City. The base price of the vehicle is 35,000, and you've added 3,000 worth of dealer-installed accessories. The combined sales tax rate in New York City is 8.875%, which includes the state sales tax of 4% and local taxes of up to 4.875%.
To calculate the sales tax on this purchase, you'd perform the following calculation:
Sales Tax = ($35,000 + $3,000) * 0.08875 = $3,416.25
So, the sales tax on this Ford Mustang purchase in New York City would be $3,416.25.
Example 2: Electric Vehicle Purchase in California
Consider a scenario where you’re buying a 2023 Tesla Model 3 in Los Angeles, California. The base price of the vehicle is 45,000, and you're eligible for the <strong>California Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP)</strong>, which provides a rebate of up to 7,000 for electric vehicle purchases. The combined sales tax rate in Los Angeles is 10%, including the state sales tax of 7.25% and local taxes of up to 2.75%.
First, calculate the sales tax without considering the rebate:
Sales Tax = $45,000 * 0.10 = $4,500
However, with the CVRP rebate, you'd subtract the rebate amount from the purchase price before calculating the sales tax:
Adjusted Purchase Price = $45,000 - $7,000 = $38,000
Sales Tax = $38,000 * 0.10 = $3,800
So, the sales tax on this Tesla Model 3 purchase in Los Angeles would be $3,800, taking into account the CVRP rebate.
Future Trends and Implications
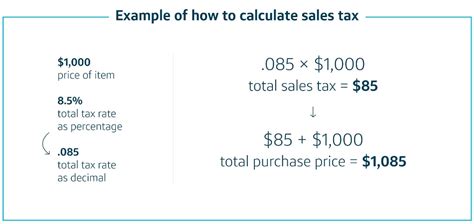
The landscape of auto sales tax is continually evolving, influenced by economic, political, and technological factors. Here are some key trends and implications to consider for the future:
Increasing Focus on Electric Vehicles (EVs)
As the automotive industry shifts towards electric vehicles, many states are offering tax incentives and rebates to encourage EV adoption. These incentives are expected to continue and may even expand, making EVs a more financially attractive option for consumers.
Online Sales and Remote Transactions
With the rise of e-commerce, more vehicle purchases are being made online or through remote transactions. This trend presents challenges for states in terms of tax collection and enforcement, particularly when buyers and sellers are located in different jurisdictions. States may need to adapt their tax policies to accommodate these changing purchase patterns.
Revenue Needs and Budgetary Considerations
Sales tax revenue is a significant source of funding for state and local governments, and budgetary considerations can impact tax rates and policies. In times of economic hardship or fiscal constraints, governments may increase sales tax rates or introduce new taxes to generate additional revenue. Conversely, during periods of economic prosperity, tax rates may be reduced or incentives introduced to stimulate consumer spending.
Technological Advancements and Automation
Advancements in technology and automation are transforming the automotive industry, and this trend is likely to continue. Self-driving cars, electric vehicles, and connected car technologies are already influencing the industry, and their widespread adoption could have implications for sales tax collection and enforcement. Governments will need to adapt their tax policies and enforcement mechanisms to keep pace with these technological advancements.
Conclusion
Understanding auto sales tax is a crucial aspect of the vehicle purchasing process. By familiarizing yourself with the fundamentals, calculation methods, and strategies for minimizing tax burdens, you can make more informed decisions and potentially save significant amounts of money. Remember to research the specific tax policies and incentives in your jurisdiction, as well as stay informed about evolving trends and implications that could impact your financial planning.
What is the average auto sales tax rate in the United States?
+
The average auto sales tax rate in the U.S. varies significantly by state, ranging from 0% in states like Alaska and Delaware to over 10% in states like California and New York (including local taxes). It’s essential to research the specific sales tax rate in your state and local jurisdiction to understand the exact tax burden.
Are there any states that do not impose a sales tax on vehicles?
+
Yes, there are several states that do not impose a statewide sales tax on vehicles, including Alaska, Delaware, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon. However, it’s important to note that these states may still collect other fees or taxes related to vehicle registration and ownership.
Can I negotiate the sales tax on my vehicle purchase?
+
No, the sales tax rate is set by the government and cannot be negotiated with the dealership. However, you can negotiate the purchase price of the vehicle, which will indirectly impact the sales tax amount. A lower purchase price can lead to reduced sales tax, so it’s worth aiming for a competitive deal.
Are there any tax incentives or rebates available for purchasing specific types of vehicles?
+
Yes, many states offer tax incentives or rebates for purchasing electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid cars, or other environmentally friendly vehicles. These incentives can significantly reduce the sales tax burden. It’s advisable to research the specific incentives available in your state to take advantage of these opportunities.
How often do sales tax rates change, and how can I stay updated on them?
+
Sales tax rates can change periodically, often annually or biennially, as determined by state and local governments. To stay updated on sales tax rates and any changes, you can regularly check the websites of your state’s Department of Revenue or Taxation. Additionally, many online resources and tax calculators provide up-to-date information on sales tax rates for various jurisdictions.



