Alabama Income Tax Rate
Welcome to this comprehensive exploration of Alabama's income tax system, a crucial aspect of the state's fiscal landscape. Alabama, like many other U.S. states, imposes an income tax on its residents, a revenue stream that significantly contributes to the state's budget. This article aims to delve deep into the specifics of Alabama's income tax rate, shedding light on its structure, current rates, and how it compares to other states.
Understanding Alabama’s Income Tax Structure

Alabama’s income tax system is a flat tax structure, meaning that regardless of an individual’s income level, the same tax rate is applied. This simplicity makes it one of the more straightforward tax systems in the country. The flat tax rate applies to all taxable income, including wages, salaries, commissions, bonuses, and various other sources of income.
The state's tax system is administered by the Alabama Department of Revenue (ADOR), which is responsible for collecting and enforcing tax laws. The ADOR ensures compliance with state tax laws and provides guidance to taxpayers to ensure accurate filing and payment of taxes.
Taxable Income Categories
Alabama’s income tax system categorizes income into three broad categories: earned income, unearned income, and passive income. Earned income includes wages, salaries, tips, and other compensation received for personal services. Unearned income covers interest, dividends, and capital gains, while passive income refers to rental income and income from partnerships or trusts.
| Income Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Earned Income | Wages, salaries, tips, and personal services compensation. |
| Unearned Income | Interest, dividends, and capital gains. |
| Passive Income | Rental income, partnerships, and trust income. |

Alabama’s Current Income Tax Rate
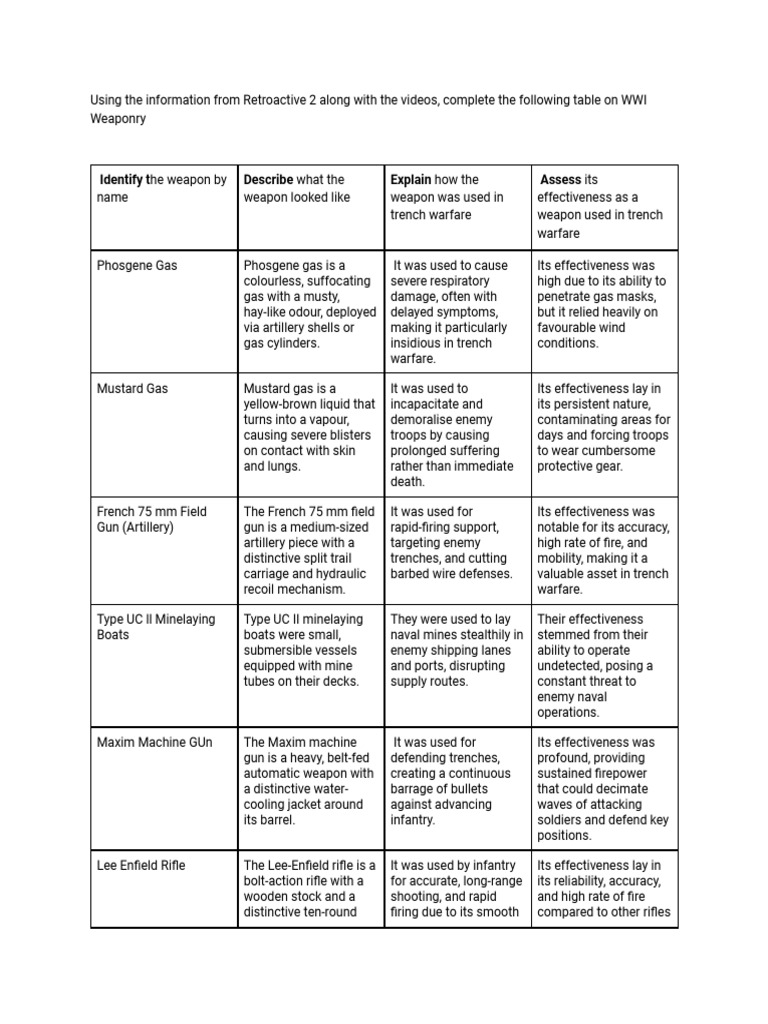
As of the most recent tax year, Alabama imposes a flat income tax rate of 5% on all taxable income. This rate is applicable to individuals, trusts, and estates, making it one of the lowest income tax rates among U.S. states.
The 5% rate is a notable decrease from the previous tax year, where the rate stood at 5.5%. This reduction was part of a tax reform initiative aimed at stimulating economic growth and making Alabama more competitive in the regional and national business landscape.
Comparative Analysis: Alabama vs. Other States

Alabama’s flat tax rate of 5% positions it as one of the states with the lowest income tax rates in the nation. This rate is significantly lower than many other states, particularly those with progressive tax systems where rates increase with income levels.
For instance, California, with its highest marginal tax rate of 13.3%, stands in stark contrast to Alabama. Similarly, New York's top marginal rate of 8.82% and Pennsylvania's 3.07% make Alabama's flat tax system even more appealing to businesses and individuals seeking a more tax-friendly environment.
The Impact of Flat Tax Rates
Alabama’s flat tax rate has significant implications for the state’s economy and its residents. A flat tax rate is often seen as more transparent and easier to understand, which can lead to increased tax compliance. Additionally, it can attract businesses and individuals seeking a simpler tax structure, potentially boosting economic growth and job creation.
However, it's important to note that while Alabama's flat tax rate may be attractive, it also means that higher-income earners pay a lower percentage of their income in taxes compared to progressive tax systems. This can result in a shift in the tax burden onto lower and middle-income earners, which has been a subject of debate in tax policy discussions.
Tax Relief and Exemptions in Alabama
Alabama offers various tax credits and exemptions to reduce the tax burden on its residents. These incentives are designed to support specific sectors of the population or industries, encouraging economic development and providing relief to those in need.
Tax Credits
- Low-Income Tax Credit: Alabama provides a tax credit for low-income earners, helping reduce the tax burden for those with limited financial means. This credit can significantly reduce the amount of tax owed, providing much-needed relief for low-income families.
- Retirement Income Deduction: Alabama allows a deduction for a portion of retirement income, encouraging retirement savings and providing an incentive for individuals to plan for their retirement years.
- Educational Tax Credits: The state offers tax credits for educational expenses, including tuition and fees, providing an incentive for families to invest in their children’s education.
Tax Exemptions
- Military Service Exemption: Alabama exempts military service members from paying income tax on their military pay, recognizing the sacrifices made by those serving in the armed forces.
- Senior Citizen Exemption: Alabama offers an income tax exemption for senior citizens, allowing them to exclude a portion of their retirement income from taxable income.
- Agricultural Property Tax Exemption: The state provides an exemption for agricultural property, encouraging agricultural development and supporting the state’s farming industry.
The Future of Alabama’s Income Tax System
Alabama’s income tax system is subject to ongoing discussions and potential reforms. As the state’s economy evolves and new challenges arise, the tax system may need to adapt to meet these changing needs.
One potential area of focus is ensuring that the tax system remains progressive enough to provide adequate revenue for essential public services while also maintaining its competitiveness with other states. Finding the right balance between revenue generation and economic competitiveness will be a key challenge for Alabama's policymakers.
Additionally, the state may consider expanding its tax credits and exemptions to further support specific sectors or individuals, particularly in the face of economic challenges or social needs.
Expert Insights
Conclusion

Alabama’s income tax system, with its flat 5% rate, offers a straightforward and competitive tax environment. This simplicity has its advantages, making tax compliance easier and potentially attracting businesses and individuals. However, it also presents challenges in ensuring the state can fund essential services and support those most in need.
As Alabama continues to navigate its fiscal landscape, the income tax system will remain a critical component, requiring ongoing review and adaptation to meet the state's evolving needs and challenges.
What is the difference between a flat tax and a progressive tax system?
+A flat tax applies the same tax rate to all income levels, while a progressive tax system imposes higher tax rates on higher income levels. Progressive tax systems aim to reduce the tax burden on lower-income earners, promoting a more equitable distribution of tax responsibilities.
How does Alabama’s income tax rate compare to other southern states?
+Alabama’s 5% flat tax rate is lower than many other southern states. For instance, Florida has no income tax, while Georgia has a top rate of 5.75%. This makes Alabama’s tax system more competitive in attracting businesses and individuals.
Are there any plans to change Alabama’s income tax rate in the near future?
+Currently, there are no immediate plans to change the income tax rate. However, tax policy is subject to ongoing discussions, and any changes would require legislative approval and careful consideration of the state’s fiscal needs and economic landscape.