Arkansas State Tax

Arkansas, the Natural State, is renowned for its diverse landscapes, vibrant culture, and thriving industries. As a resident or business owner in Arkansas, understanding the state's tax landscape is crucial for financial planning and compliance. The Arkansas tax system, while comprehensive, offers a range of benefits and considerations that impact individuals and businesses alike. This article delves into the intricacies of Arkansas State Tax, providing an expert-level guide to help navigate this complex yet essential aspect of financial management.
Unraveling the Arkansas Tax System
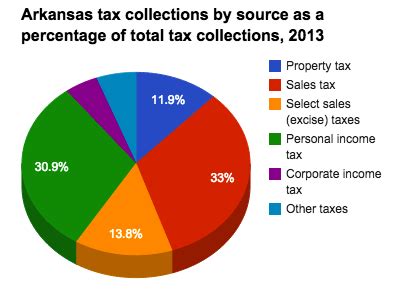
Arkansas employs a progressive income tax system, meaning the tax rate increases as your income rises. This system ensures fairness and contributes to the state’s revenue, which is essential for funding public services and infrastructure. The state also levies taxes on various goods and services, known as sales and use taxes, which are a significant source of revenue for local governments and the state.
Income Tax: A Progressive Approach
Arkansas’s income tax system is designed to be progressive, with tax rates ranging from 1.0% to 6.5%. The tax brackets are structured to accommodate various income levels, ensuring that higher-income earners contribute a larger proportion of their income as taxes. This approach aims to maintain fairness and support the state’s economic growth.
For the 2024 tax year, Arkansas has set the following income tax rates:
| Tax Rate | Income Range |
|---|---|
| 1.0% | Up to 2,100</td> </tr> <tr> <td>2.5%</td> <td>2,101 - 3,600</td> </tr> <tr> <td>3.0%</td> <td>3,601 - 5,500</td> </tr> <tr> <td>4.0%</td> <td>5,501 - 10,000</td> </tr> <tr> <td>5.0%</td> <td>10,001 - 25,000</td> </tr> <tr> <td>5.9%</td> <td>25,001 - 75,000</td> </tr> <tr> <td>6.5%</td> <td>Over 75,000 |
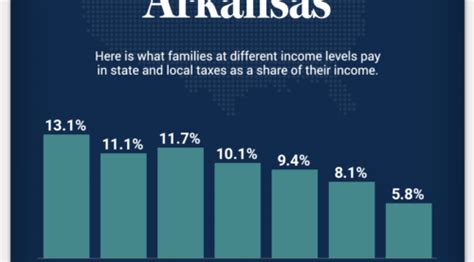
These rates apply to both individuals and married couples filing jointly. However, for married individuals filing separately, the tax rates are slightly different.
Sales and Use Taxes: A Dual Approach
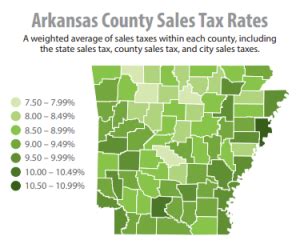
Arkansas has a state sales tax rate of 6.5%, which is applied to most tangible personal property and certain services. However, it’s important to note that local governments can also impose additional sales taxes, leading to varying tax rates across the state.
For instance, in the city of Little Rock, the total sales tax rate is 9.5%, which includes a 3% city sales tax. Similarly, the city of Fayetteville has a total sales tax rate of 10.25%, with an additional 3.75% city tax. These variations are important for businesses to consider when planning their pricing strategies and for consumers when budgeting for purchases.
Arkansas Tax Incentives and Credits
Arkansas offers various tax incentives and credits to promote economic development and support specific industries. These incentives are designed to attract businesses, create jobs, and stimulate the state’s economy.
- Economic Development Incentives: The state provides tax credits and abatements to encourage business investment and job creation. These incentives are often tailored to specific industries, such as manufacturing, technology, and renewable energy.
- Historic Preservation Tax Credits: Arkansas offers tax credits for the rehabilitation of historic buildings. This incentive aims to preserve the state’s architectural heritage and promote economic development in historic districts.
- Research and Development Tax Credits: Businesses engaged in research and development activities can benefit from tax credits, encouraging innovation and technological advancements.
Tax Filing and Compliance
Ensuring compliance with Arkansas tax laws is essential to avoid penalties and maintain a positive relationship with the state’s revenue agencies. Here’s an overview of the tax filing process and compliance requirements.
Income Tax Filing
Arkansas residents and businesses with income sourced from within the state are required to file income tax returns annually. The filing deadline is typically April 15th, in line with the federal tax deadline. However, it’s important to note that for those who are unable to meet the deadline, the state offers a six-month extension until October 15th.
The Arkansas Department of Finance and Administration (DFA) provides various resources to assist taxpayers in filing their returns accurately and efficiently. This includes online filing options, paper forms, and guidance on calculating taxes and claiming deductions and credits.
Sales and Use Tax Compliance
For businesses engaged in selling goods or services in Arkansas, compliance with sales and use tax regulations is crucial. This includes registering with the DFA, collecting the appropriate tax rates, and filing returns regularly. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties and interest charges.
The DFA offers a range of resources to help businesses understand their sales tax obligations, including guidance on taxability of goods and services, exemption certificates, and tax rate lookup tools.
Tax Audits and Appeals
Arkansas’s revenue agencies conduct audits to ensure compliance with tax laws. If a taxpayer is selected for an audit, it’s important to cooperate fully and provide the necessary documentation. The DFA provides guidance on the audit process and taxpayer rights during an audit.
In the event of a dispute with the DFA, taxpayers have the right to appeal. The appeals process involves several stages, including an informal conference, a formal hearing, and, if necessary, litigation.
Arkansas Tax Outlook and Future Implications
The Arkansas tax landscape is dynamic, with ongoing discussions and legislative changes aimed at improving the state’s fiscal health and competitiveness. Understanding these developments is crucial for long-term financial planning.
Legislative Updates and Proposed Changes
The Arkansas legislature regularly reviews and amends tax laws to adapt to changing economic conditions and priorities. Recent legislative updates include modifications to tax rates, deductions, and credits to support specific industries and promote economic growth.
For instance, in 2023, the legislature approved a bill to extend the state’s sales tax exemption for gold, silver, and other precious metals until 2025. This exemption is designed to stimulate investment in precious metals and support the state’s economy.
Economic Impact and Forecasts
Arkansas’s tax system plays a crucial role in the state’s economic growth and development. The revenue generated through taxes funds essential public services, infrastructure projects, and economic development initiatives. As such, the state’s economic health is closely tied to its tax policies and compliance.
According to a recent report by the Arkansas Economic Development Commission, the state’s diverse economy, which includes sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, and technology, is expected to experience steady growth over the next decade. This growth is forecast to drive an increase in tax revenues, which will be essential for funding public services and infrastructure projects.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries within Arkansas face unique tax considerations and opportunities. For instance, the state’s agriculture sector benefits from tax incentives aimed at supporting the industry’s growth and sustainability. Similarly, the technology sector enjoys incentives to encourage innovation and job creation.
Understanding these industry-specific tax considerations is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their financial strategies and maximize their potential in Arkansas.
Conclusion: Navigating Arkansas’s Tax Landscape
Understanding and navigating Arkansas’s tax system is a complex but crucial aspect of financial management for both individuals and businesses. From progressive income tax rates to varied sales and use taxes, Arkansas’s tax landscape is designed to support the state’s economic growth and fund essential public services.
By staying informed about tax laws, incentives, and compliance requirements, taxpayers can make informed financial decisions and contribute to the state’s economic vitality. Arkansas’s tax system, while comprehensive, offers a range of opportunities for individuals and businesses to thrive, provided they understand and leverage the system effectively.
What are the key differences between Arkansas’s income tax rates for individuals and married couples filing separately?
+Arkansas’s income tax rates for married couples filing separately are slightly different compared to those for individuals or married couples filing jointly. The tax rates for married couples filing separately are generally higher, especially in the higher income brackets. This is because the tax brackets are structured based on the assumption that married couples filing separately will have higher incomes due to filing individually.
How often are Arkansas’s tax laws reviewed and updated?
+Arkansas’s tax laws are regularly reviewed and updated by the state legislature. This process typically occurs annually, with the legislature considering modifications to tax rates, deductions, credits, and other aspects of the tax code to align with changing economic conditions and priorities. These updates ensure that the tax system remains fair, competitive, and supportive of the state’s economic growth.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with Arkansas’s tax laws for businesses?
+Non-compliance with Arkansas’s tax laws for businesses can result in severe consequences. These may include penalties, interest charges, and even criminal charges in cases of tax fraud. Businesses that fail to comply with sales tax regulations, for instance, may face penalties for underreporting or failing to collect the appropriate tax rates. It’s crucial for businesses to understand their tax obligations and seek professional advice if needed to ensure compliance.



