Arizona Tax Percentage

When discussing Arizona's tax system, it's essential to delve into the various taxes imposed by the state and understand how they affect individuals and businesses. Arizona's tax structure consists of several components, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and various other taxes and fees. In this article, we will explore the Arizona tax percentage in detail, providing an in-depth analysis of each tax type and its impact on the state's economy and residents.
Income Tax: A Progressive Approach

Arizona employs a progressive income tax system, meaning that higher income earners are taxed at a higher rate compared to those with lower incomes. This approach aims to ensure a fair distribution of tax burdens and promote social equity. The state’s income tax rates are divided into five tax brackets, each with its own applicable tax percentage.
- Tax Bracket 1: For taxable income up to 10,400, the tax rate is 2.59%.</li> <li><strong>Tax Bracket 2:</strong> Income between 10,400.01 and 25,900 is taxed at 3.34%.</li> <li><strong>Tax Bracket 3:</strong> Taxable income ranging from 25,900.01 to 51,800 is subject to a rate of 4.17%.</li> <li><strong>Tax Bracket 4:</strong> Income between 51,800.01 and 155,400 is taxed at 4.50%.</li> <li><strong>Tax Bracket 5:</strong> For the highest income bracket, income exceeding 155,400 is taxed at a rate of 4.50%.
These tax brackets are applicable to individuals, married couples filing jointly, and qualifying widow(er)s. However, for married couples filing separately and heads of household, the income thresholds are different, resulting in varying tax percentages.
Income Tax for Businesses
Arizona also imposes income taxes on businesses, including corporations and partnerships. The tax rate for corporations is a flat rate of 4.9%, while partnerships and limited liability companies (LLCs) are taxed at the individual income tax rates, based on the income distribution to partners or members.
It’s worth noting that Arizona offers various tax credits and incentives to attract businesses and promote economic growth. These incentives can significantly impact the effective tax rate for businesses operating in the state.
Sales Tax: A State and Local Affair

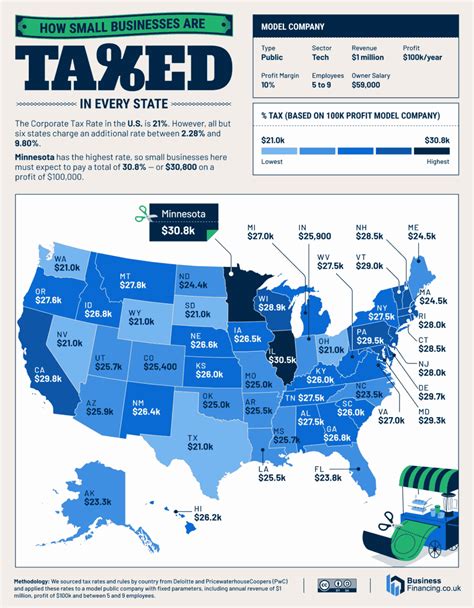
Arizona’s sales tax is a combined state and local tax, with the state imposing a base sales tax rate and allowing local jurisdictions to levy additional taxes. The state sales tax rate in Arizona is 5.6%, which is applicable to the sale of most goods and some services. However, it’s important to consider that local sales taxes can vary significantly across different counties and cities.
For example, in the city of Phoenix, the total sales tax rate is 8.1%, which includes the state sales tax of 5.6% and a local tax rate of 2.5%. Similarly, Tucson has a total sales tax rate of 7.45%, with a local tax rate of 1.85% on top of the state sales tax.
| City | State Sales Tax | Local Sales Tax | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phoenix | 5.6% | 2.5% | 8.1% |
| Tucson | 5.6% | 1.85% | 7.45% |
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
Arizona offers some sales tax exemptions and special considerations. For instance, certain food items, prescription drugs, and some medical devices are exempt from sales tax. Additionally, there are specific tax rates for lodging, restaurant meals, and rental car services.
Property Tax: Assessed Values and Rates
Property taxes in Arizona are levied on real estate and personal property. The tax rate is determined by the assessed value of the property and the tax rate set by the local jurisdiction. The assessed value is typically based on the property’s full cash value, which is then multiplied by an assessment ratio to arrive at the assessed value for tax purposes.
The assessment ratio can vary depending on the property type and location. For residential properties, the assessment ratio is typically 10%, while for commercial and industrial properties, it can range from 16% to 25%. This means that a residential property with a full cash value of 200,000 would have an assessed value of 20,000 for tax purposes.
The tax rate for property taxes in Arizona is set by local governments, such as counties and municipalities. These rates can vary significantly across different areas. As a result, the effective property tax rate can differ greatly depending on the specific location of the property.
Property Tax Incentives and Exemptions
Arizona provides various property tax incentives and exemptions to encourage economic development and support certain sectors. For instance, there are exemptions for certain agricultural lands, military personnel, and disabled veterans. Additionally, the state offers property tax relief programs for elderly and disabled residents.
Other Taxes and Fees
Arizona imposes several other taxes and fees to generate revenue and support specific programs. These include:
- Transaction Privilege Tax (TPT): A tax on the privilege of doing business in Arizona, similar to a sales tax, with rates varying by industry and location.
- Use Tax: A tax on the use, storage, or consumption of goods purchased outside of Arizona but brought into the state.
- Motor Vehicle Taxes: Taxes on the registration and ownership of vehicles, including license and title fees.
- Excise Taxes: Taxes on specific goods and services, such as tobacco products, alcohol, and fuel.
- Severance Taxes: Taxes on the extraction of natural resources, such as oil and gas.
Tax Incentives and Credits
Arizona offers a range of tax incentives and credits to attract businesses and promote specific industries. These incentives can include tax credits for research and development, job creation, and investment in renewable energy. Additionally, the state provides tax breaks for film and television production, encouraging the growth of the entertainment industry.
Impact of Arizona’s Tax System

Arizona’s tax system plays a crucial role in shaping the state’s economy and its residents’ financial well-being. The progressive income tax structure ensures that higher-income earners contribute a larger share, promoting fairness and social welfare. The state’s tax incentives and credits also encourage economic growth and attract businesses, contributing to job creation and a thriving business environment.
However, the variation in local sales and property tax rates can lead to disparities across different regions. While some areas may benefit from lower tax rates, others may face higher tax burdens, impacting their cost of living and business competitiveness. It is essential for individuals and businesses to understand the specific tax rates and incentives applicable to their location to make informed financial decisions.
Conclusion: Navigating Arizona’s Tax Landscape
Arizona’s tax system is a complex interplay of various taxes and incentives, each designed to serve specific purposes. From the progressive income tax to the state and local sales tax, property tax, and other taxes and fees, Arizona’s tax landscape is diverse and dynamic. Understanding these taxes and their impact is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within the state.
As the state continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic conditions, it is essential to stay informed about tax policy updates and their potential implications. By staying engaged and knowledgeable about Arizona’s tax system, residents and businesses can make informed decisions, optimize their tax obligations, and contribute to the state’s economic prosperity.
What is the average income tax rate in Arizona for individuals?
+The average income tax rate for individuals in Arizona varies depending on their taxable income. It ranges from 2.59% for the lowest income bracket to 4.50% for the highest income bracket.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Arizona?
+Yes, Arizona has designated sales tax holidays for specific items, such as back-to-school supplies and energy-efficient appliances. These holidays provide an opportunity for consumers to save on sales tax during designated periods.
How often do property tax rates change in Arizona?
+Property tax rates in Arizona can change annually, as they are determined by local jurisdictions. It is advisable to stay updated with your local government’s tax rate changes to understand the impact on your property tax obligations.
What are some common tax incentives for businesses in Arizona?
+Arizona offers various tax incentives for businesses, including tax credits for research and development, job creation, and investment in renewable energy. Additionally, the state provides tax breaks for film and television production, encouraging the growth of the entertainment industry.