A Tariff Is A Tax On ___.
Tariffs have been a significant topic of discussion and a tool utilized by governments worldwide for centuries. In the realm of international trade, tariffs play a crucial role in shaping economic policies and impacting the flow of goods and services across borders. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of tariffs, their purpose, and their far-reaching effects on various industries and economies.
Unveiling the Concept: Tariffs, Taxes, and International Trade

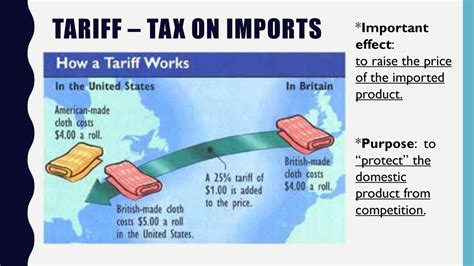
At its core, a tariff is a tax levied on imported or exported goods. It is a strategic tool employed by countries to regulate and manage their trade relationships with other nations. Tariffs are designed to influence the flow of goods, protect domestic industries, and generate revenue for the government.
When a country imposes a tariff on a specific product, it increases the price of that product for consumers within its borders. This price increase can make the domestic product more competitive and encourage consumers to support local industries. Conversely, it can also make imported goods less attractive, thereby reducing demand and impacting international trade flows.
The Historical Context of Tariffs
The history of tariffs stretches back to ancient civilizations, where they were used to fund public projects and protect local producers from foreign competition. However, the modern concept of tariffs emerged during the mercantilist era of the 16th to 18th centuries, when European powers sought to maximize their wealth and power through trade.
In the 19th century, tariffs became a key instrument for industrializing nations to nurture their domestic industries and achieve economic self-sufficiency. Countries like the United States and Germany utilized tariffs to protect their infant industries, allowing them to develop and compete globally. This era also saw the rise of free trade advocates, who argued that tariffs hindered economic growth and innovation.
Types of Tariffs and Their Applications
Tariffs can be categorized into various types, each serving different purposes:
- Import Tariffs: These are taxes imposed on goods entering a country. They are designed to protect domestic industries and generate revenue. Import tariffs can be used to encourage the development of local alternatives and reduce reliance on foreign goods.
- Export Tariffs: Less common, export tariffs are taxes on goods leaving a country. They are typically used to control the export of certain resources or to manage the balance of trade. Export tariffs can also be a tool for diplomatic leverage.
- Protective Tariffs: Designed to protect domestic industries from foreign competition, protective tariffs are often employed when a country's industry is deemed essential to national interests or when it is at a competitive disadvantage.
- Revenue Tariffs: As the name suggests, revenue tariffs are primarily imposed to generate government revenue. They are often applied to non-essential or luxury goods, as they can be increased without significantly impacting consumer behavior.
- Countervailing Duties: These are tariffs imposed to neutralize the effects of subsidies or other support given to foreign producers. They aim to create a level playing field for domestic industries.
The Impact of Tariffs on Industries and Consumers
Tariffs have a profound impact on various sectors of the economy. While they can provide a much-needed boost to certain industries, they can also disrupt supply chains, increase costs for businesses, and lead to price hikes for consumers.
| Industry | Impact of Tariffs |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Tariffs on imported raw materials can increase production costs, impacting the competitiveness of domestic manufacturers. Protective tariffs can provide a temporary advantage, but may hinder innovation and long-term sustainability. |
| Agriculture | Agricultural tariffs can protect local farmers from cheaper foreign produce, but they can also limit access to diverse, high-quality imports. This can affect both farmers and consumers, potentially leading to higher food prices. |
| Retail and E-commerce | Tariffs on consumer goods can directly impact retail prices, affecting consumer spending and business profitability. Online retailers, especially those dependent on cross-border trade, may face significant challenges due to increased costs and logistical complexities. |

Moreover, the implementation of tariffs can lead to retaliatory measures from trading partners, escalating into trade wars that disrupt global supply chains and hinder economic growth. The complex web of international trade agreements and organizations, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), plays a crucial role in mediating and regulating these trade disputes.
Analyzing the Effectiveness of Tariffs

The effectiveness of tariffs as a policy tool is a subject of ongoing debate among economists and policymakers. While they can provide short-term benefits, such as protecting domestic jobs and industries, the long-term effects are less clear-cut.
Pros and Cons of Tariff Implementation
- Pros:
- Tariffs can provide a temporary boost to domestic industries, helping them compete with foreign rivals.
- They can generate significant government revenue, especially when applied to luxury goods or specific industries.
- In certain cases, tariffs can be used to address unfair trade practices or to negotiate better trade deals.
- Cons:
- Tariffs can lead to higher prices for consumers, reducing their purchasing power and impacting their standard of living.
- They can disrupt global supply chains, making it harder for businesses to access critical components or resources.
- Retaliatory tariffs from trading partners can hurt exports, negatively affecting domestic industries that rely on international markets.
Case Studies: The Real-World Impact of Tariffs
Examining specific instances of tariff implementation can provide valuable insights into their effectiveness and potential pitfalls.
- The US-China Trade War: The imposition of tariffs by the United States on Chinese goods, and China's retaliatory measures, had a significant impact on global supply chains and economic growth. It disrupted industries reliant on Chinese components, increased costs for businesses, and led to job losses in both countries.
- The EU's Agricultural Tariffs: The European Union's protective tariffs on agricultural products have been a source of tension in trade negotiations. While they support EU farmers, they also limit access to diverse, high-quality food products and increase prices for consumers.
- India's Solar Panel Tariffs: India's decision to impose tariffs on solar panel imports aimed to boost its domestic solar industry. However, it faced criticism for potentially hindering the country's transition to renewable energy and disrupting global supply chains for solar technology.
The Future of Tariffs: Trends and Predictions
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the role and impact of tariffs are likely to evolve. Here are some key trends and predictions for the future of tariffs:
- Regional Trade Agreements: The trend towards regional trade blocs, such as the European Union and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), may lead to a reduction in tariffs within these regions. However, it could also result in higher tariffs for countries outside these blocs.
- Digital Trade and E-commerce: With the rise of digital trade and e-commerce, the application of tariffs to digital goods and services is a growing area of focus. Governments are grappling with how to tax and regulate this rapidly evolving sector.
- Sustainable Development Goals: As countries work towards achieving the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals, tariffs may be used as a tool to encourage sustainable practices and discourage environmentally harmful activities.
- Technological Advances: Advances in technology, such as 3D printing and automation, may reduce the reliance on imported goods, potentially diminishing the impact of tariffs on certain industries.
Conclusion: Navigating the Tariff Landscape
Tariffs are a complex and multifaceted tool, with far-reaching implications for economies, industries, and consumers. While they can provide short-term benefits, their long-term effectiveness and impact are subject to careful consideration and analysis. As the world continues to globalize, the strategic use of tariffs will remain a crucial aspect of international trade policy, requiring a delicate balance between protectionism and free trade.
Understanding the intricacies of tariffs and their potential consequences is essential for businesses, policymakers, and consumers alike. By staying informed and adapting to the evolving landscape of international trade, stakeholders can navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by tariffs, shaping a more sustainable and prosperous future.
What is the primary purpose of a tariff?
+Tariffs are primarily used to protect domestic industries, regulate trade, and generate government revenue. They can be a strategic tool to influence the flow of goods and services across borders.
How do tariffs impact consumers?
+Tariffs can lead to higher prices for consumers, as the cost of imported goods increases. This can impact their purchasing power and overall standard of living.
Are tariffs always detrimental to economic growth?
+While tariffs can have negative effects, they can also provide short-term benefits, such as protecting domestic jobs and industries. However, their long-term impact is complex and depends on various factors, including the specific industry and the overall trade landscape.
How do tariffs affect international trade relationships?
+Tariffs can strain trade relationships, leading to retaliatory measures and potential trade wars. They can disrupt supply chains and impact the competitiveness of industries in both the imposing and retaliating countries.
What role do tariffs play in the digital age?
+With the rise of digital trade, the application of tariffs to digital goods and services is a growing concern. Governments are navigating how to regulate and tax this rapidly evolving sector, which has implications for both businesses and consumers.


