Alabama State Tax Rate
When it comes to state taxes, Alabama operates under a relatively straightforward system with a flat income tax rate. However, the state also imposes various other taxes, including sales tax, property tax, and corporate income tax. Understanding the Alabama state tax rate is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within the state, as it impacts their financial planning and obligations.
Alabama’s Flat Income Tax Rate

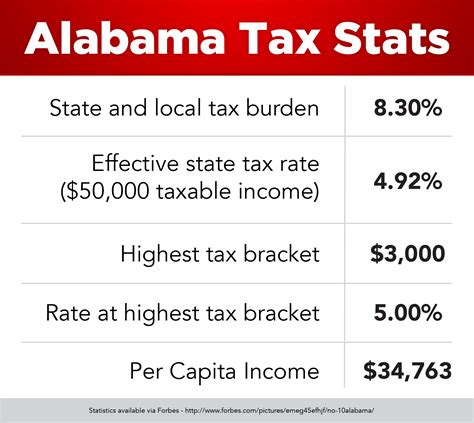
Alabama’s income tax system is characterized by a flat tax rate, meaning that all taxable income is taxed at the same rate, regardless of the income level. This approach simplifies the tax filing process and provides a sense of fairness to taxpayers. As of [most recent tax year], the flat income tax rate in Alabama stands at 5%, which applies to both individual and corporate taxable income.
The flat tax rate is advantageous for taxpayers, as it eliminates the need to calculate varying tax brackets and rates. It also ensures that individuals and businesses can easily estimate their tax liabilities based on their taxable income. Additionally, the flat rate system in Alabama promotes consistency and stability, as the tax rate remains constant across different income levels.
However, it's important to note that Alabama also offers certain tax credits and deductions that can reduce the overall tax liability. These include credits for low-income individuals, education expenses, and various business-related deductions. Taxpayers can utilize these incentives to further optimize their tax obligations.
Taxable Income Calculation
Determining taxable income in Alabama involves considering various factors. The state follows a system where certain income sources are exempt from taxation, while others are fully taxable. For individuals, taxable income includes wages, salaries, bonuses, commissions, and investment income. However, certain items like Social Security benefits and certain retirement income are exempt.
For businesses, taxable income includes net income from operations, capital gains, and income from investments. Alabama provides specific guidelines and forms for businesses to calculate their taxable income accurately. It's essential for businesses to understand these rules to ensure compliance and take advantage of any available deductions or credits.
| Taxable Income Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Wages and Salaries | Income earned from employment, including bonuses and commissions. |
| Investment Income | Income from stocks, bonds, rental properties, and other investments. |
| Business Income | Net income from sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. |
| Capital Gains | Profits from the sale of assets, such as stocks or real estate. |

Sales and Use Tax in Alabama
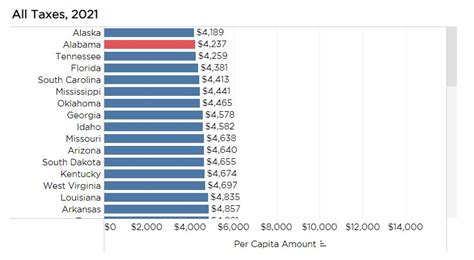
In addition to the income tax, Alabama imposes a sales and use tax on the purchase of goods and certain services within the state. The sales tax rate varies depending on the location of the transaction and the type of goods or services involved. As of [most recent tax year], the statewide sales tax rate is 4%, with additional local taxes ranging from 1% to 3%, resulting in a combined rate that can reach 7% or higher in certain jurisdictions.
The sales tax is collected by businesses and remitted to the Alabama Department of Revenue. It applies to most tangible personal property and certain services, including restaurant meals, hotel accommodations, and entertainment events. However, certain items, such as groceries, prescription drugs, and non-prepared food items, are exempt from sales tax.
Alabama also has a use tax, which is similar to a sales tax but applies to goods and services purchased outside the state and brought into Alabama. The use tax ensures that all transactions are taxed fairly, regardless of where the purchase was made. This includes online purchases and items purchased out of state but used or consumed within Alabama.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Incentives
While the sales tax is a significant source of revenue for the state, Alabama does offer certain exemptions and incentives to promote economic development and support specific industries. These exemptions and incentives vary based on the type of business, the industry, and the location of the transaction. For example, manufacturing and agricultural businesses often benefit from reduced or exempt sales tax rates.
Additionally, Alabama provides tax incentives for research and development, job creation, and certain infrastructure projects. These incentives aim to attract new businesses and encourage economic growth within the state. It's crucial for businesses to stay informed about these incentives and exemptions to optimize their tax obligations and take advantage of potential savings.
Property Tax in Alabama
Property tax is another essential component of Alabama’s tax system. Property taxes are levied on real estate, including land and buildings, as well as certain personal property. The property tax rate varies depending on the location of the property and the assessed value. The tax rate is determined by local taxing authorities, such as counties and municipalities.
As of [most recent tax year], the average property tax rate in Alabama is approximately 0.5% to 1.0% of the assessed value. However, it's important to note that property tax rates can vary significantly across different counties and municipalities within the state. Factors such as budget requirements, local services, and debt obligations influence the property tax rates in each jurisdiction.
Alabama property owners are typically responsible for paying property taxes annually. The tax bills are sent by the local taxing authority, and the payment deadline is typically set by the county or municipality. Failure to pay property taxes on time can result in penalties, interest, and, in some cases, the loss of the property through tax foreclosure.
Property Tax Assessment and Appeals
Property tax assessments in Alabama are conducted by local assessors. These assessments determine the taxable value of the property, which forms the basis for calculating the property tax. Property owners have the right to appeal their assessments if they believe the value assigned to their property is inaccurate or unfair.
The appeal process involves submitting documentation and evidence to support the claim that the property's assessed value is too high. This may include recent sales of comparable properties, appraisals, or other relevant information. The local taxing authority will review the appeal and make a determination, which can be further appealed to higher authorities if necessary.
It's important for property owners to stay informed about their property's assessed value and the assessment process to ensure fairness and accuracy. Regular monitoring and engagement with the local taxing authority can help identify and address any potential issues with property tax assessments.
Corporate Income Tax in Alabama
Alabama imposes a corporate income tax on businesses operating within the state. Similar to the individual income tax, the corporate income tax rate is also flat, standing at 6.5% as of [most recent tax year]. This rate applies to the net income of corporations, including C-corporations and S-corporations.
Alabama provides certain incentives and deductions for corporations to promote business growth and investment. These incentives can include tax credits for research and development, job creation, and capital investment. Additionally, certain industries, such as manufacturing and technology, may be eligible for reduced tax rates or tax exemptions.
Corporations operating in Alabama must file annual tax returns and pay their tax liabilities by the specified deadlines. The Alabama Department of Revenue provides guidance and resources to assist corporations in understanding their tax obligations and ensuring compliance.
Doing Business in Alabama: Tax Considerations
For businesses considering expansion or relocation to Alabama, understanding the state’s tax landscape is crucial. Alabama offers a competitive tax environment with its flat income tax rate and various incentives. However, businesses should carefully evaluate the tax implications of their operations, including sales tax, property tax, and corporate income tax.
Additionally, businesses should consider the tax incentives and exemptions available to them based on their industry and location. Engaging with local economic development agencies and tax professionals can provide valuable insights and guidance on optimizing tax obligations and taking advantage of available incentives.
Conclusion
Alabama’s state tax system, characterized by its flat income tax rate, provides simplicity and consistency for taxpayers. However, the state also imposes sales tax, property tax, and corporate income tax, each with its own set of rules and rates. Understanding these taxes and their implications is essential for individuals and businesses operating within Alabama.
By staying informed about tax rates, exemptions, and incentives, taxpayers can optimize their financial planning and ensure compliance with Alabama's tax regulations. Consulting with tax professionals and staying updated on any changes or developments in the state's tax landscape is advisable to navigate the tax system effectively.
What is the current sales tax rate in Alabama?
+The statewide sales tax rate in Alabama is 4%, with additional local taxes ranging from 1% to 3%, resulting in a combined rate of up to 7% or higher in certain areas.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in Alabama?
+Yes, Alabama offers various tax incentives for businesses, including tax credits for research and development, job creation, and capital investment. These incentives vary based on industry and location.
How often do property tax rates change in Alabama?
+Property tax rates in Alabama can change annually, as they are determined by local taxing authorities. It’s important for property owners to stay informed about any changes to their local tax rates.