Are Medical Premiums Tax Deductible
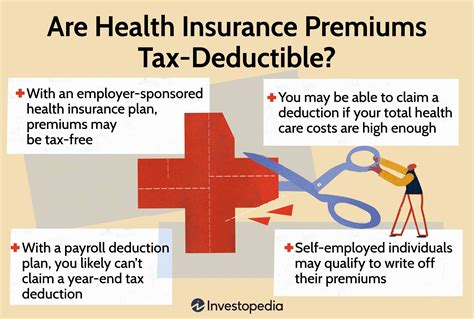
In the realm of personal finance and healthcare, understanding the tax implications of medical premiums is crucial. Many individuals and families grapple with the question: Are medical premiums tax deductible? In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of medical premium tax deductibility, exploring the regulations, eligibility criteria, and potential benefits. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of whether and how these expenses can be claimed on your tax return, empowering you to optimize your financial strategies.
The Tax Treatment of Medical Premiums

Medical premiums, often associated with health insurance plans, play a vital role in ensuring access to healthcare services. However, their tax treatment can be complex and varies depending on several factors. Let’s unravel the complexities and provide clarity on this important financial aspect.
Understanding Medical Premium Deductibility
Medical premiums are generally considered personal expenses, and as such, they are typically not tax-deductible. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers these costs as a private financial responsibility, similar to other daily expenses like groceries or utility bills. However, there are specific circumstances and conditions under which medical premiums can become eligible for tax deductions, offering a financial advantage to certain taxpayers.
To understand the deductibility of medical premiums, we must first examine the concept of tax deductions and how they apply to healthcare-related expenses. Tax deductions are reductions in taxable income, which can result in a lower tax liability. By claiming eligible deductions, individuals can effectively reduce the amount of income subject to taxation, potentially leading to significant savings.
Eligibility Criteria for Medical Premium Deductions
The deductibility of medical premiums is contingent upon meeting specific eligibility criteria set forth by the IRS. Here are the key factors that determine whether you can claim a tax deduction for your medical premiums:
- Tax Filing Status: Your tax filing status plays a crucial role. Generally, individuals who file as single, married filing jointly, or head of household may be eligible for medical premium deductions. However, it's essential to consult the latest tax guidelines for any updates or specific requirements.
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): The amount of your adjusted gross income is a critical factor. Medical premium deductions are subject to income limitations. If your AGI exceeds a certain threshold, you may not be able to claim the deduction. This threshold varies annually and is determined by the IRS based on inflation and other economic factors.
- Itemized Deductions: To claim a medical premium deduction, you must itemize your deductions on Schedule A of your tax return. This means you cannot claim the standard deduction and must instead list each eligible expense individually. Itemizing deductions can be advantageous if your total eligible expenses exceed the standard deduction amount.
How to Claim Medical Premium Deductions
If you meet the eligibility criteria and have qualified medical expenses, including premiums, you can claim a deduction on your tax return. Here’s a step-by-step guide to claiming medical premium deductions:
- Gather Documentation: Collect all relevant documents, including insurance policies, premium payment receipts, and any other supporting materials for your medical expenses. Ensure that these records are accurate and up-to-date.
- Calculate Your Deduction: Determine the total amount of qualified medical expenses, including premiums, that you incurred during the tax year. Remember to exclude any amounts reimbursed by insurance or other sources.
- Complete Schedule A: On Schedule A, Itemized Deductions, report your qualified medical expenses, including premiums, in the appropriate section. Ensure that you understand the specific guidelines for reporting these expenses accurately.
- File Your Tax Return: Submit your tax return, including Schedule A, by the due date. Be sure to review your return carefully and ensure that all information is accurate and complete.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of medical premium deductions, let’s examine a few real-world scenarios and their tax implications:
| Scenario | Annual Premium | Tax Filing Status | AGI | Eligible Deduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| John and Jane Smith | $12,000 | Married Filing Jointly | $75,000 | $6,000 |
| Emily Johnson | $8,500 | Single | $50,000 | $4,250 |
| Michael and Sarah Davis | $15,000 | Head of Household | $90,000 | $0 |

In these examples, the Smiths and Emily Johnson would be eligible for partial deductions based on their filing status and AGI. However, the Davises would not be able to claim a deduction due to their higher AGI exceeding the income limitation threshold.
Future Implications and Strategies

Understanding the tax treatment of medical premiums empowers individuals to make informed financial decisions. By strategically planning your healthcare expenses and tax strategies, you can potentially maximize your deductions and minimize your tax liability. Here are some key takeaways and future considerations:
- Stay Informed: Tax laws and regulations can change annually. Stay updated with the latest guidelines to ensure you are aware of any modifications to eligibility criteria or income thresholds.
- Consider Itemizing: If you have significant medical expenses, including premiums, consider itemizing your deductions. This strategy may provide a greater tax benefit compared to claiming the standard deduction.
- Explore Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): HSAs offer a tax-advantaged way to save for medical expenses. Contributions to HSAs are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. Consider opening an HSA if eligible.
- Review Insurance Options: Evaluate your health insurance options regularly. Different plans have varying premium costs and coverage levels. Choosing a plan that aligns with your healthcare needs and financial situation can help optimize your tax deductions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I deduct medical premiums for myself and my dependents?
+Yes, you can deduct qualified medical expenses, including premiums, for yourself, your spouse, and your dependents. Ensure that you meet the eligibility criteria and itemize your deductions.
Are there any limitations on the amount of medical premium deductions I can claim?
+Yes, there are income limitations. The deductibility of medical premiums is subject to an AGI threshold. If your AGI exceeds this threshold, you may not be able to claim the deduction.
Can I deduct medical premiums if I pay them with my pre-tax income?
+No, if you pay your medical premiums with pre-tax income through your employer’s cafeteria plan or a flexible spending account (FSA), those premiums are not eligible for deduction. However, other qualified medical expenses paid with pre-tax income may still be deductible.
Are there any alternatives to deducting medical premiums if I don’t meet the eligibility criteria?
+Yes, you may consider opening a Health Savings Account (HSA) if eligible. HSAs offer tax-deductible contributions and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses, providing a tax-advantaged way to save for healthcare costs.
Can I deduct medical premiums for alternative medicine treatments?
+The deductibility of alternative medicine treatments depends on their qualification as medical expenses. Consult a tax professional or refer to IRS guidelines to determine if specific treatments are eligible for deduction.
By navigating the complexities of medical premium tax deductibility, you can make informed choices about your healthcare and financial strategies. Stay informed, consult experts when needed, and optimize your tax savings to achieve financial wellness.



